Please provide answer to all these - apologies for terrible photos
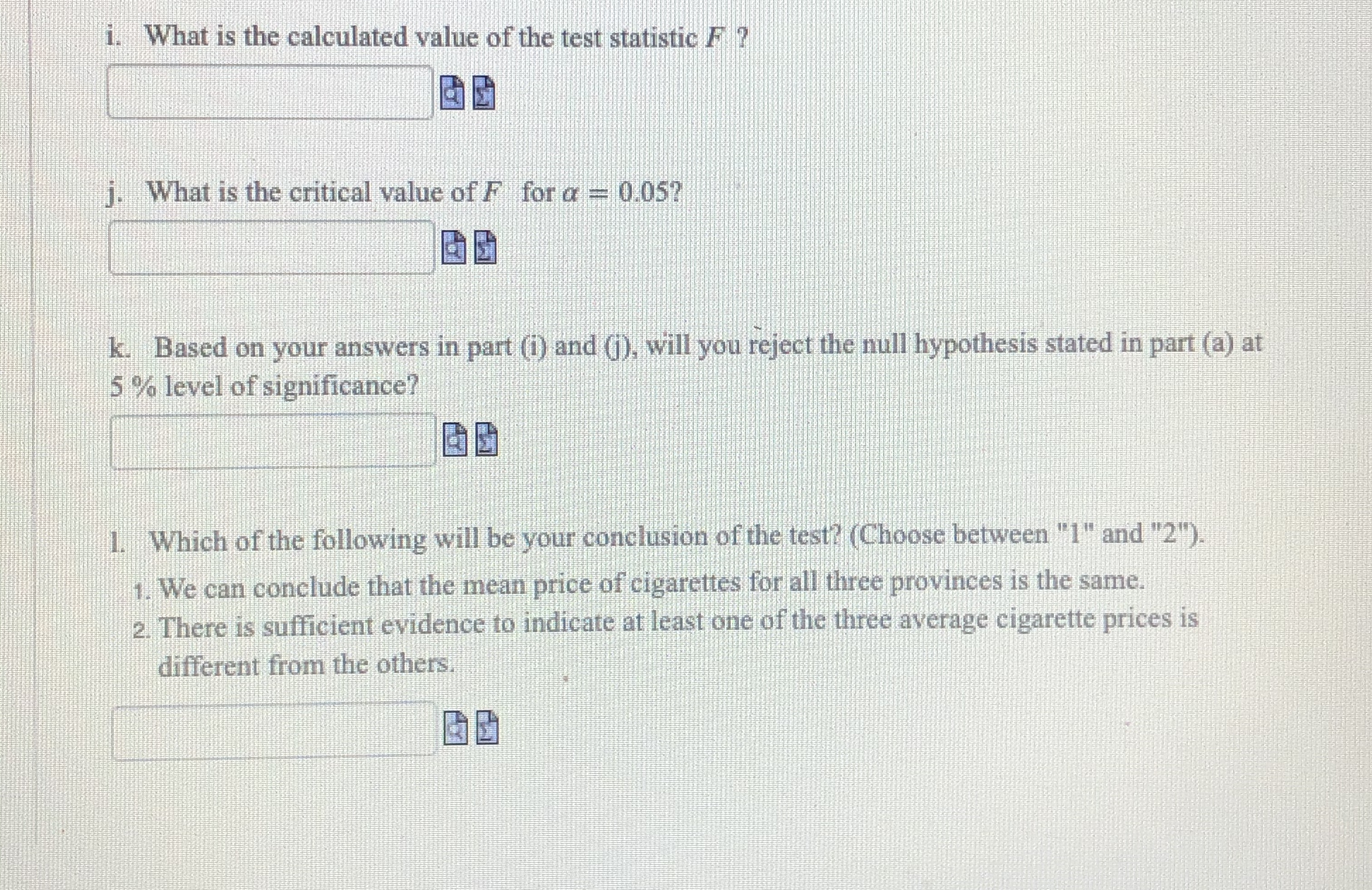
i. What is the calculated value of the test statistic F ? j. What is the critical value of F for a = 0.057 k. Based on your answers in part (i) and (j), will you reject the null hypothesis stated in part (a) at 5% level of significance? 1. Which of the following will be your conclusion of the test? (Choose between "1" and "2"). 1. We can conclude that the mean price of cigarettes for all three provinces is the same. 2. There is sufficient evidence to indicate at least one of the three average cigarette prices is different from the others.Public health advocates in all provinces and territories strongly believe that further price (tax) increases on cigarettes can be immensely effective in reducing the consumption of tobacco A health researcher wants to compare the prices of a carton of 200 cigarettes among three western provinces - Alberta, British Columbia and Saskatchewan. He randomly selects 5 stores that sell tobacco in each of the three provinces. The prices are given in the table below (all provincial and federal taxes including GST included) Price of a Carton of 200 Cigarettes Alberta British Columbia Saskatchewan $ 91.92 $ 97.08 $ 91.25 88.99 95.49 89.99 93.99 94.70 93.32 92.90 92.99 94.99 89.79 98.95 96.99 The health researcher wants to test if the mean price of a carton of 200 cigarettes is the same for all three provinces. Assuing that all the assumptions required to apply for the one-way ANOVA prodedure hold true, answer the following questions (round all sum of squares to four decimals. and F-values to two decimals). a. Which of the following is the correct pair of the null and alternative hypotheses? Choose the number that shows the correct pair 1. Ho : P1 - H2 - P3. H : Not all three means are equal 3. Ho . H1 = #2 - #3 = 14 = 15, Hj : Not all means are equal 4. HO : #1 = #2. H1 : HI# #2b. Calculate the sum of squares for treatments (between-samples sum of squares) denoted by SSB. C. Calculate the sum of squares for error (within-samples sum of squares) denoted by SSW. d. Find the total sum of squares denoted by SST. ell What is the number of degrees of freedom for the numerator (umerator ) ? What is the number of degrees of freedom for the denominator (ddenominator ) ? g. Calculate the mean sum of squares for treatments (between-samples variance) denoted by MSB. h. Calculate the sum of squares for error (within-samples variance) denoted by MSW. i. What is the calculated value of the test statistic F