Question: please use matlab format, Thank you very much 5. A matrix A is tridiagonal if ai 0 whenever li -jl>1. For example, 0 4 1
please use matlab format, Thank you very much
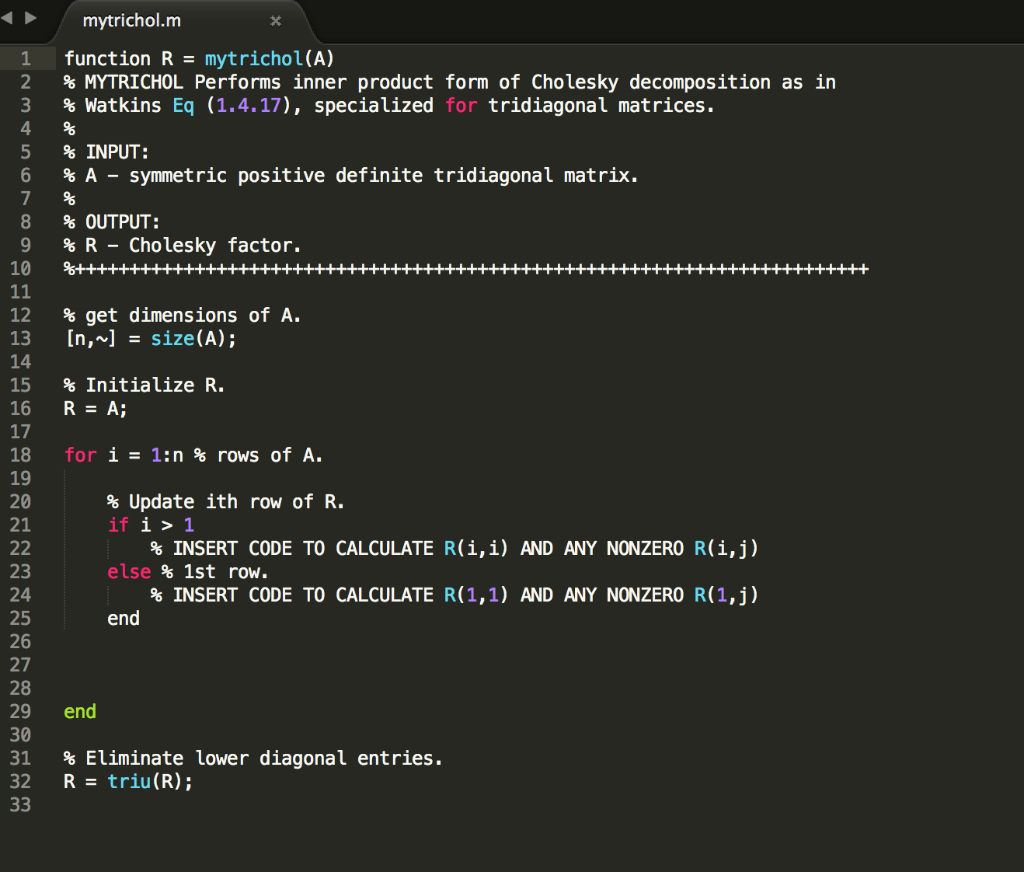
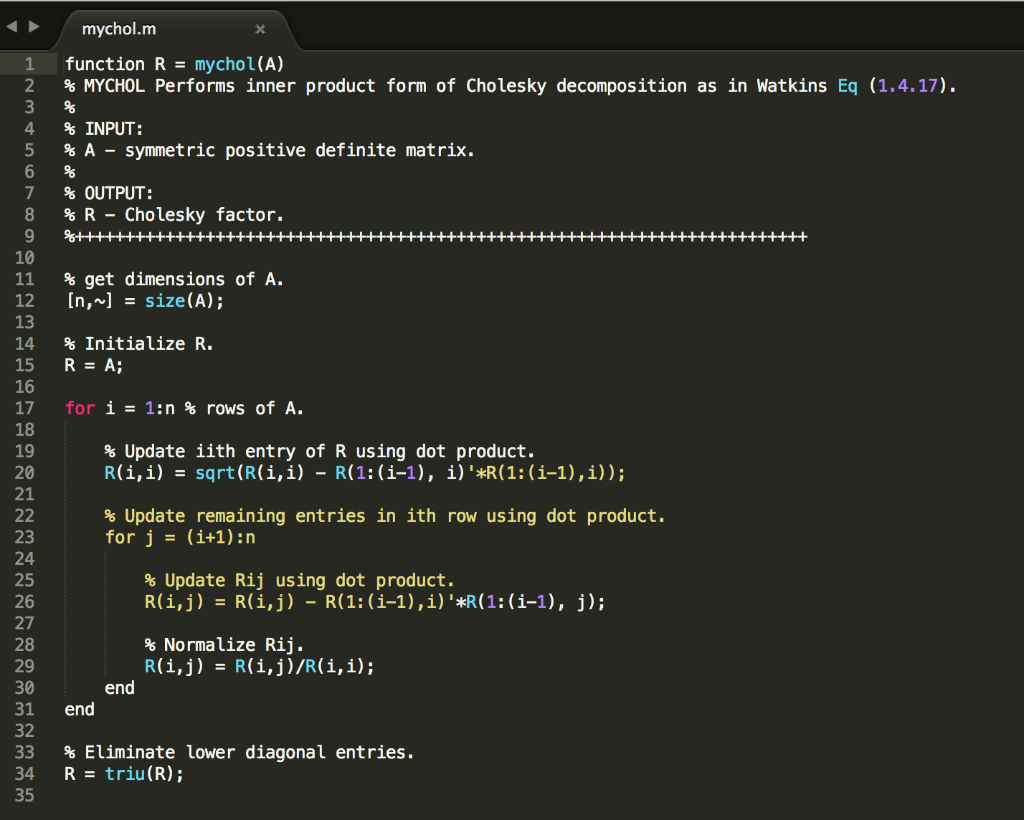
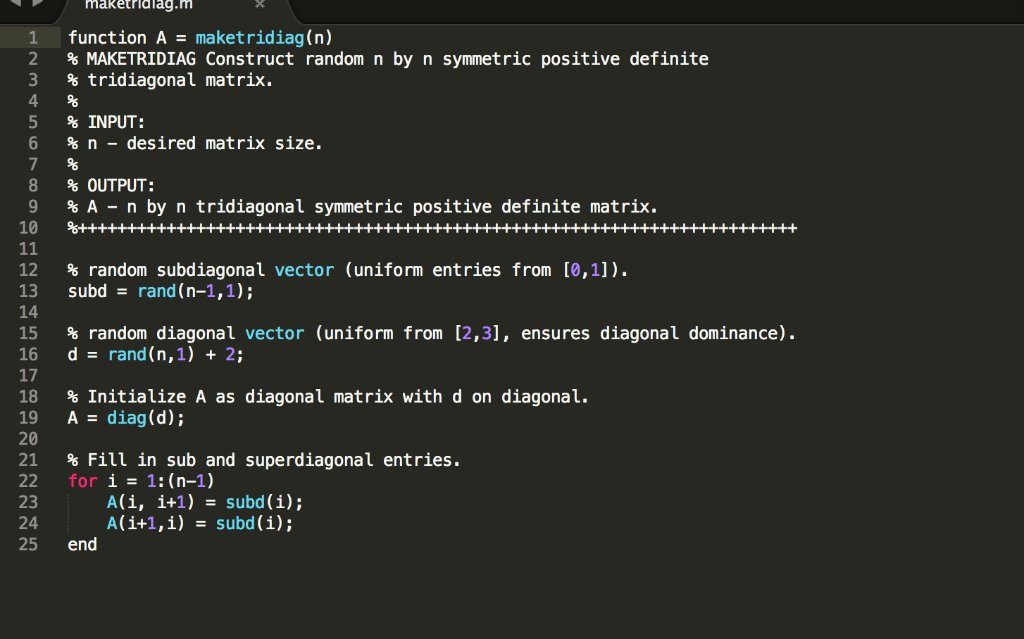
5. A matrix A is tridiagonal if ai 0 whenever li -jl>1. For example, 0 4 1 5 is a 4 x 4 tridiagonal matrix (a) Explain how the inner product form of the Cholesky decomposition algorithm can be modified to avoid unnecessary arithmetic operations if the input matrix A is symmetric positive definite and tridiagonal. Provide pseudocode detailing the modified algorithm and provide the number of arithmetic operations required by your modified algorithrm (b) Modify the given file mytrichol.m to implement your algorithm from Part (a) (c) The file mychol.m is an implementation of the inner product form of the Cholesky decomposition algorithm. The Matlab command chol will also compute the Cholesky factorization. Modify and run the script testchol.m to compare the performance of the two Cholesky algorithms for randomly generated nn tridiagonal positive definite matrices; the function maketridiag.m samples random matrices from a distribution with this property. In particular, for each given n, generate 20 tridiagonal positive definite matrices using maketridiag and call both mytrichol and mychol to calculate the Cholesky factorization. Plot the average run-times of each method (as a function of n) and explain the observed phenomena. Submit all Matlab files as a single compressed file. Your submission should contain any source files used image files of any plots made (in PNG format), and a log-file (saved using the command diary) mytrichol.nm 1 function R mytrichol(A) 2 % MYTRICHOL Performs inner product form of Cholesky decomposition as in 3 % Watkins Eq (1.4.17), specialized for tridiagonal matrices. % INPUT: % A-symmetric positive definite tridiagonal matrix. 5 8 9 10 %OUTPUT: R-Cholesky factor. 12 % get dimensions of A. 13 [n,~] - size (A); 14 15 % Initialize R. 16 RA; 17 18 for 1 1:n % rows of A. 19 20 21 % Update ith row of R. % INSERT CODE TO CALCULATE R(,) AND ANY NONZERO R(i,j) else % 1st row. 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 end 30 31 ELiminate lower diagonal entries. 