Question
PLEASE SHOW ALL WORK AND EXPLANATIONS Requirement 1. Compute the variable overhead cost and efficiency variances and fixed overhead cost and volume variances. A standard
PLEASE SHOW ALL WORK AND EXPLANATIONS
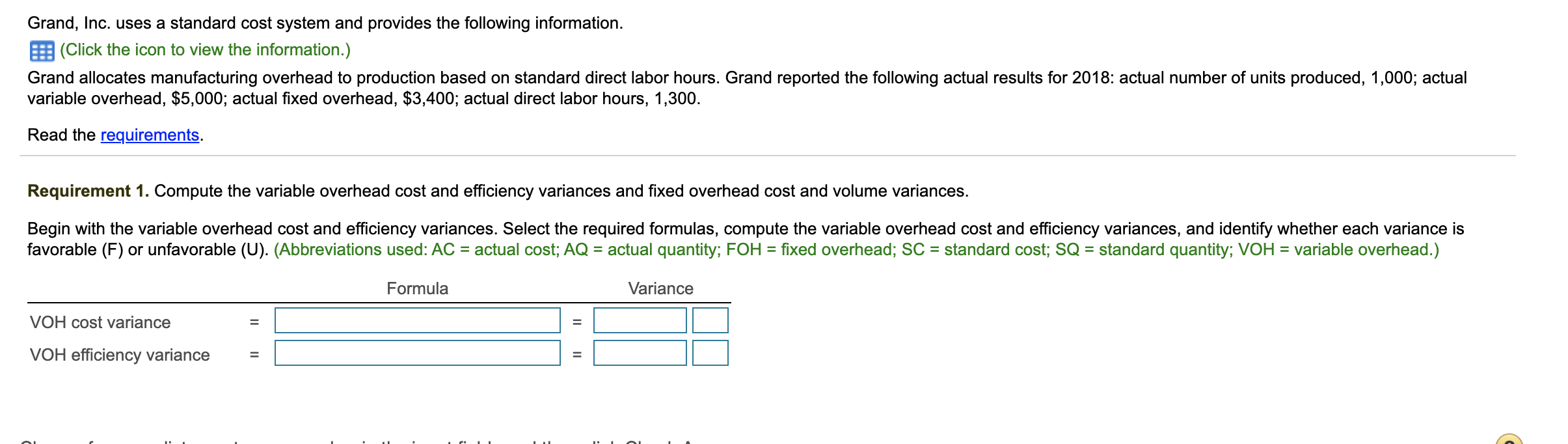
Requirement 1. Compute the variable overhead cost and efficiency variances and fixed overhead cost and volume variances.
A standard costing system is an accounting system that uses standards for product costs
long dash
direct materials, direct labor, and manufacturing overhead. A standard cost system allows management to determine how much a product should cost. Once standards are established, managers can use the standards to assign costs to production. At least once per year, managers will compare the actual production costs to the standard costs to locate variances
long dash
cost variances and efficiency variances. The figure below shows the formulas for computing the cost and efficiency variances.
LOADING...
(Click the icon to view the formulas for computing the cost and efficiency variances.)
| Variable | ||
|
| Overhead |
|
| Actual quantity at Actual cost [Actual VOH] | $ | |
| Standard cost (SC) | $ | per hr. |
| Actual quantity (AQ) | hours | |
| Standard quantity (SQ) | hours |
Compute the variable overhead cost and efficiency variances using the amounts we have previously determined, and identify whether each variance is favorable (F) or unfavorable (U). The variance is favorable when actual amounts are less than standards and unfavorable when actual amounts exceed standards.
|
|
| Formula |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Variance | |
| VOH cost variance | = | Actual VOH - (SC x AQ) | = | $ | - ( | $ | x | ) = | $ | U | |
| VOH efficiency variance | = | (AQ - SQ) x SC | = ( | - | ) x | $ | = | $ | F | ||
Now let's take a look at the fixed overhead cost and volume variances.
Superior
Superior will use a slightly different approach to analyze the fixed overhead variances. Remember that fixed costs are not expected to change in total within the relevant range, but they do change per unit when there is a change in volume. To analyze fixed overhead costs, we will need three amounts:
bullet
Actual fixed overhead costs incurred
bullet
Budgeted fixed overhead costs
bullet
Allocated fixed overhead costs
Begin by identifying the actual fixed overhead (FOH) costs incurred, the budgeted FOH costs, and the allocated FOH costs. Note that we are given the actual and budgeted FOH in the information given. We must calculate allocated fixed overhead costs by multiplying the standard fixed overhead allocation rate by the standard quantity of direct labor hours, which we previously determined to be
2 comma 000
2,000 hours.
| Fixed | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Overhead |
| Actual fixed overhead costs incurred | = | $ | ||||
| Budgeted fixed overhead costs |
| = | $ | |||
| Allocated fixed overhead costs |
|
|
| = |
Now compute the fixed overhead cost and volume variances using the amounts you identified above.
|
|
| Formula |
|
|
|
|
| Variance | |
| FOH cost variance | = | Actual FOH - Budgeted FOH | = | $ | - | $ | = | $ | U |
| FOH volume variance | = | Bugeted FOH - Allocated FOH | = | $ | - | $ | = | $ | F |
Requirement 2. Explain why the variances are favorable or unfavorable.
.
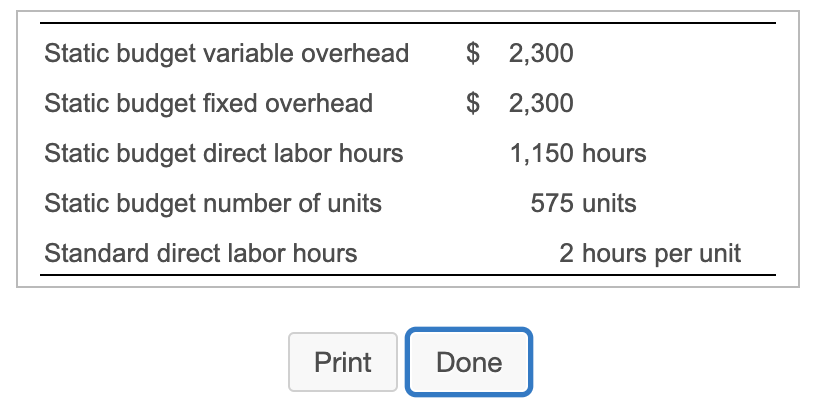
Grand, Inc. uses a standard cost system and provides the following information. |(Click the icon to view the information.) Grand allocates manufacturing overhead to production based on standard direct labor hours. Grand reported the following actual results for 2018: actual number of units produced, 1,000; actual variable overhead, $5,000; actual fixed overhead, $3,400; actual direct labor hours, 1,300. Read the requirements. Requirement 1. Compute the variable overhead cost and efficiency variances and fixed overhead cost and volume variances. Begin with the variable overhead cost and efficiency variances. Select the required formulas, compute the variable overhead cost and efficiency variances, and identify whether each variance is favorable (F) or unfavorable (U). (Abbreviations used: AC = actual cost; AQ = actual quantity; FOH = fixed overhead; SC = standard cost; SQ = standard quantity; VOH = variable overhead.) Formula Variance VOH cost variance VOH efficiency variance II $ 2,300 $ 2,300 Static budget variable overhead Static budget fixed overhead Static budget direct labor hours Static budget number of units 1,150 hours 575 units Standard direct labor hours 2 hours per unit Print DoneStep by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


