Question
Please write the C++ code that meet all the requirements and get the same outputs as are in the screenshot. Thanks!!! 1. Date Class Using
Please write the C++ code that meet all the requirements and get the same outputs as are in the screenshot. Thanks!!!
1. Date Class
Using the below Date.h:
#ifndef DATE_H_INCLUDED #define DATE_H_INCLUDED #include
using namespace std;
// Date class class Date { private: int month, date, year; static string months[]; // a static array of strings which will be initialized to the months names
public: // function to set the variables month, day and year to the parameter values void set(int month_, int date_, int year_) { month = month_; date = date_; year = year_; }
/* Overloaded date + this->month*100 + this->year * 10000;
//// (d1
return false; }
/* overloaded
return false; }
/* overloaded == relational operator. (d1 == d2) is true if and only if the month, day and year are equal */ bool operator==(Date &d) { // check if the date month and year are the same. if(d.date == this->date && d.month == this->month && d.year == this->year) { return true; }
return false; }
/* overloaded operator. If d2 > d1, (d2 d1) returns the number of days elapsed from d1 to d2. For example, if d1 is 02/13/2100 and d2 is 02/14/2100, (d2 d1) is equal to 1. If d2 == d1, (d2 d1) should be zero. If d2
// The number of days in each month in the array const int monthDays[12] = {31, 28, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31};
// Add days for months in given date for (int i=0; i
// Count total number of days before 'dt2' long int n2 = this->year*365 + this->date; for (int i = 0; i month - 1; i++) { n2 += monthDays[i]; }
// return difference between two counts return (n2 - n1); }
/* Prints the date in the format month d, yyyy, where month is the months name. For example: March 9, 2100. The function print() should use the static array monthName. */ void print() { // static month names string months[] = {"January", "February", "March", "April", "May", "June", "July","August", "September", "October", "November", "December" };
cout
}; // end Date class
#endif // DATE_H_INCLUDED
________________________________________________________________________________________________
2. Account Class
