
 Please show me how to do all these problems please (formulas)
Please show me how to do all these problems please (formulas)
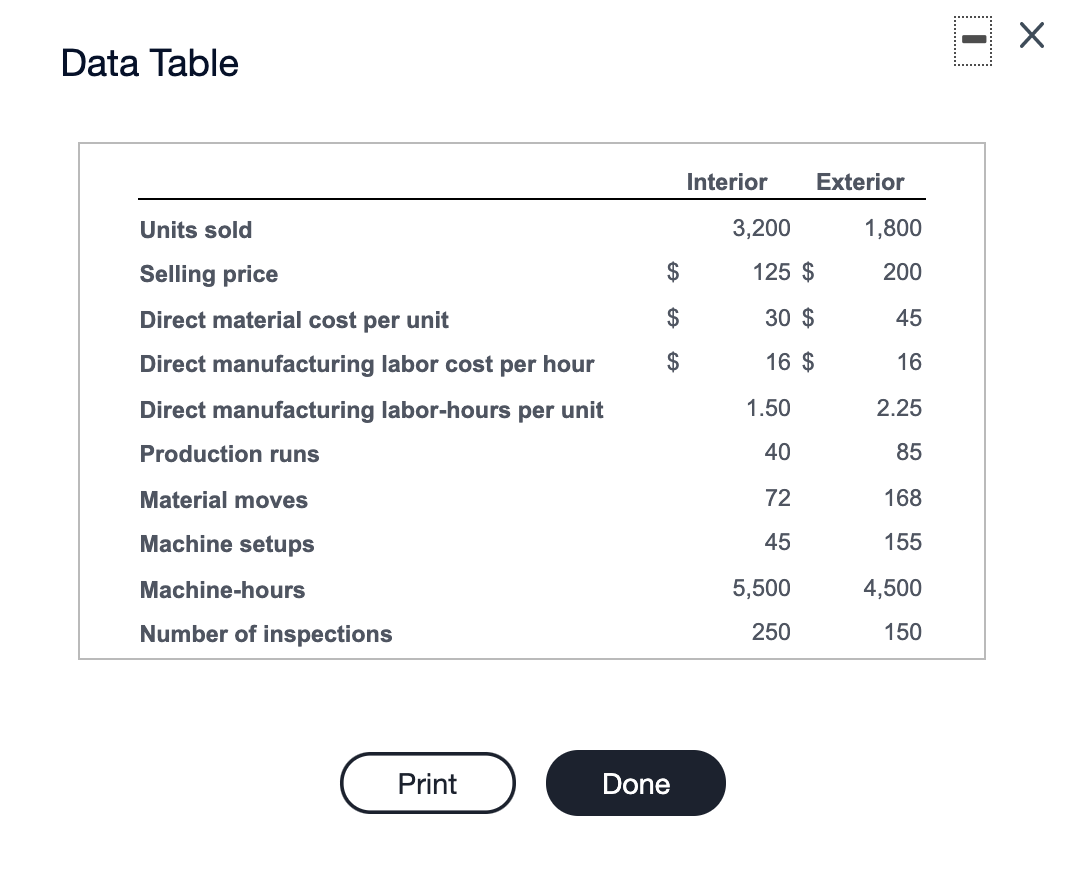
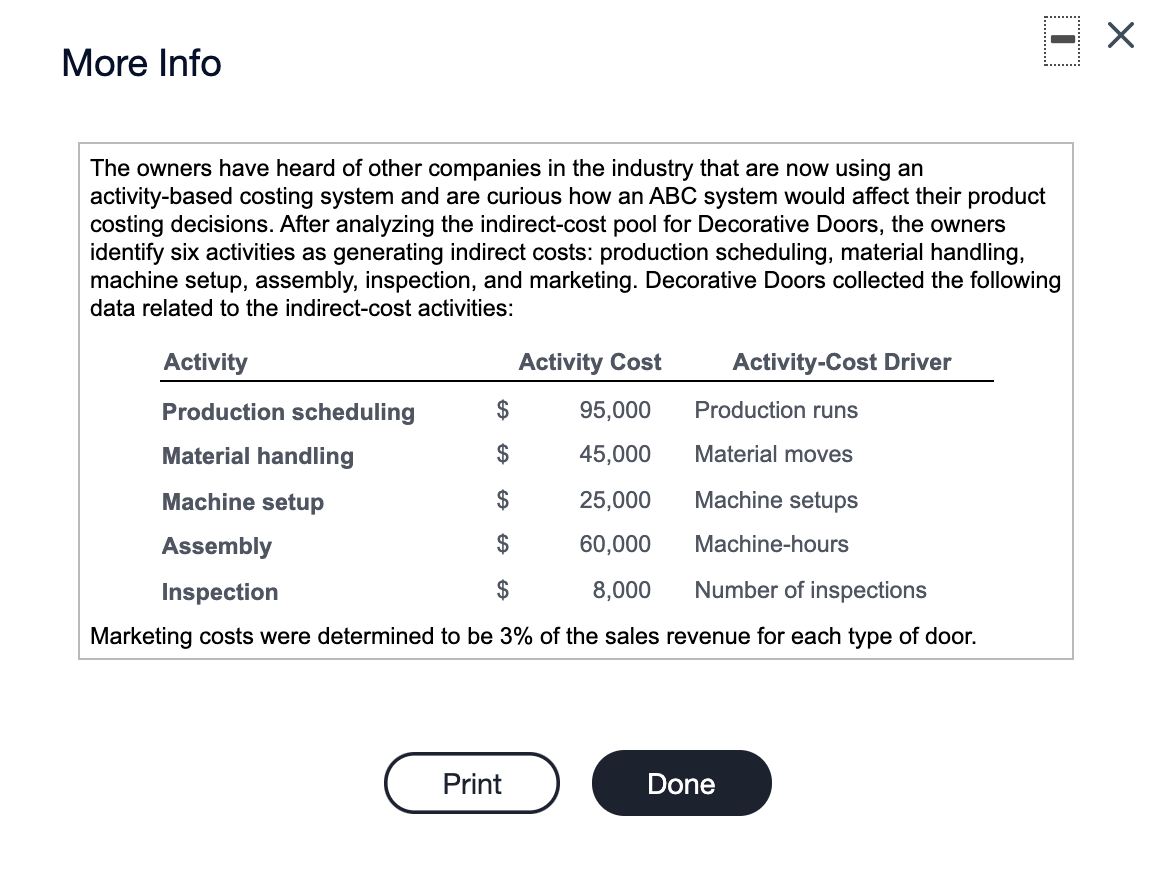
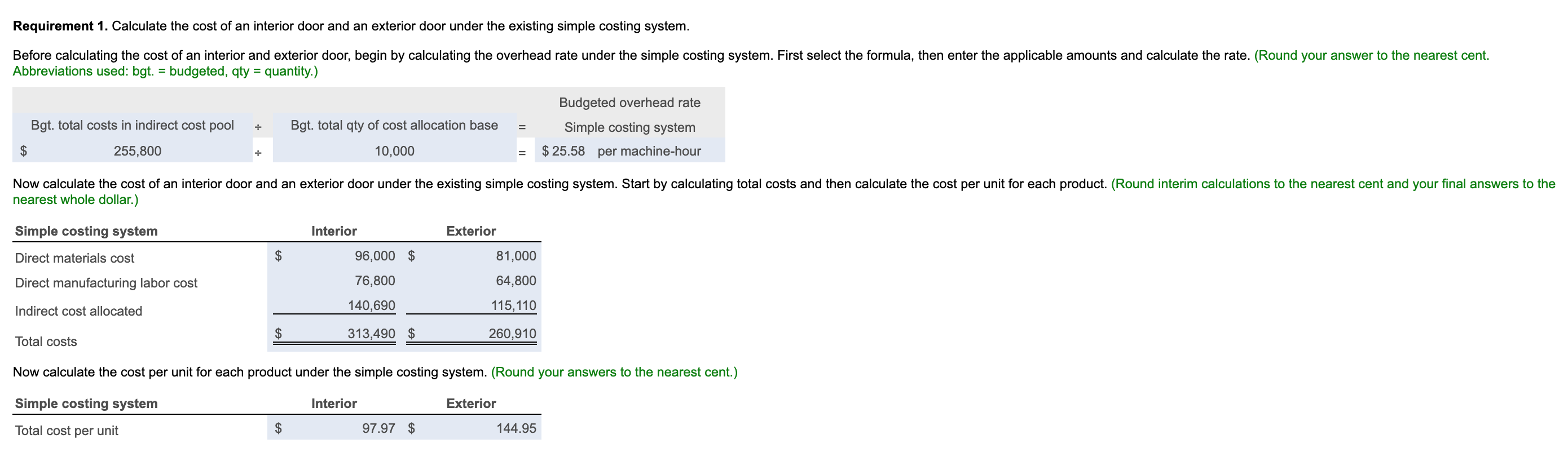
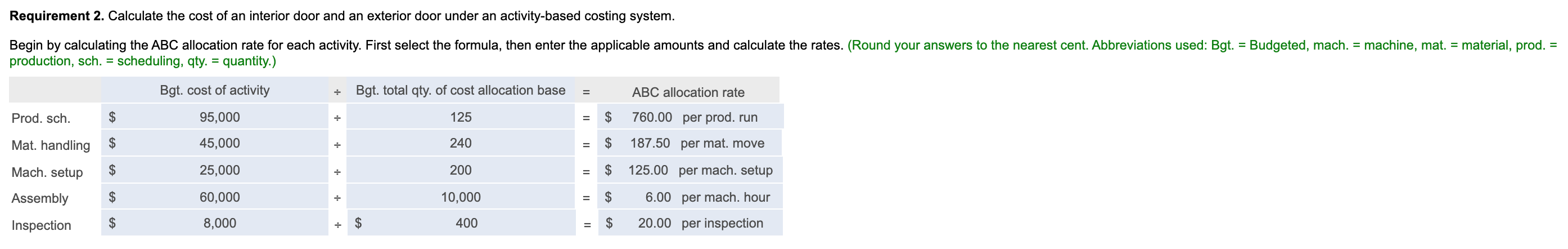
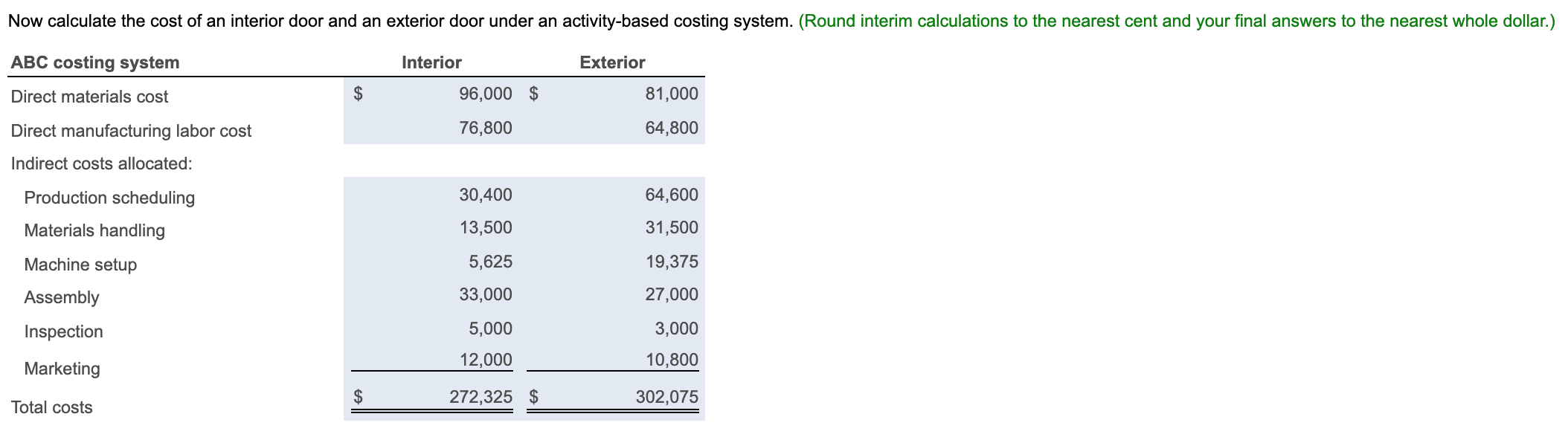
Decorative Doors, Inc., produces two types of doors, interior and exterior. The company's simple costing system has two direct-cost categories (materials and labor) and one indirect-cost pool. The simple costing system allocates indirect costs on the basis of machine-hours. Recently, the owners of Decorative Doors have been concerned about a decline in the market share for their interior doors, usually their biggest seller. Information related to Decorative Doors production for the most recent year follows: (Click the icon to view the production data.) (Click the icon to view additional information.) Read the requirements. ----- Data Table Interior Exterior 3,200 1,800 $ 125 $ 200 Units sold Selling price Direct material cost per unit Direct manufacturing labor cost per hour Direct manufacturing labor-hours per unit $ 30 $ 45 $ 16 $ 16 1.50 2.25 Production runs 40 85 72 168 45 155 Material moves Machine setups Machine-hours Number of inspections 5,500 4,500 250 150 Print Done More Info The owners have heard of other companies in the industry that are now using an activity-based costing system and are curious how an ABC system would affect their product costing decisions. After analyzing the indirect-cost pool for Decorative Doors, the owners identify six activities as generating indirect costs: production scheduling, material handling, machine setup, assembly, inspection, and