Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Please show your work & typed. We know that the Modigliani Miller (MM) propositions provide the framework for the analysis of impact of financing decisions
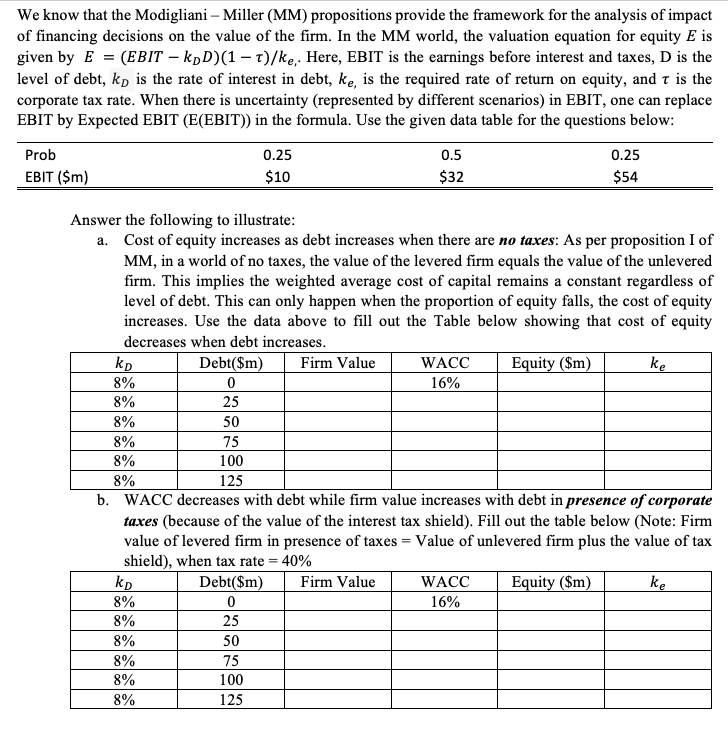
Please show your work & typed.
We know that the Modigliani Miller (MM) propositions provide the framework for the analysis of impact of financing decisions on the value of the firm. In the MM world, the valuation equation for equity E is given by E = (EBIT kpD)(1 t)/ke, Here, EBIT is the earnings before interest and taxes, D is the level of debt, kp is the rate of interest in debt, ke, is the required rate of return on equity, and t is the corporate tax rate. When there is uncertainty (represented by different scenarios) in EBIT, one can replace EBIT by Expected EBIT (E(EBIT)) in the formula. Use the given data table for the questions below: Prob EBIT ($m) 0.25 $10 0.5 $32 0.25 $54 Answer the following to illustrate: a. Cost of equity increases as debt increases when there are no taxes: As per proposition I of MM, in a world of no taxes, the value of the levered firm equals the value of the unlevered firm. This implies the weighted average cost of capital remains a constant regardless of level of debt. This can only happen when the proportion of equity falls, the cost of equity increases. Use the data above to fill out the Table below showing that cost of equity decreases when debt increases. Debt($m) Firm Value WACC Equity ($m) ke 8% 0 16% 8% 25 8% 50 8% 75 8% 100 8% 125 b. WACC decreases with debt while firm value increases with debt in presence of corporate taxes (because of the value of the interest tax shield). Fill out the table below (Note: Firm value of levered firm in presence of taxes = Value of unlevered firm plus the value of tax shield), when tax rate = 40% Debt($m) Firm Value WACC Equity ($m) ke 8% 0 16% 8% 8% 50 8% 75 8% 100 8% 125 25 We know that the Modigliani Miller (MM) propositions provide the framework for the analysis of impact of financing decisions on the value of the firm. In the MM world, the valuation equation for equity E is given by E = (EBIT kpD)(1 t)/ke, Here, EBIT is the earnings before interest and taxes, D is the level of debt, kp is the rate of interest in debt, ke, is the required rate of return on equity, and t is the corporate tax rate. When there is uncertainty (represented by different scenarios) in EBIT, one can replace EBIT by Expected EBIT (E(EBIT)) in the formula. Use the given data table for the questions below: Prob EBIT ($m) 0.25 $10 0.5 $32 0.25 $54 Answer the following to illustrate: a. Cost of equity increases as debt increases when there are no taxes: As per proposition I of MM, in a world of no taxes, the value of the levered firm equals the value of the unlevered firm. This implies the weighted average cost of capital remains a constant regardless of level of debt. This can only happen when the proportion of equity falls, the cost of equity increases. Use the data above to fill out the Table below showing that cost of equity decreases when debt increases. Debt($m) Firm Value WACC Equity ($m) ke 8% 0 16% 8% 25 8% 50 8% 75 8% 100 8% 125 b. WACC decreases with debt while firm value increases with debt in presence of corporate taxes (because of the value of the interest tax shield). Fill out the table below (Note: Firm value of levered firm in presence of taxes = Value of unlevered firm plus the value of tax shield), when tax rate = 40% Debt($m) Firm Value WACC Equity ($m) ke 8% 0 16% 8% 8% 50 8% 75 8% 100 8% 125 25Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