Using the Account.h below:
#pragma once #include "Date.h" #ifndef ACCOUNT_H_INCLUDED #define ACCOUNT_H_INCLUDED #include
using namespace std;
/*struct Date { int month; int day; int year; };*/
struct Transaction { Date transactionDate; int type; double amount; };
struct Person { string name; Date dob; string address; };
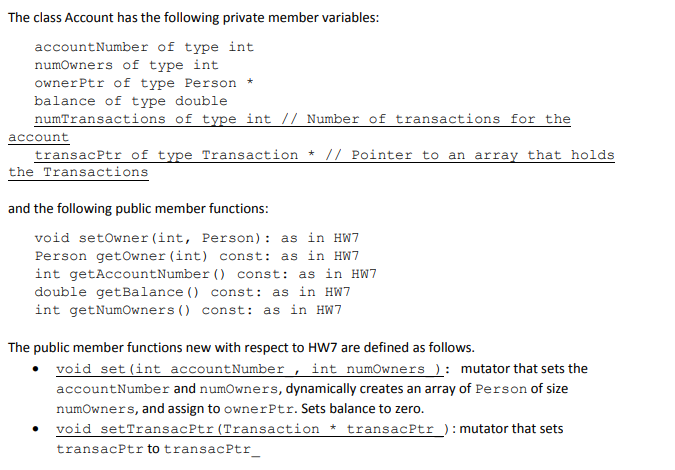
class Account { private: int accountNumber; int numOwners; // number of account co-owners Person *ownerPtr; // ownerPtr points to an array of Person double balance; //static int accountCounter; // incremented at each account creation, used to automate account number assignment int numTransactions; Transaction *transacPtr; public: void setOwner( int, Person ) {
ownerPtr[ id ].name = p.name;
ownerPtr[ id ].dob = p.dob;
ownerPtr[ id ].address = p.address;
}
Person getOwner( int ) const {
return ownerPtr[ id ];
}
int getAccountNumber() const {
return accountNumber;
}
double getBalance() const {
return balance;
}
int getNumOwners() const {
return numOwner;
}
void set( int accountNumber, int numOwners ) {
this->accountNumber = accountNumber;
this->numOwner = numOwners;
ownerPtr = new Person[ numOwners ];
this->balance = 0;
}
void setTransacPtr( Transaction* transacPtr_ ) { this->transacPtr = transacPtr_; }
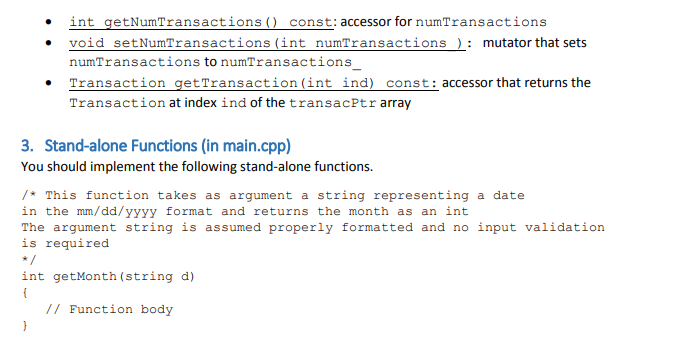
int getNumTransactions() const { return numTransactions; }
void setNumTransactions( int numTransactions_ ) { numTransactions = numTransactions_; }
Transaction getTransaction( int ind ) const { return transacPtr[ind]; }
Account(); // constructor
~Account() { if(ownerPtr) { delete [] ownerPtr; }
if(transacPtr) { delete [] transacPtr; } }
________________________________________________________________________


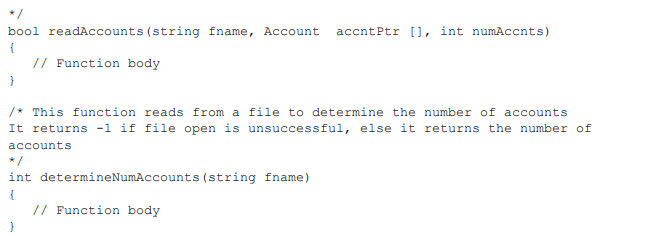
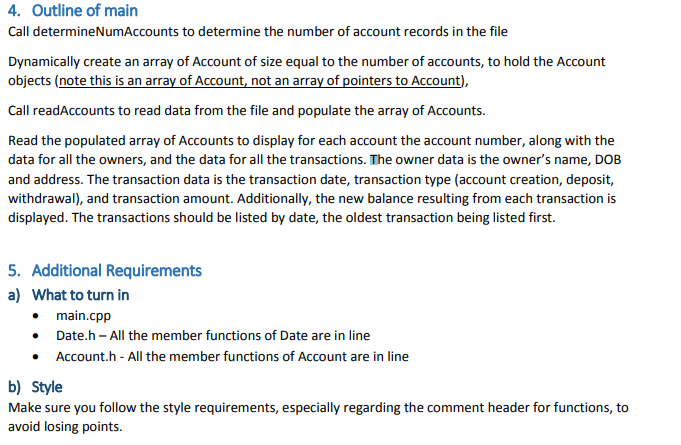

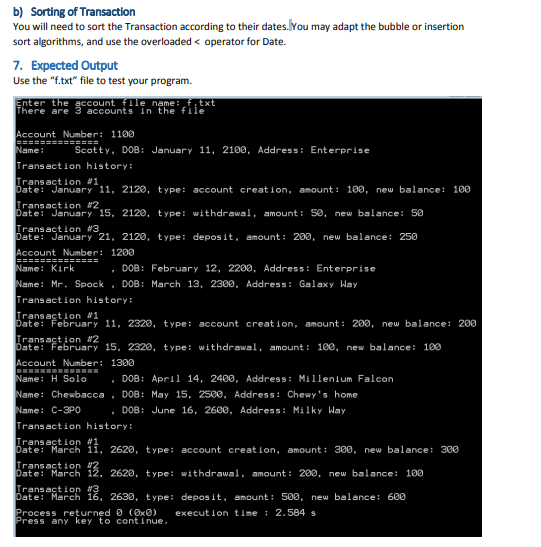
Using f.txt file below:
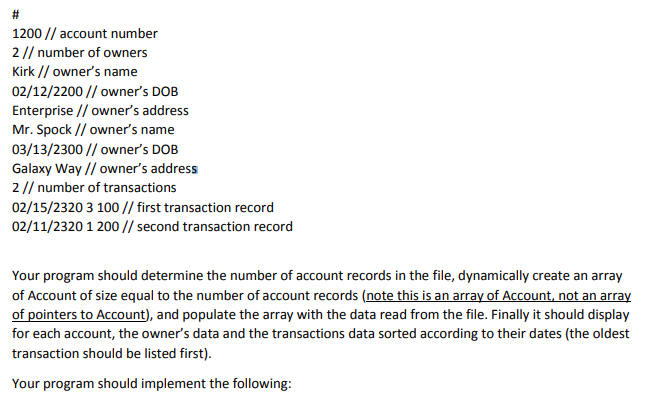
# 1100 1 Scotty 01/11/2100 Enterprise 3 01/11/2120 1 100 01/21/2120 2 200 01/15/2120 3 50 # 1200 2 Kirk 02/12/2200 Enterprise Mr. Spock 03/13/2300 Galaxy Way 2 02/15/2320 3 100 02/11/2320 1 200 # 1300 3 H Solo 04/14/2400 Millenium Falcon Chewbacca 05/15/2500 Chewy's home C-3PO 06/16/2600 Milky Way 3 03/16/2630 2 500 03/11/2620 1 300 03/12/2620 3 200
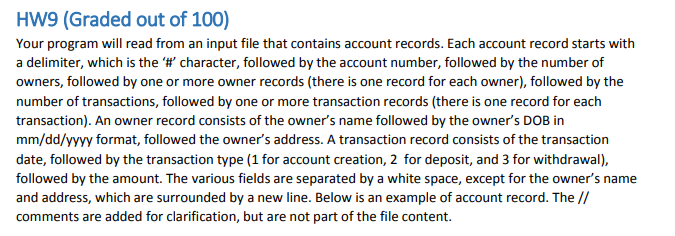
