 Please show work of answers.
Please show work of answers.
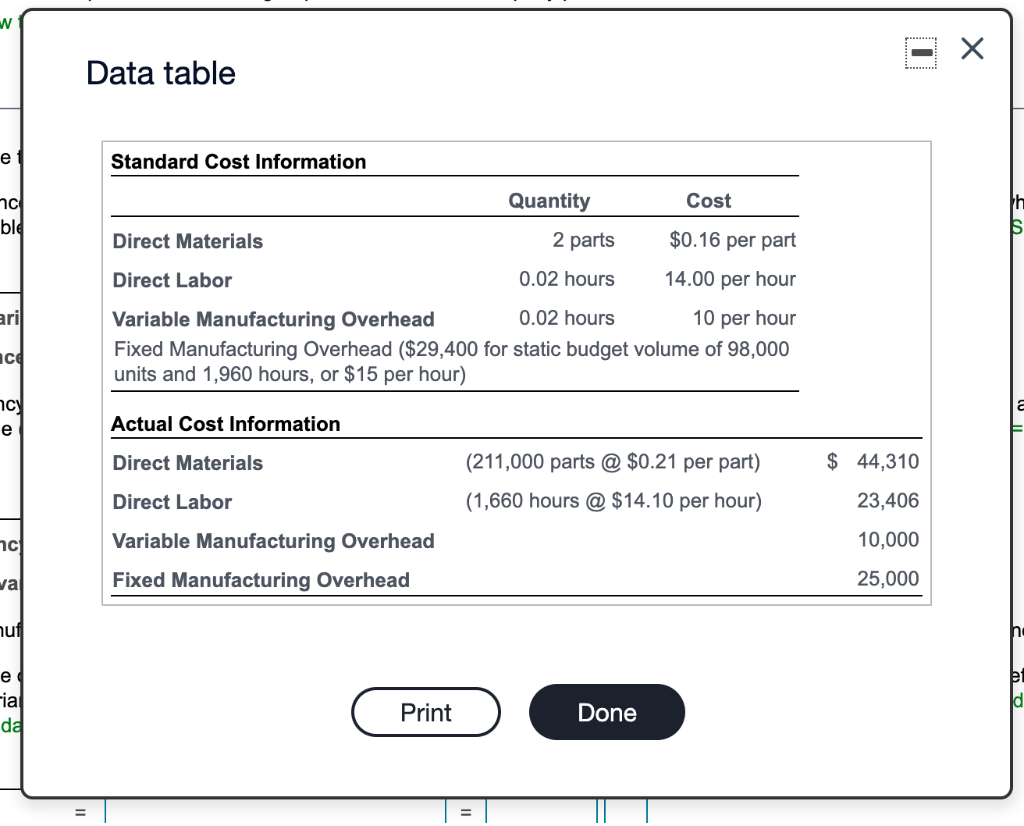
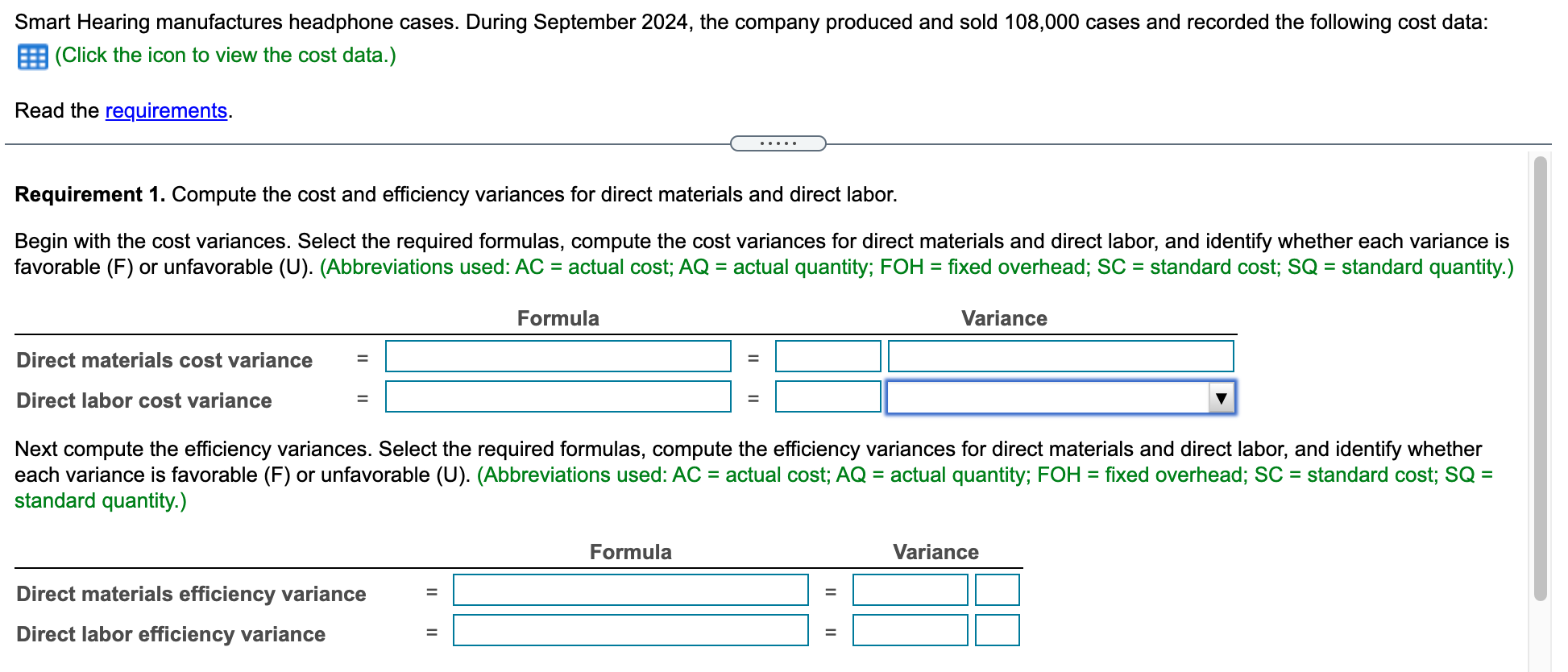
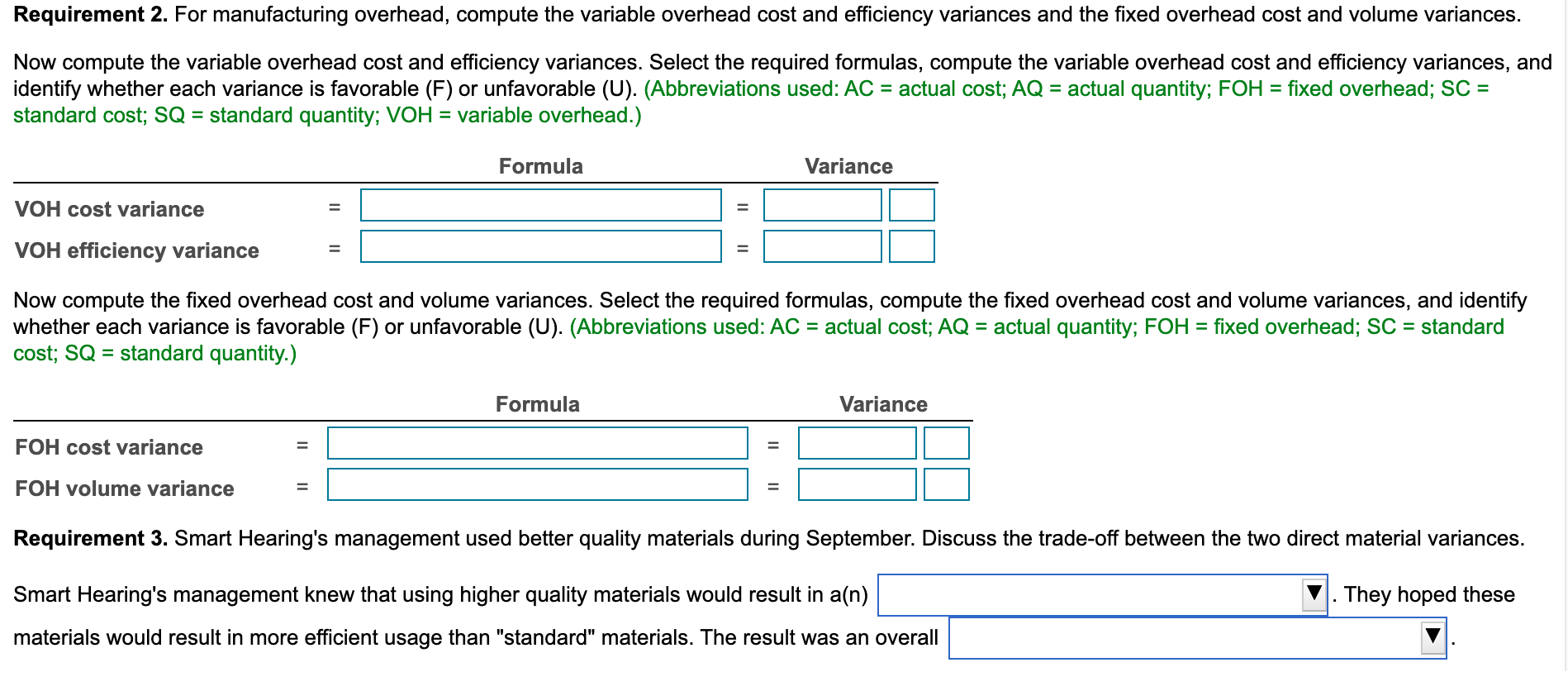
w = Data table e Standard Cost Information Quantity Cost nc ble Direct Materials 2 parts $0.16 per part aril Direct Labor 0.02 hours 14.00 per hour Variable Manufacturing Overhead 0.02 hours 10 per hour Fixed Manufacturing Overhead ($29,400 for static budget volume of 98,000 units and 1,960 hours, or $15 per hour) ce ncy a e Actual Cost Information Direct Materials $ 44, (211,000 parts @ $0.21 per part) (1,660 hours @ $14.10 per hour) nc Direct Labor Variable Manufacturing Overhead Fixed Manufacturing Overhead 23,406 10,000 25,000 va nuf e Fial dd b ld Print Done Smart Hearing manufactures headphone cases. During September 2024, the company produced and sold 108,000 cases and recorded the following cost data: |(Click the icon to view the cost data.) Read the requirements. Requirement 1. Compute the cost and efficiency variances for direct materials and direct labor. Begin with the cost variances. Select the required