Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
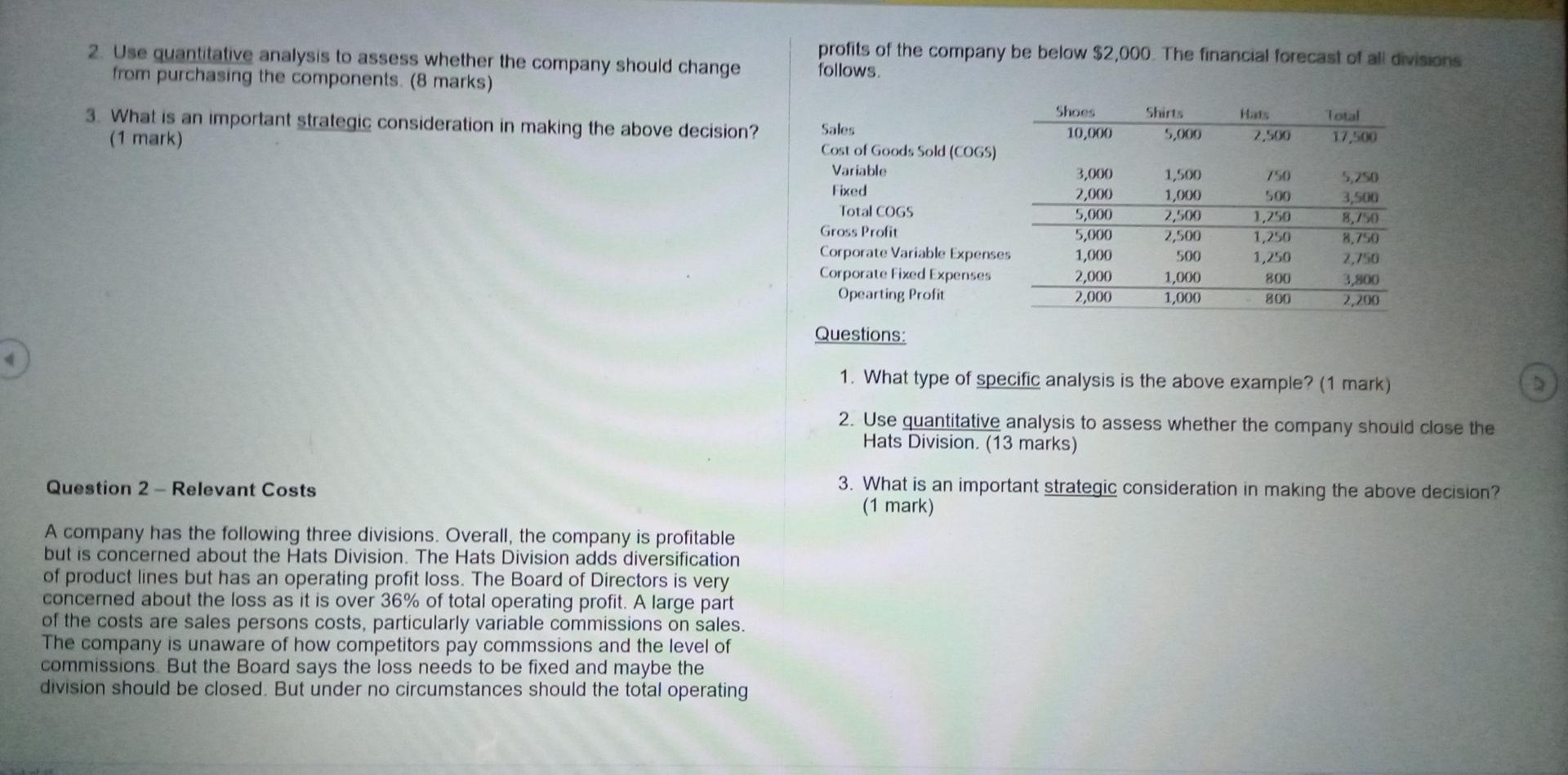
plz help in assignment Question 1 - Relevant Costs a A manufacturer has been purchasing components for $350 a unit as an input to its

plz help in assignment
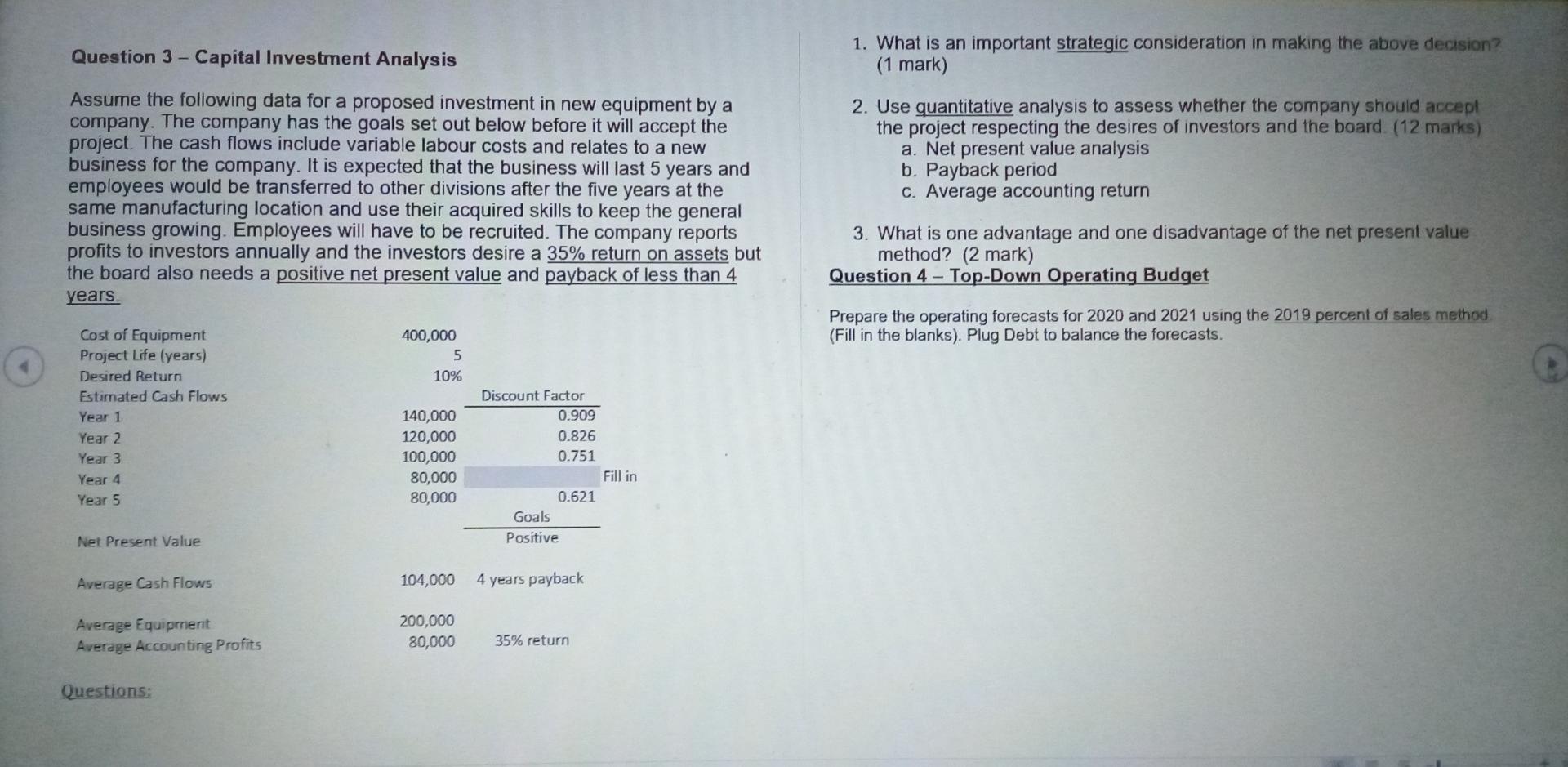
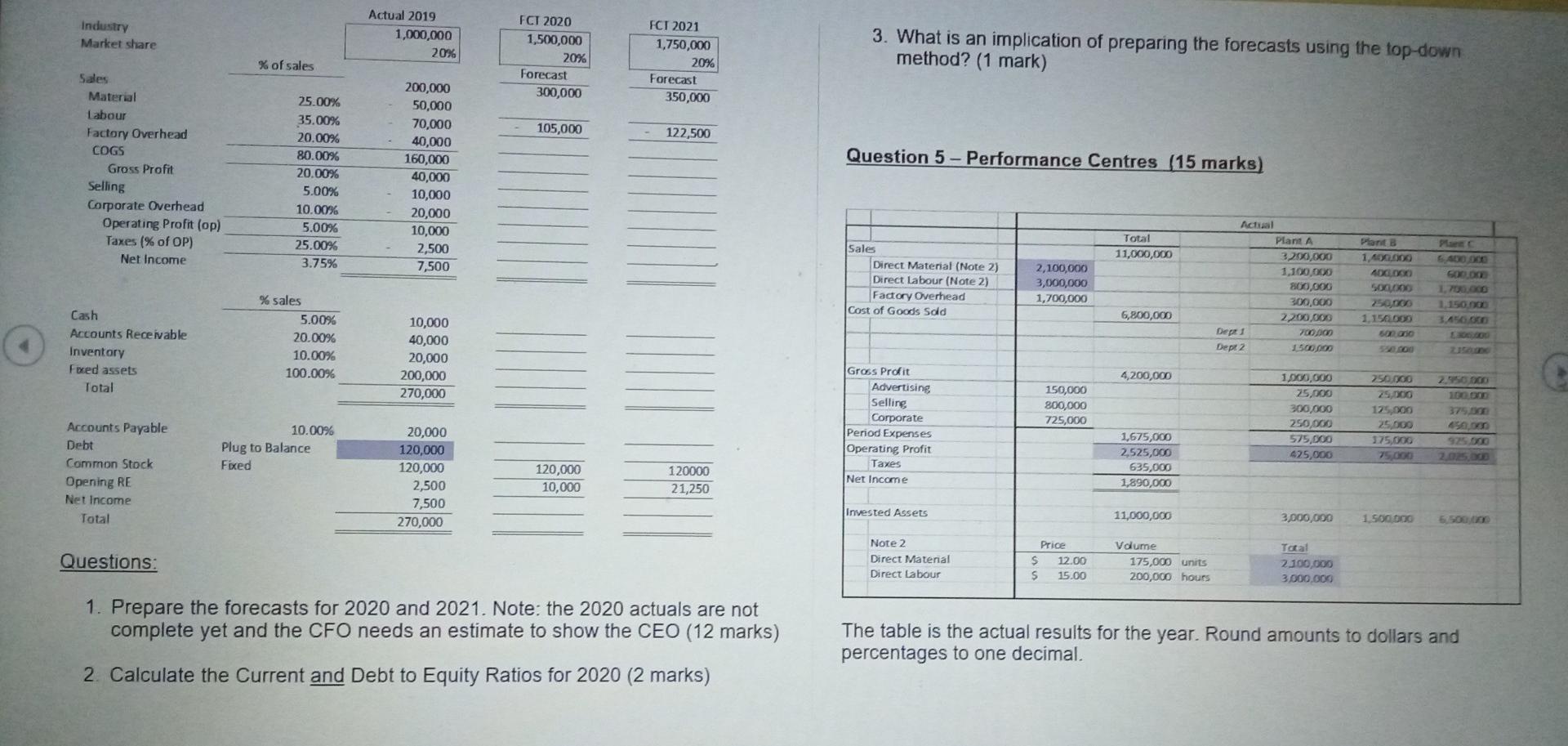
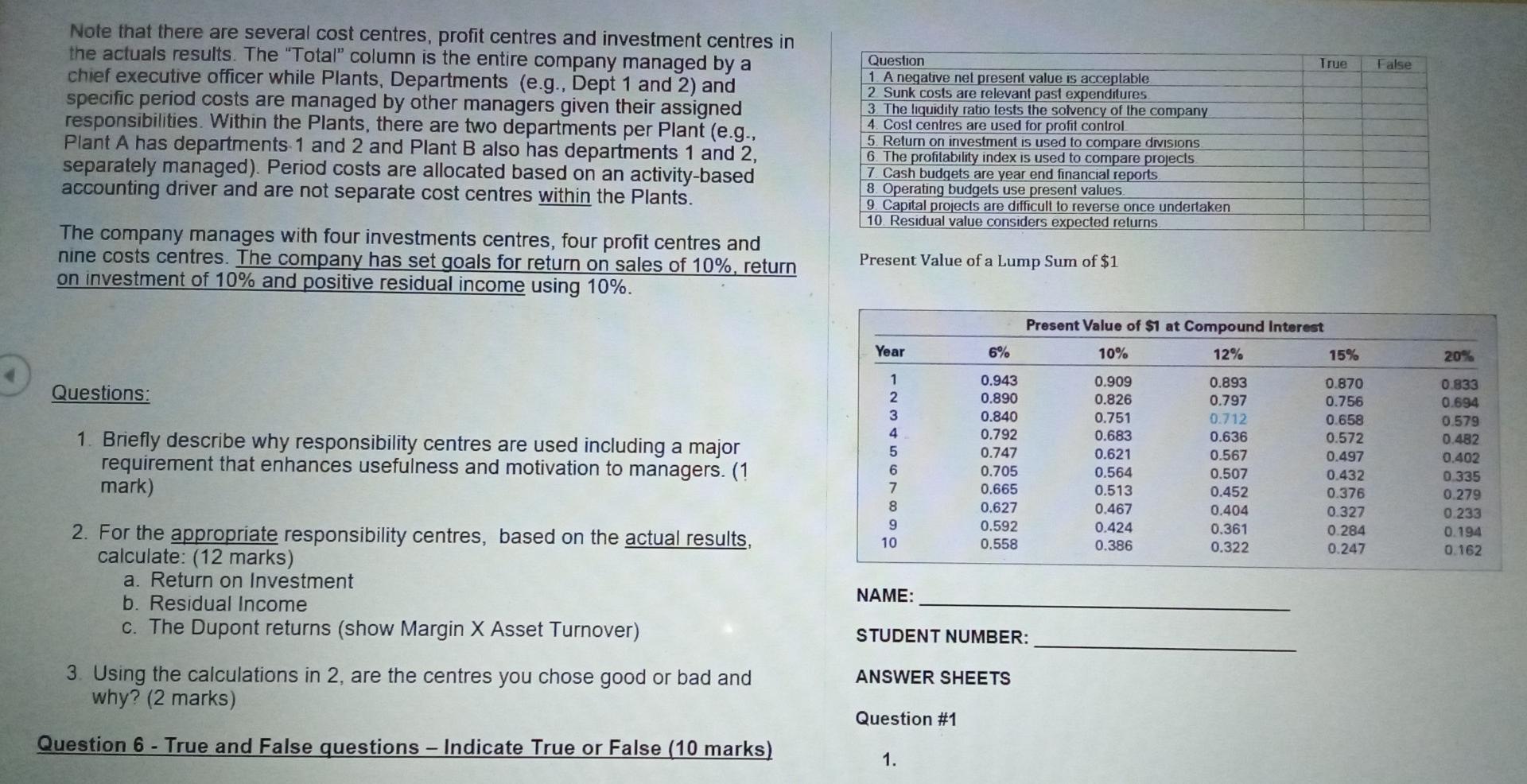
Question 1 - Relevant Costs a A manufacturer has been purchasing components for $350 a unit as an input to its manufacturing process. The factory currently operates at 80% of capacity. The company has skilled labour and a training budget to update skills of workers. The company operates in a city where skilled labour is tough to find. The cost per unit to make these components at the factory is estimated as follows: Direct materials Direct labour Variable factory overhead Depreciation on factory equipment Other fixed factory overhead Total estimated cost per unit Purchases have been Total budget estimate $ 100 175 50 25 50 $ 400 10,000 units $4,000,000 Questions: 1. What type of specific analysis is the above example? (1 mark) 2. Use quantitative analysis to assess whether the company should change from purchasing the components. (8 marks) profits of the company be below $2,000. The financial forecast of all divisions follows 3. What is an important strategic consideration in making the above decision? (1 mark) Shoes 10,000 Shirts 5,000 Total 17,500 2.500 