Question: Please, use CTRL and + to zoom the task. Every method should work as it is defined in the task! The input file can be
Please, use CTRL and + to zoom the task. Every method should work as it is defined in the task! The input file can be different(different numbers). Thank you! Should be done in Java!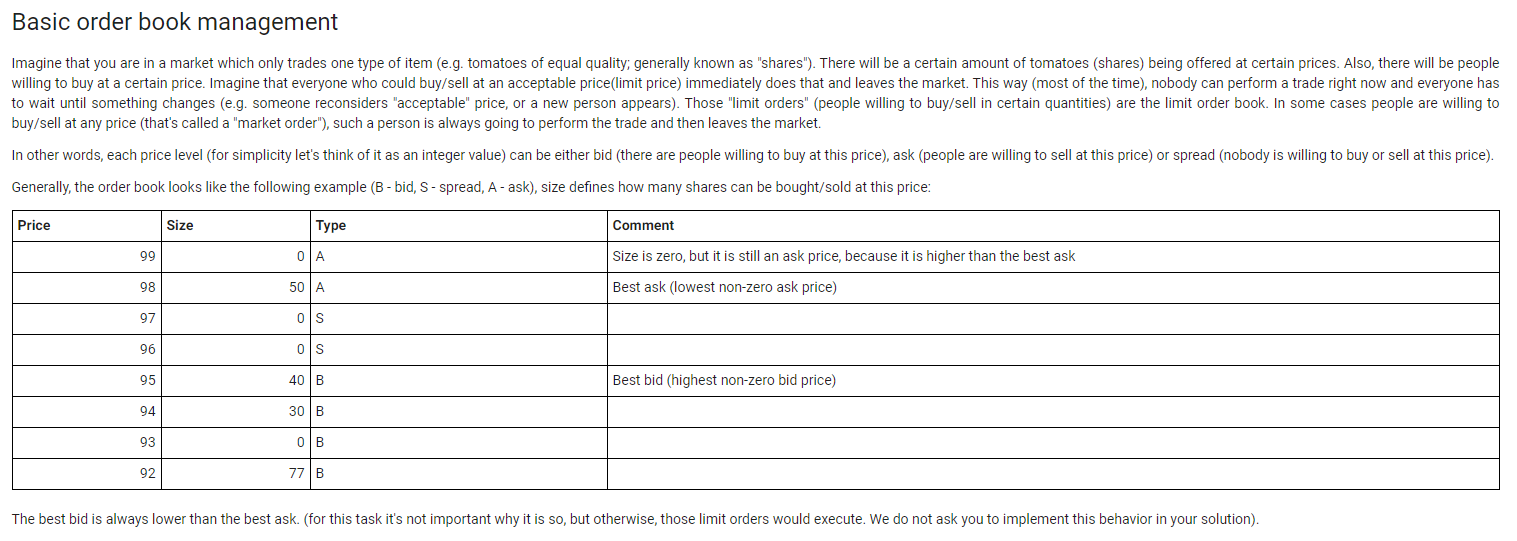
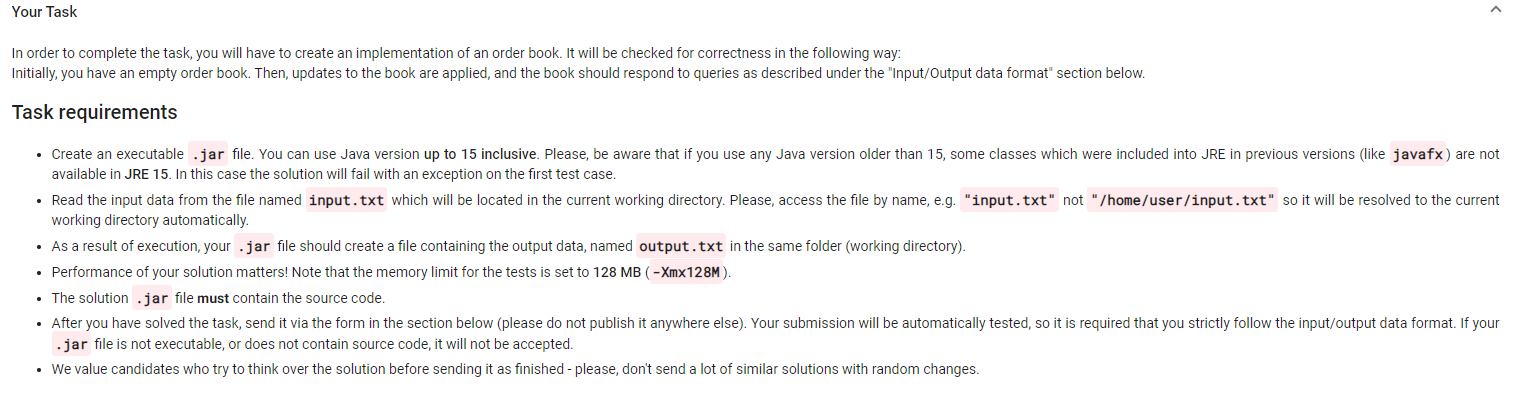
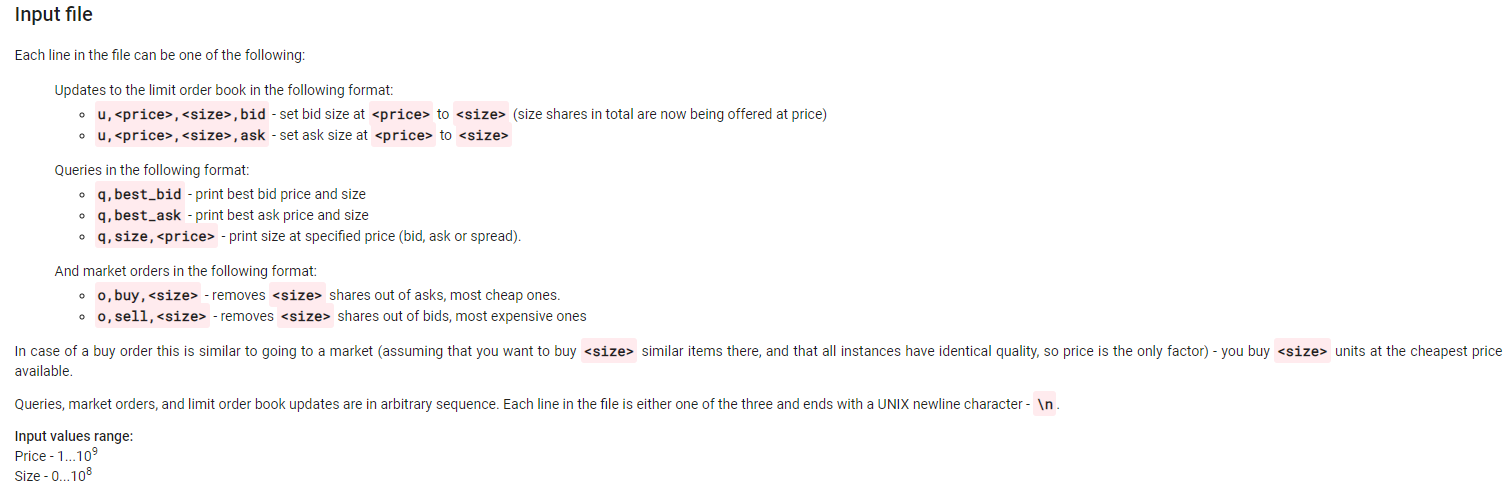
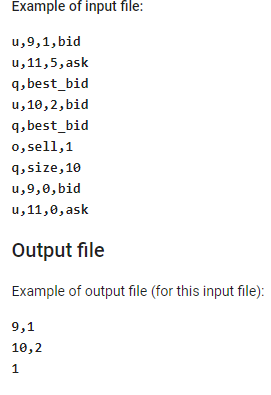
Basic order book management Imagine that you are in a market which only trades one type of item (e.g. tomatoes of equal quality, generally known as "shares"). There will be a certain amount of tomatoes (shares) being offered at certain prices. Also, there will be people willing to buy at a certain price. Imagine that everyone who could buy/sell at an acceptable price(limit price) immediately does that and leaves the market. This way (most of the time), nobody can perform a trade right now and everyone has to wait until something changes (e.g. someone reconsiders "acceptable" price, or a new person appears). Those "limit orders" (people willing to buy/sell in certain quantities) are the limit order book. In some cases people are willing to buy/sell at any price (that's called a "market order"), such a person is always going to perform the trade and then leaves the market. In other words, each price level (for simplicity let's think of it as an integer value) can be either bid (there are people willing to buy at this price), ask (people are willing to sell at this price) or spread (nobody is willing to buy or sell at this price). Generally, the order book looks like the following example (B-bid, S-spread, A-ask), size defines how many shares can be bought/sold at this price: Price Size Type Comment 99 OLA Size is zero, but it is still an ask price, because it is higher than the best ask 98 50 A Best ask (lowest non-zero ask price) 97 Os 96 os 95 40 B Best bid (highest non-zero bid price) 94 30 B 93 OB 92 77 B The best bid is always lower than the best ask. (for this task it's not important why it is so, but otherwise, those limit orders would execute. We do not ask you to implement this behavior in your solution). Your Task In order to complete the task, you will have to create an implementation of an order book. It will be checked for correctness in the following way: Initially, you have an empty order book. Then, updates to the book are applied, and the book should respond to queries as described under the "Input/Output data format" section below. Task requirements Create an executable .jar file. You can use Java version up to 15 inclusive. Please, be aware that if you use any Java version older than 15, some classes which were included into JRE in previous versions (like javafx) are not available in JRE 15. In this case the solution will fail with an exception on the first test case. Read the input data from the file named input.txt which will be located in the current working directory. Please, access the file by name, e.g. "input.txt" not "/home/user/input.txt" so it will be resolved to the current working directory automatically. As a result of execution, your .jar file should create a file containing the output data, named output.txt in the same folder (working directory). Performance