formulas, compute the cost variances for direct materials and direct labor, and identify whether each variance is favorable (F) or unfavorable (U). (Abbreviations used: AC = actual cost; AQ = actual quantity; FOH = fixed overhead; SC = standard cost; SQ = standard quantity.) Formula Variance Direct materials cost variance = Direct labor cost variance Next compute the efficiency variances. Select the required formulas, compute the efficiency variances for direct materials and direct labor, and identify whether each variance is favorable (F) or unfavorable (U). (Abbreviations used: AC = actual cost; AQ = actual quantity; FOH = fixed overhead; SC = standard cost; SQ = standard quantity.) = Formula Variance Direct materials efficiency variance II Direct labor efficiency variance Requirement 2. For manufacturing overhead, compute the variable overhead cost and efficiency variances and the fixed overhead cost and volume variances. Now compute the variable overhead cost and efficiency variances. Select the required formulas, compute the variable overhead cost and efficiency variances, and identify whether each variance is favorable (F) or unfavorable (U). (Abbreviations used: AC = actual cost; AQ = actual quantity; FOH = fixed overhead; SC = standard cost; SQ = standard quantity; VOH = variable overhead.) Formula Variance VOH cost variance = VOH efficiency variance - Now compute the fixed overhead cost and volume variances. Select the required formulas, compute the fixed overhead cost and volume variances, and identify whether each variance is favorable (F) or unfavorable (U). (Abbreviations used: AC = actual cost; AQ = actual quantity; FOH = fixed overhead; SC = standard cost; SQ = standard quantity.) Formula Variance FOH cost variance = FOH volume variance Requirement 3. Smart Hearing's management used better quality materials during September. Discuss the trade-off between the two direct material variances. Smart Hearing's management knew that using higher quality materials would result in a(n) . They hoped these materials would result in more efficient usage than "standard" materials. The result was an overall


 Please show work of answers.
Please show work of answers.