HW9 (Graded out of 100) Your program will read from an input file that contains account records. Each account record starts with a delimiter, which is the character, followed by the account number, followed by the number of owners, followed by one or more owner records (there is one record for each owner), followed by the number of transactions, followed by one or more transaction records (there is one record for each transaction). An owner record consists of the owner's name followed by the owner's DOB in mm/dd/yyyy format, followed the owner's address. A transaction record consists of the transaction date, followed by the transaction type (1 for account creation, 2 for deposit, and 3 for withdrawal) followed by the amount. The various fields are separated by a white space, except for the owner's name and address, which are surrounded by a new line. Below is an example of account record. The // comments are added for clarification, but are not part of the file content. HW9 (Graded out of 100) Your program will read from an input file that contains account records. Each account record starts with a delimiter, which is the character, followed by the account number, followed by the number of owners, followed by one or more owner records (there is one record for each owner), followed by the number of transactions, followed by one or more transaction records (there is one record for each transaction). An owner record consists of the owner's name followed by the owner's DOB in mm/dd/yyyy format, followed the owner's address. A transaction record consists of the transaction date, followed by the transaction type (1 for account creation, 2 for deposit, and 3 for withdrawal) followed by the amount. The various fields are separated by a white space, except for the owner's name and address, which are surrounded by a new line. Below is an example of account record. The // comments are added for clarification, but are not part of the file content
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


