Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
please show working the question is complete. 16 a) b)c)d) approxma 02, supplemented with overtime.) 16. MT makes small camping and snowmobile trailers. The demand
please show working 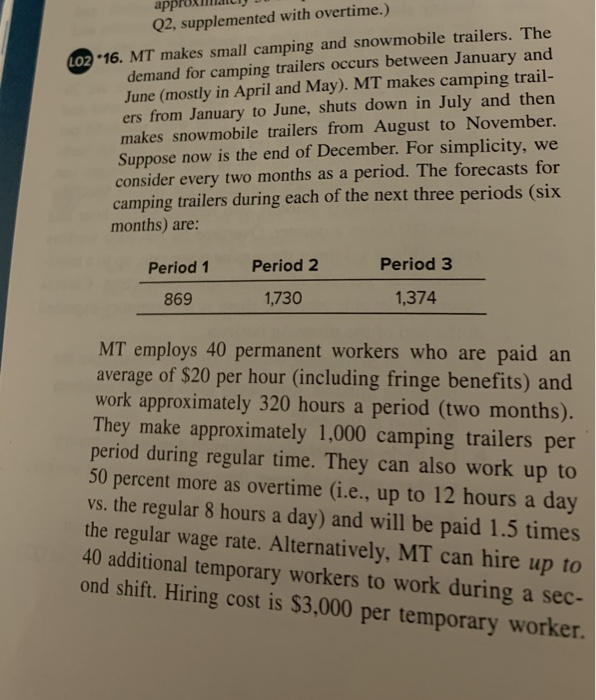


the question is complete. 16 a) b)c)d)
approxma 02, supplemented with overtime.) 16. MT makes small camping and snowmobile trailers. The demand for camping trailers occurs between January and June (mostly in April and May). MT makes camping trail- ers from January to June, shuts down in July and then makes snowmobile trailers from August to November. Suppose now is the end of December. For simplicity, we consider every two months as a period. The forecasts for camping trailers during each of the next three periods (six months) are Lo2 Period 3 Period2 Period 1 869 1,730 1,374 MT employs 40 permanent workers who are paid an average of $20 per hour (including fringe benefits) and work approximately 320 hours a period (two months). They make approximately 1,000 camping trailers per period during regular time. They can also work up to 50 percent more as overtime (i.e., up to 12 hours a day vs. the regular 8 hours a day) and will be paid 1.5 times the regular wage rate. Alternatively, MT can hire up to 40 additional temporary workers to work during a sec- ond shift. Hiring cost is $3,000 per temporary worker. ing and Master Scheduling Assume temporary workers' wa ity are the same as permanent worke temporary workers work only during rate and productiv. :. Also assume reezers, and that temporary workers work onlyd (no overtime) and are kept for whole two months or four months). Inventoue, for per camping trailer per period is S180, ad to average inventory level during each period. c there are no camping trailers on hand, and the en inventory at the end of period 3 is zero small positive number is also acceptable). MT to meet the total demand, but shortage durine wishes (except last) is acceptable, in w is assumed to be back ordered at the cost of sorage camping trailer per period. a. Calculate all the relevant unit costs. b. Suppose MT uses permanent workers during regular time and overtime. Determine the minimum cost plan in this case. (Hint: Use overtime in each de ion planner regular time ods (i.e., nt manager each quar- 3: 35,000 in Janu- , is.$180, and ischarged r of next ance in sirable. (althouc d that e are a period hich case the s per p to per ime our ry rs period.) c. Suppose MT hires temporary workers, but decides not to use permanent workers during overtime (just regu- lar time). Determine the minimum cost plan in this case. (Hint: Hire 15 temps for two periods and nine temps for one period starting in period 2.) d. Would overtime production by permanent workers and regular time production by temporary workers simul- taneously result in a lower total cost? Do a trade-of analysis. What is the overall minimum cost plan? 02 17. Mity-Lite (ML) is a manufout approxma 02, supplemented with overtime.) 16. MT makes small camping and snowmobile trailers. The demand for camping trailers occurs between January and June (mostly in April and May). MT makes camping trail- ers from January to June, shuts down in July and then makes snowmobile trailers from August to November. Suppose now is the end of December. For simplicity, we consider every two months as a period. The forecasts for camping trailers during each of the next three periods (six months) are Lo2 Period 3 Period2 Period 1 869 1,730 1,374 MT employs 40 permanent workers who are paid an average of $20 per hour (including fringe benefits) and work approximately 320 hours a period (two months). They make approximately 1,000 camping trailers per period during regular time. They can also work up to 50 percent more as overtime (i.e., up to 12 hours a day vs. the regular 8 hours a day) and will be paid 1.5 times the regular wage rate. Alternatively, MT can hire up to 40 additional temporary workers to work during a sec- ond shift. Hiring cost is $3,000 per temporary worker. ing and Master Scheduling Assume temporary workers' wa ity are the same as permanent worke temporary workers work only during rate and productiv. :. Also assume reezers, and that temporary workers work onlyd (no overtime) and are kept for whole two months or four months). Inventoue, for per camping trailer per period is S180, ad to average inventory level during each period. c there are no camping trailers on hand, and the en inventory at the end of period 3 is zero small positive number is also acceptable). MT to meet the total demand, but shortage durine wishes (except last) is acceptable, in w is assumed to be back ordered at the cost of sorage camping trailer per period. a. Calculate all the relevant unit costs. b. Suppose MT uses permanent workers during regular time and overtime. Determine the minimum cost plan in this case. (Hint: Use overtime in each de ion planner regular time ods (i.e., nt manager each quar- 3: 35,000 in Janu- , is.$180, and ischarged r of next ance in sirable. (althouc d that e are a period hich case the s per p to per ime our ry rs period.) c. Suppose MT hires temporary workers, but decides not to use permanent workers during overtime (just regu- lar time). Determine the minimum cost plan in this case. (Hint: Hire 15 temps for two periods and nine temps for one period starting in period 2.) d. Would overtime production by permanent workers and regular time production by temporary workers simul- taneously result in a lower total cost? Do a trade-of analysis. What is the overall minimum cost plan? 02 17. Mity-Lite (ML) is a manufout Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