Sales Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) Variable Fixed Total COGS Gross Profit Corporate Variable Expenses Corporate Fixed Expenses Opearting Profit 3,000 2,000 5,000 5,000 1,000 2,000 2,000 1,500 1,000 2,500 2,500 500 1,000 1,000 500 1,250 1,250 1,250 800 800 5,250 3,500 8,750 8,750 2,750 3,800 2,200 Questions: 1. What type of specific analysis is the above example? (1 mark) 2. Use quantitative analysis to assess whether the company should close the Hats Division. (13 marks) Question 2 - Relevant Costs 3. What is an important strategic consideration in making the above decision? (1 mark) A company has the following three divisions. Overall, the company is profitable but is concerned about the Hats Division. The Hats Division adds diversification of product lines but has an operating profit loss. The Board of Directors is very concerned about the loss as it is over 36% of total operating profit. A large part of the costs are sales persons costs, particularly variable commissions on sales. The company is unaware of how competitors pay commssions and the level of commissions. But the Board says the loss needs to be fixed and maybe the division should be closed. But under no circumstances should the total operating Question 3 - - Capital Investment Analysis 1. What is an important strategic consideration in making the above decision? (1 mark) Assume the following data for a proposed investment in new equipment by a company. The company has the goals set out below before it will accept the project. The cash flows include variable labour costs and relates to a new business for the company. It is expected that the business will last 5 years and employees would be transferred to other divisions after the five years at the same manufacturing location and use their acquired skills to keep the general business growing. Employees will have to be recruited. The company reports profits to investors annually and the investors desire a 35% return on assets but the board also needs a positive net present value and payback of less than 4 years 2. Use quantitative analysis to assess whether the company should accept the project respecting the desires of investors and the board (12 marks) a. Net present value analysis b. Payback period c. Average accounting return 3. What is one advantage and one disadvantage of the net present value method? (2 mark) Question 4 - Top-Down Operating Budget Prepare the operating forecasts for 2020 and 2021 using the 2019 percent of sales method. (Fill in the blanks). Plug Debt balance the forecasts. 400,000 5 10% Cost of Equipment Project Life (years) Desired Return Estimated Cash Flows Year 1 Year 2 Year 3 Year 4 Year 5 140,000 120,000 100,000 80,000 80,000 Discount Factor 0.909 0.826 0.751 Fill in 0.621 Goals Positive Net Present Value Average Cash Flows 104,000 4 years payback Average Equipment Average Accounting Profits 200,000 80,000 