32 R=triu (R) ; % INSERT CODE TO CALCULATE R(1,1) AND ANY NONZERO R(1, j) end mychol.m 1 function R mychol(A) 2 MYCHOL Performs inner product form of Cholesky decomposition as in Watkins Eq (1.4.17). 4 % INPUT: 5 % A-symmetric positive definite matrix 7 %OUTPUT: R-Cholesky factor. 10 11 % get dimensions of A. 12 n,~] - size(A); 13 14 % Initialize R. 15 R A; 16 17 for i-1:n % rows of A. 18 19 20 21 % Update iith entry of R using dot product. % Update remaining entries in ith row using dot product. for j- (i+1):n 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 end 32 33 % Eliminate lower diagonal entries. 34 R triu(R); 35 % Update Rij using dot product. % Normalize Rij. end maketridlad.m 1 function A maketridiag(n) % MAKETRDIAG Construct random n by n symmetric positive definite % tridiagonal matrix. 5 % INPUT: 6 % n-desired matrix size. 8 %OUTPUT: 9 % A-n by n tridiagonal symmetric positive definite matrix. 12 % random subdiagonal vector (uniform entries from [0,1]). 13 subd rand (n-1,1); 14 15 % random diagonal vector (uniform from [2,3], ensures diagonal dominance). 16 d rand (n,1) 2 17 18 % Initialize A as diagonal matrix with d on diagonal. 19 A- diag(d); 20 21 % Fill in sub and superdiagonal entries. 22 for i-1: (n-1) 23 24 25 end A(i, +1) subd (1); A(i+1,i)subd (i); 5. A matrix A is tridiagonal if ai 0 whenever li -jl>1. For example, 0 4 1 5 is a 4 x 4 tridiagonal matrix (a) Explain how the inner product form of the Cholesky decomposition algorithm can be modified to avoid unnecessary arithmetic operations if the input matrix A is symmetric positive definite and tridiagonal. Provide pseudocode detailing the modified algorithm and provide the number of arithmetic operations required by your modified algorithrm (b) Modify the given file mytrichol.m to implement your algorithm from Part (a) (c) The file mychol.m is an implementation of the inner product form of the Cholesky decomposition algorithm. The Matlab command chol will also compute the Cholesky factorization. Modify and run the script testchol.m to compare the performance of the two Cholesky algorithms for randomly generated nn tridiagonal positive definite matrices; the function maketridiag.m samples random matrices from a distribution with this property. In particular, for each given n, generate 20 tridiagonal positive definite