of your solution matters! Note that the memory limit for the tests is set to 128 MB (-Xmx128M). The solution .jar file must contain the source code. After you have solved the task, send it via the form in the section below (please do not publish it anywhere else). Your submission will be automatically tested, so it is required that you strictly follow the input/output data format. If your .jar file is not executable, or does not contain source code, it will not be accepted. We value candidates who try to think over the solution before sending it as finished - please, don't send a lot of similar solutions with random changes. Input file Each line in the file can be one of the following: Updates to the limit order book in the following format: ou, , , bid - set bid size at to (size shares in total are now being offered at price) u, , , ask - set ask size at to Queries in the following format: oq, best_bid - print best bid price and size oq, best_ask - print best ask price and size o q, size, - print size at specified price (bid, ask or spread). And market orders in the following format: o o, buy, - removes shares out of asks, most cheap ones. oo, sell, - removes shares out of bids, most expensive ones In case of a buy order this is similar to going to a market (assuming that you want to buy similar items there, and that all instances have identical quality, so price is the only factor) - you buy units at the cheapest price available. Queries, market orders, and limit order book updates are in arbitrary sequence. Each line in the file is either one of the three and ends with a UNIX newline character - In. Input values range: Price - 1...10 Size - 0...108 Example of input file: u,9,1,bid u, 11,5, ask q, best_bid u,10,2,bid q, best_bid 0, sell,1 9,size, 10 u,9,0, bid u, 11,0, ask Output file Example of output file (for this input file): 9,1 10,2 1 Basic order book management Imagine that you are in a market which only trades one type of item (e.g. tomatoes of equal quality, generally known as "shares"). There will be a certain amount of tomatoes (shares) being offered at certain prices. Also, there will be people willing to buy at a certain price. Imagine that everyone who could buy/sell at an acceptable price(limit price) immediately does that and leaves the market. This way (most of the time), nobody can perform a trade right now and everyone has to wait until something changes (e.g. someone reconsiders "acceptable" price, or a new person appears). Those "limit orders" (people willing to buy/sell in certain quantities) are the limit order book. In some cases people are willing to buy/sell at any price (that's called a "market order"), such a person is always going to perform the trade and then leaves the market. In other words, each price level (for simplicity let's think of it as an integer value) can be either bid (there are people willing to buy at this price), ask (people are willing to sell at this price) or spread (nobody is willing to buy or sell at this price). Generally, the order book looks like the following example (B-bid, S-spread, A-ask), size defines how many shares can be bought/sold at this price: Price Size Type Comment 99 OLA Size is zero, but it is still an ask price, because it is higher than the best ask 98 50 A Best