35% return Questions: Industry Market share Actual 2019 1,000,000 FCT 2020 1,500,000 20% Forecast 300,000 20% 3. What is an implication of preparing the forecasts using the top-down method? (1 mark) FCT 2021 1,750,000 20% Forecast 350,000 % of sales 200,000 50,000 105,000 122,500 Question 5 - Performance Centres (15 marks) Sales Material Labour Factory Overhead COGS Gross Profit Selling Corporate Overhead Operating Profit (op) Taxes (% of OP) Net Income 25.00% 35.00% 20.00% 80.00% 20.00% 5.00% 10.00% 5.00% 25.00% 3.75% 70,000 40,000 160,000 40,000 10,000 20,000 10,000 2,500 7,500 Total 11,000,000 PC Sales Direct Material (Note 2) Direct labour (Note 2) Factory Overhead Cost of Goods Sold 2,100,000 3,000,000 1,700,000 Actual Plant A 3,200,000 1.100.000 800,000 300,000 2,200.00 Dept 1 700.00 Dept 2 1.500 noo Plant B 1.400.000 400.000 5000 250,000 1.150.000 son 500 GB 1.700 1.150. 3450.000 6,800,000 Cash Accounts Receivable Inventory Fved assets Total % sales 5.00% 20.00% 10.00% 100.00% 10,000 40,000 20,000 200,000 270,000 4,200,000 150,000 800,000 725,000 Gross Profit Advertising Selling Corporate Period Expenses Operating Profit Taxes Net Income 000,000 25,000 300,000 250,000 575,000 425,000 250.000 25,000 175,000 25.000 175,000 75,000 2.550.000 100.000 379.000 499.00 Accounts Payable Debt Common Stock Opening RE Net Income Total 10.00% Plug to Balance Fixed 20,000 120,000 120,000 2,500 7,500 270,000 1,675,000 2.525,000 635,000 