Question
PLEASE PLEASE HELP, this is my last question for my chegg subscription so did half of each of these questions and Im struggling on the
PLEASE PLEASE HELP, this is my last question for my chegg subscription so did half of each of these questions and Im struggling on the other halves, Theyre due tonight. it would be so appreciated if someone could help with each of these.
1) Hart Company made 3,900 bookshelves using 30,000 board feet of wood costing $390,000. The company's direct materials standards for one bookshelf are 8 board feet of wood at $12.90 per board foot.
Hart Company records standard costs in its accounts and its materials variances in separate accounts when it assigns materials costs to the Work in Process Inventory account. (1) Prepare the journal entry that both charges the direct materials costs to the Work in Process Inventory account and records the materials variances in their proper accounts. (2) Assume that Hart's materials variances are the only variances accumulated in the accounting period and that they are immaterial. Prepare the adjusting journal entry to close the variance accounts at period-end.
2) World Company expects to operate at 60% of its productive capacity of 19,000 units per month. At this planned level, the company expects to use 4,560 standard hours of direct labor. Overhead is allocated to products using a predetermined standard rate of 0.400 direct labor hours per unit. At the 60% capacity level, the total budgeted cost includes $13,680 fixed overhead cost and $86,640 variable overhead cost. In the current month, the company incurred $43,460 actual overhead and 1,210 actual labor hours while producing 4,200 units. (Do not round intermediate calculations. Round "OH costs per DL hour" to 2 decimal places.) 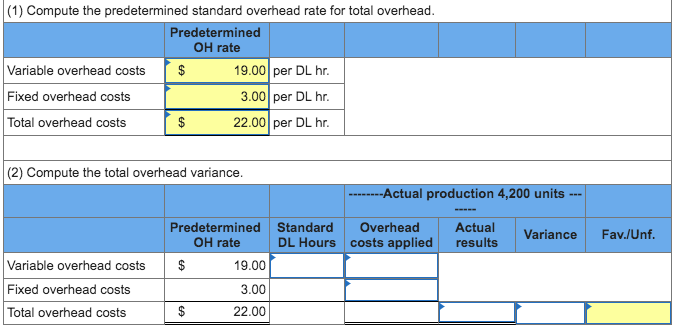
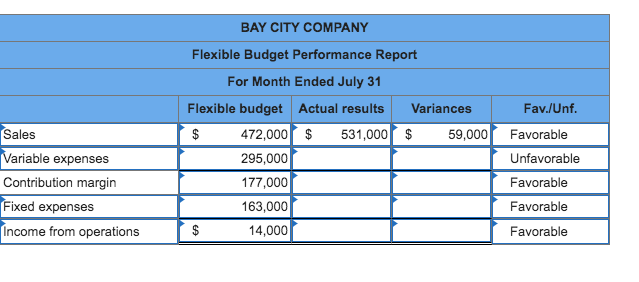
3) Bay City Companys fixed budget performance report for July follows. The $513,000 budgeted total expenses include $350,000 variable expenses and $163,000 fixed expenses. Actual expenses include $153,000 fixed expenses.
| Fixed Budget | Actual Results | Variances | ||||||||
| Sales (in units) | 7,000 | 5,900 | ||||||||
| Sales (in dollars) | $ | 560,000 | $ | 531,000 | $ | 29,000 | U | |||
| Total expenses | 513,000 | 479,000 | 34,000 | F | ||||||
| Income from operations | $ | 47,000 | $ | 52,000 | $ | 5,000 | U | |||
Prepare a flexible budget performance report that shows any variances between budgeted results and actual results. List fixed and variable expenses separately.
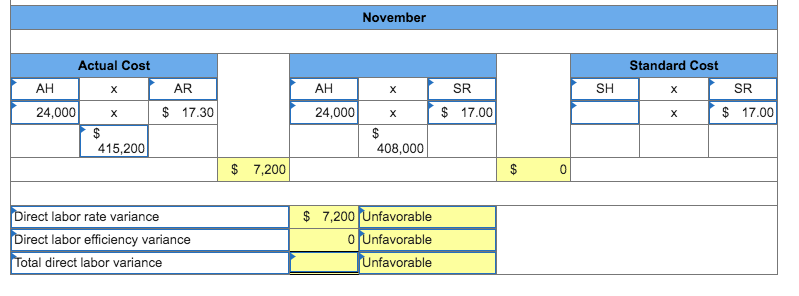
4) After evaluating Null Companys manufacturing process, management decides to establish standards of 2 hours of direct labor per unit of product and $17.00 per hour for the labor rate. During October, the company uses 14,500 hours of direct labor at a $249,400 total cost to produce 7,600 units of product. In November, the company uses 24,000 hours of direct labor at a $415,200 total cost to produce 8,000 units of product.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