ask (lowest non-zero ask price) 97 Os 96 os 95 40 B Best bid (highest non-zero bid price) 94 30 B 93 OB 92 77 B The best bid is always lower than the best ask. (for this task it's not important why it is so, but otherwise, those limit orders would execute. We do not ask you to implement this behavior in your solution). Your Task In order to complete the task, you will have to create an implementation of an order book. It will be checked for correctness in the following way: Initially, you have an empty order book. Then, updates to the book are applied, and the book should respond to queries as described under the "Input/Output data format" section below. Task requirements Create an executable .jar file. You can use Java version up to 15 inclusive. Please, be aware that if you use any Java version older than 15, some classes which were included into JRE in previous versions (like javafx) are not available in JRE 15. In this case the solution will fail with an exception on the first test case. Read the input data from the file named input.txt which will be located in the current working directory. Please, access the file by name, e.g. "input.txt" not "/home/user/input.txt" so it will be resolved to the current working directory automatically. As a result of execution, your .jar file should create a file containing the output data, named output.txt in the same folder (working directory). Performance of your solution matters! Note that the memory limit for the tests is set to 128 MB (-Xmx128M). The solution .jar file must contain the source code. After you have solved the task, send it via the form in the section below (please do not publish it anywhere else). Your submission will be automatically tested, so it is required that you strictly follow the input/output data format. If your .jar file is not executable, or does not contain source code, it will not be accepted. We value candidates who try to think over the solution before sending it as finished - please, don't send a lot of similar solutions with random changes. Input file Each line in the file can be one of the following: Updates to the limit order book in the following format: ou, , , bid - set bid size at to (size shares in total are now being offered at price) u, , , ask - set ask size at to Queries in the following format: oq, best_bid - print best bid price and size oq, best_ask - print best ask price and size o q, size, - print size at specified price (bid, ask or spread). And market orders in the following format: o o, buy, - removes shares out of asks, most cheap ones. oo, sell, - removes shares out of bids, most expensive ones In case of a buy order this is similar to going to a market (assuming that you want to buy similar items there, and that all instances have identical quality, so price is the only factor) - you buy units at the cheapest price available. Queries, market orders, and limit order book updates are in arbitrary sequence. Each line in the file is either one of the three and ends with a UNIX newline character - In. Input values range: Price - 1...10 Size - 0...108 Example of input file: u,9,1,bid u, 11,5, ask q, best_bid u,10,2,bid q, best_bid 0, sell,1 9,size, 10 u,9,0, bid u, 11,0, ask Output file Example of output file (for this input file): 9,1 10,2 1