1,890,000 120,000 10,000 120000 21,250 Invested Assets 11,000,000 3,000,000 1.500.000 650 000 Questions: Note 2 Direct Material Direct labour Price S 12.00 S 15.00 Volume 175,000 units 200,000 hours Total 2 100.000 3.000.000 1. Prepare the forecasts for 2020 and 2021. Note: the 2020 actuals are not complete yet and the CFO needs an estimate to show the CEO (12 marks) The table is the actual results for the year. Round amounts to dollars and percentages to one decimal. 2. Calculate the Current and Debt to Equity Ratios for 2020 (2 marks) True False Note that there are several cost centres, profit centres and investment centres in the actuals results. The "Total" column is the entire company managed by a chief executive officer while Plants, Departments (e.g., Dept 1 and 2) and specific period costs are managed by other managers given their assigned responsibilities. Within the Plants, there are two departments per Plant (e.g., Plant A has departments 1 and 2 and Plant B also has departments 1 and 2, separately managed). Period costs are allocated based on an activity-based accounting driver and are not separate cost centres within the plants. Question 1. A negative nel present value is acceptable 2. Sunk costs are relevant past expenditures 3. The liquidity ratio tests the solvency of the company 4. Cost centres are used for profit control 5. Return on investment is used to compare divisions 6. The profitability index is used to compare