marketing. Decorative Doors collected the following data related to the indirect-cost activities: Activity Activity Cost Activity-Cost Driver Production scheduling $ 95,000 Production runs Material handling $ 45,000 Material moves Machine setup $ 25,000 Machine setups Assembly $ 60,000 Machine-hours Inspection $ 8,000 Number of inspections Marketing costs were determined to be 3% of the sales revenue for each type of door. Print Done Requirement 1. Calculate the cost of an interior door and an exterior door under the existing simple costing system. Before calculating the cost of an interior and exterior door, begin by calculating the overhead rate under the simple costing system. First select the formula, then enter the applicable amounts and calculate the rate. (Round your answer to the nearest cent. Abbreviations used: bgt. = budgeted, qty = quantity.) Budgeted overhead rate Bgt. total costs in indirect cost pool = Bgt. total qty of cost allocation base 10,000 Simple costing system $ 25.58 per machine-hour $ 255,800 + = Now calculate the cost of an interior door and an exterior door under the existing simple costing system. Start by calculating total costs and then calculate the cost per unit for each product. (Round interim calculations to the nearest cent and your final answers to the nearest whole dollar.) Simple costing system Interior Exterior Direct materials cost $ 96,000 $ 81,000 Direct manufacturing labor cost 76,800 64,800 Indirect cost allocated 140,690 115,110 $ 313,490 $ 260,910 Total costs Now calculate the cost per unit for each product under the simple costing system. (Round your answers to the nearest cent.) Simple costing system Interior Exterior Total cost per unit $ 