Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Please show all work Problem 5-35 (Algo) (LO 5-2, 5-3, 5-4, 5-5, 5-7) On January 1, 2019, Monica Company acquired 70 percent of Young Company's

Please show all work
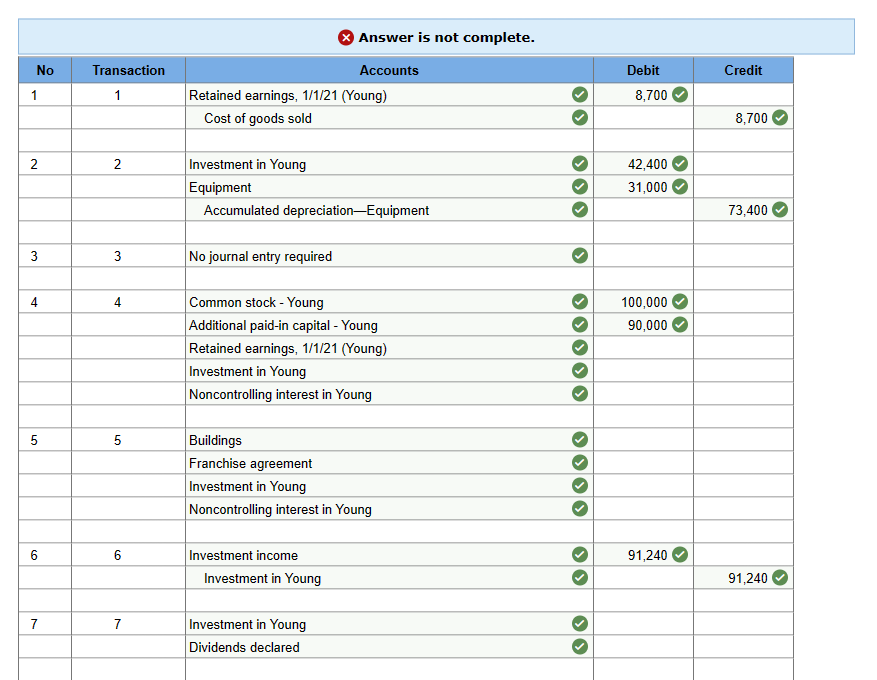
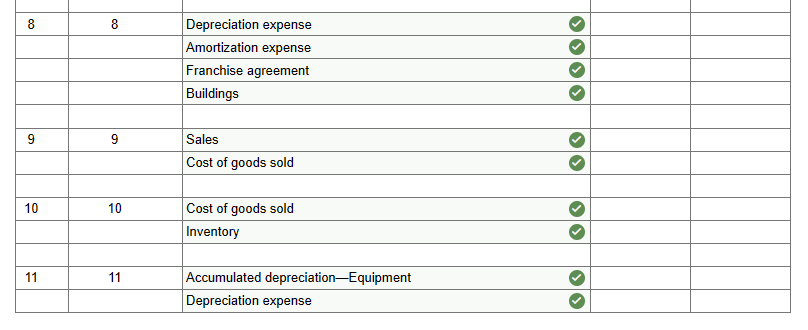
Problem 5-35 (Algo) (LO 5-2, 5-3, 5-4, 5-5, 5-7) On January 1, 2019, Monica Company acquired 70 percent of Young Company's outstanding common stock for $742,000. The fair value of the noncontrolling interest at the acquisition date was $318,000. Young reported stockholders' equity accounts on that date as follows: In establishing the acquisition value, Monica appraised Young's assets and ascertained that the accounting records undervalued a building (with a five-year remaining life) by $40,000. Any remaining excess acquisition-date fair value was allocated to a franchise agreement to be amortized over 10 years. During the subsequent years, Young sold Monica inventory at a 30 percent gross profit rate. Monica consistently resold this merchandise in the year of acquisition or in the period immediately following. Transfers for the three years after this business combination was created amounted to the following: In addition, Monica sold Young several pieces of fully depreciated equipment on January 1, 2020, for $53,000. The equipment had originally cost Monica $84,000. Young plans to depreciate these assets over a 5-year period. In 2021, Young earns a net income of $150,000 and declares and pays $40,000 in cash dividends. These figures increase the subsidiary's Retained Earnings to a $910,000 balance at the end of 2021. Monica employs the equity method of accounting. Hence, it reports $91,240 investment income for 2021 with an Investment account balance of $864,550. Prepare the worksheet entries required for the consolidation of Monica Company and Young Company. (If no entry is required for a transaction/event, select "No Journal Entry Required" in the first account field.) \begin{tabular}{|c|c|c|c|c|c|} \hline \multicolumn{6}{|c|}{ Answer is not complete. } \\ \hline No & Transaction & Accounts & & Debit & Credit \\ \hline \multirow[t]{2}{*}{1} & 1 & Retained earnings, 1/1/21 (Young) & 2 & 8,700 & \\ \hline & & Cost of goods sold & & & 8,700 \\ \hline \multirow[t]{3}{*}{2} & 2 & Investment in Young & 0 & 42,400 & \\ \hline & & Equipment & & 31,000 & \\ \hline & & Accumulated depreciation-Equipmen & 2 & & 73,400 \\ \hline 3 & 3 & No journal entry required & 0 & & \\ \hline \multirow[t]{5}{*}{4} & 4 & Common stock - Young & 0 & 100,000 & \\ \hline & & Additional paid-in capital - Young & & 90,000 & \\ \hline & & Retained earnings, 1/1/21 (Young) & 2 & & \\ \hline & & Investment in Young & 2 & & \\ \hline & & Noncontrolling interest in Young & 2 & & \\ \hline \multirow[t]{4}{*}{5} & 5 & Buildings & & & \\ \hline & & Franchise agreement & 2 & & \\ \hline & & Investment in Young & 2 & & \\ \hline & & Noncontrolling interest in Young & 2 & & \\ \hline \multirow[t]{2}{*}{6} & 6 & Investment income & 0 & 91,240 & \\ \hline & & Investment in Young & 2 & & 91,240 \\ \hline \multirow[t]{2}{*}{7} & 7 & Investment in Young & 0 & & \\ \hline & & Dividends declared & & & \\ \hline \end{tabular} \begin{tabular}{|c|c|c|c|c|c|} \hline \multirow[t]{4}{*}{8} & 8 & Depreciation expense & 2 & & \\ \hline & & Amortization expense & 2 & & \\ \hline & & Franchise agreement & 2 & & \\ \hline & & Buildings & 0 & & \\ \hline \multirow[t]{2}{*}{9} & 9 & Sales & 2 & & \\ \hline & & Cost of goods sold & 2 & & \\ \hline \multirow[t]{2}{*}{10} & 10 & Cost of goods sold & 2 & & \\ \hline & & Inventory & 0 & & \\ \hline \multirow[t]{2}{*}{11} & 