matrices using maketridiag and call both mytrichol and mychol to calculate the Cholesky factorization. Plot the average run-times of each method (as a function of n) and explain the observed phenomena. Submit all Matlab files as a single compressed file. Your submission should contain any source files used image files of any plots made (in PNG format), and a log-file (saved using the command diary) mytrichol.nm 1 function R mytrichol(A) 2 % MYTRICHOL Performs inner product form of Cholesky decomposition as in 3 % Watkins Eq (1.4.17), specialized for tridiagonal matrices. % INPUT: % A-symmetric positive definite tridiagonal matrix. 5 8 9 10 %OUTPUT: R-Cholesky factor. 12 % get dimensions of A. 13 [n,~] - size (A); 14 15 % Initialize R. 16 RA; 17 18 for 1 1:n % rows of A. 19 20 21 % Update ith row of R. % INSERT CODE TO CALCULATE R(,) AND ANY NONZERO R(i,j) else % 1st row. 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 end 30 31 ELiminate lower diagonal entries. 32 R=triu (R) ; % INSERT CODE TO CALCULATE R(1,1) AND ANY NONZERO R(1, j) end mychol.m 1 function R mychol(A) 2 MYCHOL Performs inner product form of Cholesky decomposition as in Watkins Eq (1.4.17). 4 % INPUT: 5 % A-symmetric positive definite matrix 7 %OUTPUT: R-Cholesky factor. 10 11 % get dimensions of A. 12 n,~] - size(A); 13 14 % Initialize R. 15 R A; 16 17 for i-1:n % rows of A. 18 19 20 21 % Update iith entry of R using dot product. % Update remaining entries in ith row using dot product. for j- (i+1):n 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 end 32 33 % Eliminate lower diagonal entries. 34 R triu(R); 35 % Update Rij using dot product. % Normalize Rij. end maketridlad.m 1 function A maketridiag(n) % MAKETRDIAG Construct random n by n symmetric positive definite % tridiagonal matrix. 5 % INPUT: 6 % n-desired matrix size. 8 %OUTPUT: 9 % A-n by n tridiagonal symmetric positive definite matrix. 12 % random subdiagonal vector (uniform entries from [0,1]). 13 subd rand (n-1,1); 14 15 % random diagonal vector (uniform from [2,3], ensures diagonal dominance). 16 d rand (n,1) 2 17 18 % Initialize A as diagonal matrix with d on diagonal. 19 A- diag(d); 20 21 % Fill in sub and superdiagonal entries. 22 for i-1: (n-1) 23 24 25 end A(i, +1) subd (1); A(i+1,i)subd (i)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


