Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
PLEASE SOLVE FOR PART B Note: You can right-click the image then open in a new tab to better see the problem Exercise 7-4 Procter
PLEASE SOLVE FOR PART B
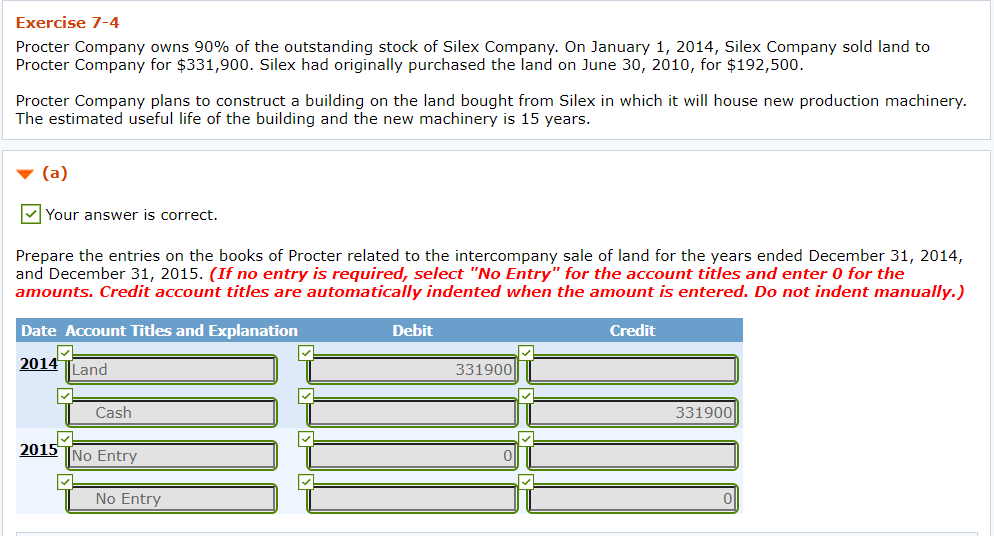
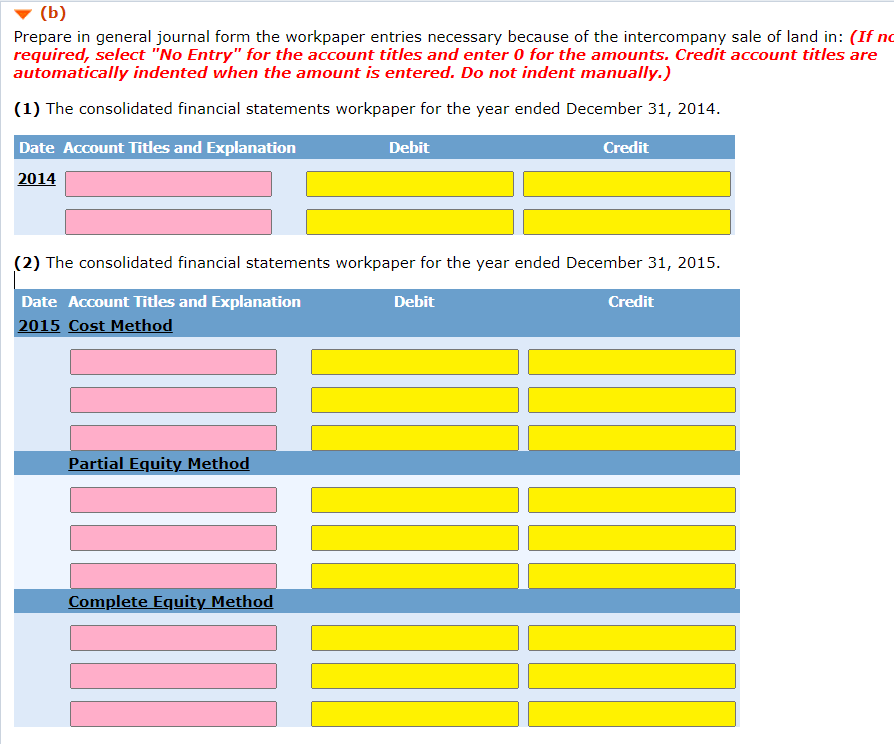
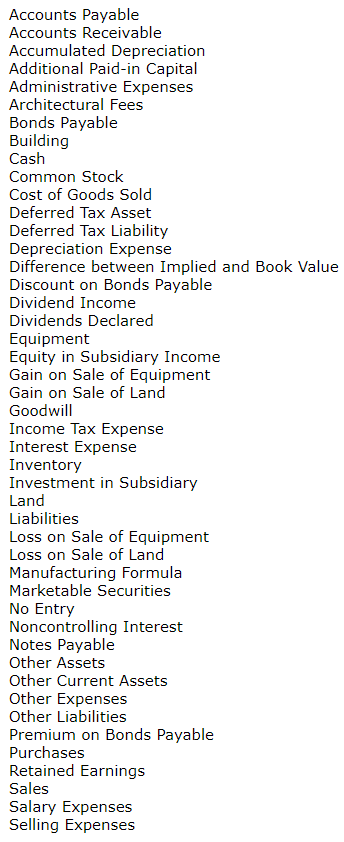
Note: You can right-click the image then open in a new tab to better see the problem
Exercise 7-4 Procter Company owns 90% of the outstanding stock of Silex Company. On January 1, 2014, Silex Company sold land to Procter Company for $331,900. Silex had originally purchased the land on June 30, 2010, for $192,500. Procter Company plans to construct a building on the land bought from Silex in which it will house new production machinery. The estimated useful life of the building and the new machinery is 15 years. (a) Your answer is correct. Prepare the entries on the books of Procter related to the intercompany sale of land for the years ended December 31, 2014, and December 31, 2015. (If no entry is required, select "No Entry" for the account titles and enter 0 for the amounts. Credit account titles are automatically indented when the amount is entered. Do not indent manually.) Date Account Titles and Explanation Debit Credit 2014 TLand 331900 Cash 331900 2015 No Entry No Entry ol (b) Prepare in general journal form the workpaper entries necessary because of the intercompany sale of land in: (If no required, select "No Entry" for the account titles and enter o for the amounts. Credit account titles are automatically indented when the amount is entered. Do not indent manually.) (1) The consolidated financial statements workpaper for the year ended December 31, 2014. Debit Credit Date Account Titles and Explanation 2014 (2) The consolidated financial statements workpaper for the year ended December 31, 2015. Debit Credit Date Account Titles and Explanation 2015 Cost Method Partial Equity Method Complete Equity Method Accounts Payable Accounts Receivable Accumulated Depreciation Additional Paid-in Capital Administrative Expenses Architectural Fees Bonds Payable Building Cash Common Stock Cost of Goods Sold Deferred Tax Asset Deferred Tax Liability Depreciation Expense Difference between Implied and Book Value Discount on Bonds Payable Dividend Income Dividends Declared Equipment Equity in Subsidiary Income Gain on Sale of Equipment Gain on Sale of Land Goodwill Income Tax Expense Interest Expense Inventory Investment in Subsidiary Land Liabilities Loss on Sale of Equipment Loss on Sale of Land Manufacturing Formula Marketable Securities No Entry Noncontrolling Interest Notes Payable Other Assets Other Current Assets Other Expenses Other Liabilities Premium on Bonds Payable Purchases Retained Earnings Sales Salary Expenses Selling ExpensesStep by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