11 & Accumulated depreciation-Equipment & 2 & & \\ \hline & & Depreciation expense & 2 & & \\ \hline \end{tabular} Problem 5-35 (Algo) (LO 5-2, 5-3, 5-4, 5-5, 5-7) On January 1, 2019, Monica Company acquired 70 percent of Young Company's outstanding common stock for $742,000. The fair value of the noncontrolling interest at the acquisition date was $318,000. Young reported stockholders' equity accounts on that date as follows: In establishing the acquisition value, Monica appraised Young's assets and ascertained that the accounting records undervalued a building (with a five-year remaining life) by $40,000. Any remaining excess acquisition-date fair value was allocated to a franchise agreement to be amortized over 10 years. During the subsequent years, Young sold Monica inventory at a 30 percent gross profit rate. Monica consistently resold this merchandise in the year of acquisition or in the period immediately following. Transfers for the three years after this business combination was created amounted to the following: In addition, Monica sold Young several pieces of fully depreciated equipment on January 1, 2020, for $53,000. The equipment had originally cost Monica $84,000. Young plans to depreciate these assets over a 5-year period. In 2021, Young earns a net income of $150,000 and declares and pays $40,000 in cash dividends. These figures increase the subsidiary's Retained Earnings to a $910,000 balance at the end of 2021. Monica employs the equity method of accounting. Hence, it reports $91,240 investment income for 2021 with an Investment account balance of $864,550. Prepare the worksheet entries required for the consolidation of Monica Company and Young Company. (If no entry is required for a transaction/event, select "No Journal Entry Required" in the first account field.) \begin{tabular}{|c|c|c|c|c|c|} \hline \multicolumn{6}{|c|}{ Answer is not complete. } \\ \hline No & Transaction & Accounts & & Debit & Credit \\ \hline \multirow[t]{2}{*}{1} & 1 & Retained earnings, 1/1/21 (Young) & 2 & 8,700 & \\ \hline & & Cost of goods sold & & & 8,700 \\ \hline \multirow[t]{3}{*}{2} & 2 & Investment in Young & 0 & 42,400 & \\ \hline & & Equipment & & 31,000 & \\ \hline & & Accumulated depreciation-Equipmen & 2 & & 73,400 \\ \hline 3 & 3 & No journal entry required & 0 & & \\ \hline \multirow[t]{5}{*}{4} & 4 & Common stock - Young & 0 & 100,000 & \\ \hline & & Additional paid-in capital - Young & & 90,000 & \\ \hline & & Retained earnings, 1/1/21 (Young) & 2 & & \\ \hline & & Investment in Young & 2 & & \\ \hline & & Noncontrolling interest in Young & 2 & & \\ \hline \multirow[t]{4}{*}{5} & 5 & Buildings & & & \\ \hline & & Franchise agreement & 2 & & \\ \hline & & Investment in Young & 2 & & \\ \hline & & Noncontrolling interest in Young & 2 & & \\ \hline \multirow[t]{2}{*}{6} & 6 & Investment income & 0 & 91,240 & \\ \hline & & Investment in Young & 2 & & 91,240 \\ \hline \multirow[t]{2}{*}{7} & 7 & Investment in Young & 0 & & \\ \hline & & Dividends declared & & & \\ \hline \end{tabular} \begin{tabular}{|c|c|c|c|c|c|} \hline \multirow[t]{4}{*}{8} & 8 & Depreciation expense & 2 & & \\ \hline & & Amortization expense & 2 & & \\ \hline & & Franchise agreement & 2 & & \\ \hline & & Buildings & 0 & & \\ \hline \multirow[t]{2}{*}{9} & 9 & Sales & 2 & & \\ \hline & & Cost of goods sold & 2 & & \\ \hline \multirow[t]{2}{*}{10} & 10 & Cost of goods sold & 2 & & \\ \hline & & Inventory & 0 & & \\ \hline \multirow[t]{2}{*}{11} & 11 & Accumulated depreciation-Equipment & 2 & & \\ \hline & & Depreciation expense & 2 & & \\ \hline \end{tabular} Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