97.97 $ 144.95 Requirement 2. Calculate the cost of an interior door and an exterior door under an activity-based costing system. = Begin by calculating the ABC allocation rate for each activity. First select the formula, then enter the applicable amounts and calculate the rates. (Round your answers to the nearest cent. Abbreviations used: Bgt. = Budgeted, mach. = machine, mat. = material, prod. production, sch. = scheduling, qty = quantity.) Bgt. cost of activity Bgt. total qty. of cost allocation base ABC allocation rate . = Prod. sch. $ 95,000 125 = $ 760.00 per prod. run Mat. handling $ 45,000 . 240 $ 187.50 per mat. move Mach. setup $ 25,000 . 200 $ 125.00 per mach. setup Assembly $ 60,000 + 10,000 $ 6.00 per mach. hour Inspection $ 8,000 ; $ 400 $ 20.00 per inspection Now calculate the cost of an interior door and an exterior door under an activity-based costing system. (Round interim calculations to the nearest cent and your final answers to the nearest whole dollar.) ABC costing system Interior Exterior Direct materials cost $ 96,000 $ 81,000 Direct manufacturing labor cost 76,800 64,800 Indirect costs allocated: 30,400 13,500 Production scheduling Materials handling Machine setup Assembly Inspection 64,600 31,500 19,375 27,000 5,625 33,000 5,000 3,000 12,000 10,800 Marketing $ 272,325 $ 302,075 Total costs Now calculate the cost per unit for each product under ABC. (Round your answers to the nearest cent.) ABC costing system Interior Exterior Total cost per unit $ 85.10 $ 167.82 Requirement 3. Compare the costs of the doors in requirements 1 and 2. Why do the simple and activity-based costing systems differ in the cost of an interior door and an exterior door? Relative to the ABC system, the