Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
please provide step-by-step calculations for part iv. down the bundle and gives brine at the bottom of the cell. The vapour raised by sea-water evaporation
please provide step-by-step calculations for part iv.
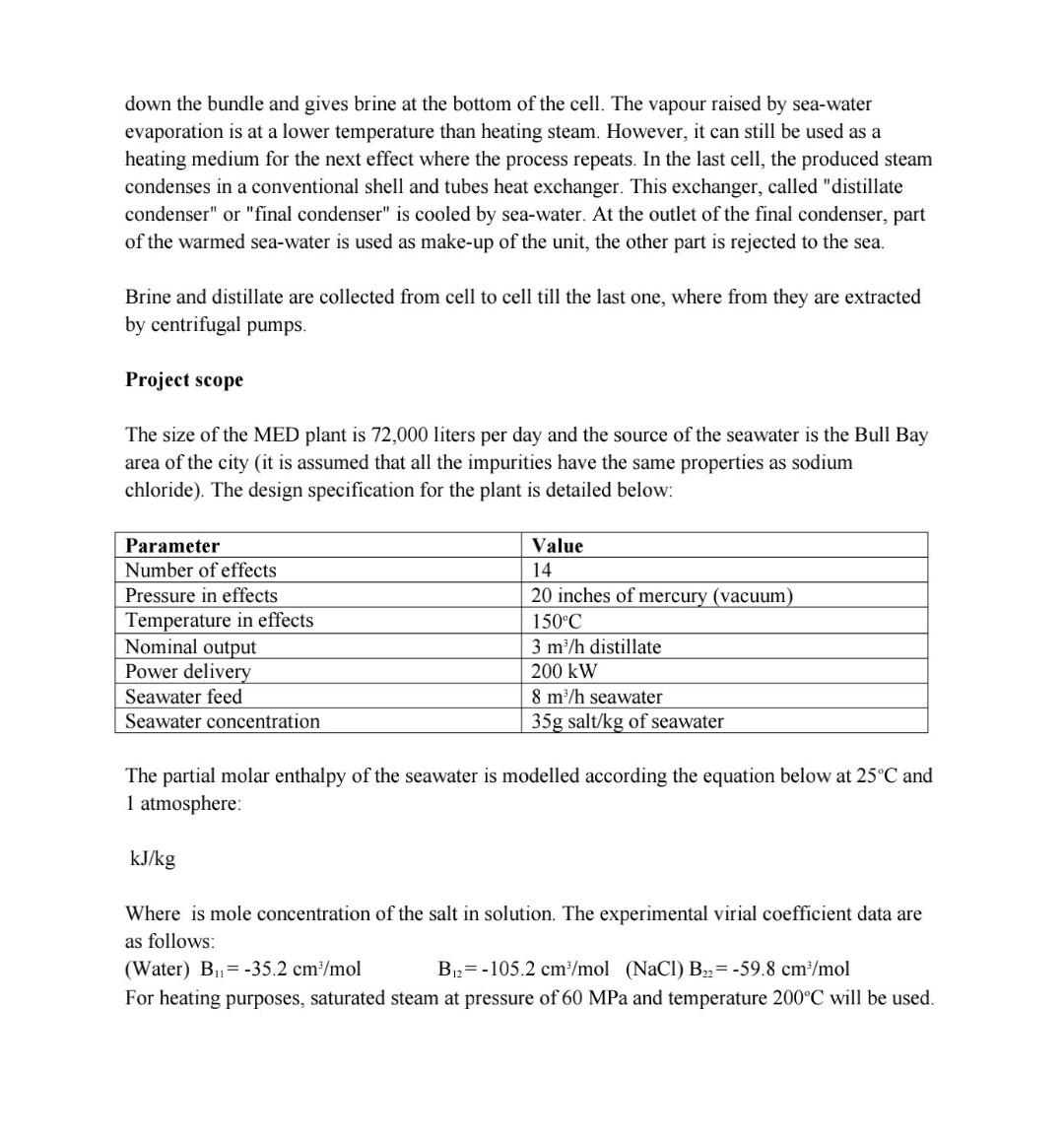

down the bundle and gives brine at the bottom of the cell. The vapour raised by sea-water evaporation is at a lower temperature than heating steam. However, it can still be used as a heating medium for the next effect where the process repeats. In the last cell, the produced steam condenses in a conventional shell and tubes heat exchanger. This exchanger, called "distillate condenser" or "final condenser" is cooled by sea-water. At the outlet of the final condenser, part of the warmed sea-water is used as make-up of the unit, the other part is rejected to the sea. Brine and distillate are collected from cell to cell till the last one, where from they are extracted by centrifugal pumps. Project scope The size of the MED plant is 72,000 liters per day and the source of the seawater is the Bull Bay area of the city (it is assumed that all the impurities have the same properties as sodium chloride). The design specification for the plant is detailed below: Parameter Number of effects Pressure in effects Temperature in effects Nominal output Power delivery Seawater feed Seawater concentration Value 14 20 inches of mercury (vacuum) 150C 3 m/h distillate 200 kW 8 m/h seawater 35g salt/kg of seawater The partial molar enthalpy of the seawater is modelled according the equation below at 25C and 1 atmosphere: kJ/kg Where is mole concentration of the salt in solution. The experimental virial coefficient data are as follows: (Water) B.1=-35.2 cm /mol B2=-105.2 cm / mol (NaCl) B2= -59.8 cm /mol For heating purposes, saturated steam at pressure of 60 MPa and temperature 200C will be used. As the process engineer, you are required to determine the following: i. Generate the table of results for partial molar enthalpy for concentrations ranging from 0.5%-30% in increments of 1%. [10 marks] ii. Generate the graph for partial molar enthalpy vs mole fraction based on data generated from part (i). [5 marks] iii. Determine the expression for the partial molar enthalpy for the water and sodium chloride components and deduce same at concentration at 3.5%. [10 marks] iv. Determine the fugacity and fugacity coefficient of the steam to be used using the virial EOS, cubic RW EOS and general correlations. Compare the values obtained from the three (3) methods. [15 marks) Determine the fugacity and fugacity coefficient of the steam distillate in the first effect using the virial EOS, and general correlations. Compare the values obtained from the two (2) methods. [10 marks] vi. Determine the fugacity and fugacity coefficient of the sodium chloride and water in the first effect using the virial EOS. [5 marks) vii. Compare the fugacities calculated from the