projects 7. Cash budgets are year end financial reports 8. Operating budgets use present values 9. Capital projects are difficult to reverse once undertaken 10. Residual value considers expected returns The company manages with four investments centres, four profit centres and nine costs centres. The company has set goals for return on sales of 10%, return on investment of 10% and positive residual income using 10%. Present Value of a Lump Sum of $1 Present Value of $1 at Compound Interest 10% 12% 15% Year 6% 20% Questions: 1. Briefly describe why responsibility centres are used including a major requirement that enhances usefulness and motivation to managers. (? mark) OVODAWN 0.943 0.890 0.840 0.792 0.747 0.705 0.665 0.627 0.592 0.558 0.909 0.826 0.751 0.683 0.621 0.564 0.513 0.467 0.424 0.386 0.893 0.797 0.712 0.636 0.567 0.507 0,452 0.404 0.361 0.322 0.870 0.756 0.658 0.572 0.497 0.432 0.376 0.327 0.284 0.247 0.833 0.694 0.579 0.482 0.402 0.335 0.279 0.233 0.194 0.162 9 10 2. For the appropriate responsibility centres, based on the actual results, calculate: (12 marks) a. Return on Investment b. Residual Income C. The Dupont returns (show Margin X Asset Turnover) NAME: STUDENT NUMBER: ANSWER SHEETS 3. Using the calculations in 2, are the centres you chose good or bad and why? (2 marks) Question #1 Question 6 - True and False questions - Indicate True or False (10 marks) - 1Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