simple costing system overcosts interior doors and undercosts exterior doors. Under the simple costing system, the volume of the production of interior doors is driving the amount of overhead allocated to the interior doors. The ABC study reveals that each exterior door requires more production runs, material moves, and setups . This is reflected in the higher indirect costs allocated to exterior doors in the ABC system. Requirement 4. How might Decorative Doors, Inc., use the new cost information from its activity-based costing system to address the declining market share for interior doors? (Select all choices that apply.) A. Decorative Doors can use the ABC information to improve its own operations. It could examine each of the indirect cost categories and analyze whether it would be possible to deliver the same level of service, but consume fewer indirect resources, or find a way to reduce the per-unit-cost-driver cost of some of those indirect resources. B. Decorative Doors, Inc. can use the information revealed by the ABC system to change its pricing based on the ABC costs. C. Decorative Doors, Inc. should consider decreasing the price of its exerior doors to be more competitive. D. Decorative Doors should consider increasing the price of its exterior doors, depending on the competition it faces in this market. E. Decorative Doors, Inc. should consider increasing the price of its interior doors depending on the competition it faces in this market. Decorative Doors, Inc. should consider decreasing the price of its interior doors to be more competitive






 Please show me how to do all these problems please (formulas)
Please show me how to do all these problems please (formulas)