RW EOS for both the heating steam and the steam distillate. Provide reasons for significant differences, if any. [5 marks] V. down the bundle and gives brine at the bottom of the cell. The vapour raised by sea-water evaporation is at a lower temperature than heating steam. However, it can still be used as a heating medium for the next effect where the process repeats. In the last cell, the produced steam condenses in a conventional shell and tubes heat exchanger. This exchanger, called "distillate condenser" or "final condenser" is cooled by sea-water. At the outlet of the final condenser, part of the warmed sea-water is used as make-up of the unit, the other part is rejected to the sea. Brine and distillate are collected from cell to cell till the last one, where from they are extracted by centrifugal pumps. Project scope The size of the MED plant is 72,000 liters per day and the source of the seawater is the Bull Bay area of the city (it is assumed that all the impurities have the same properties as sodium chloride). The design specification for the plant is detailed below: Parameter Number of effects Pressure in effects Temperature in effects Nominal output Power delivery Seawater feed Seawater concentration Value 14 20 inches of mercury (vacuum) 150C 3 m/h distillate 200 kW 8 m/h seawater 35g salt/kg of seawater The partial molar enthalpy of the seawater is modelled according the equation below at 25C and 1 atmosphere: kJ/kg Where is mole concentration of the salt in solution. The experimental virial coefficient data are as follows: (Water) B.1=-35.2 cm /mol B2=-105.2 cm / mol (NaCl) B2= -59.8 cm /mol For heating purposes, saturated steam at pressure of 60 MPa and temperature 200C will be used. As the process engineer, you are required to determine the following: i. Generate the table of results for partial molar enthalpy for concentrations ranging from 0.5%-30% in increments of 1%. [10 marks] ii. Generate the graph for partial molar enthalpy vs mole fraction based on data generated from part (i). [5 marks] iii. Determine the expression for the partial molar enthalpy for the water and sodium chloride components and deduce same at concentration at 3.5%. [10 marks] iv. Determine the fugacity and fugacity coefficient of the steam to be used using the virial EOS, cubic RW EOS and general correlations. Compare the values obtained from the three (3) methods. [15 marks) Determine the fugacity and fugacity coefficient of the steam distillate in the first effect using the virial EOS, and general correlations. Compare the values obtained from the two (2) methods. [10 marks] vi. Determine the fugacity and fugacity coefficient of the sodium chloride and water in the first effect using the virial EOS. [5 marks) vii. Compare the fugacities calculated from the RW EOS for both the heating steam and the steam distillate. Provide reasons for significant differences, if any. [5 marks] V
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


