Question: Practice Exercises Example Exercises PE 7-1A Cost flow methods EE 7-1 p 349 B.2 The following three identical units of Item A are purchased during



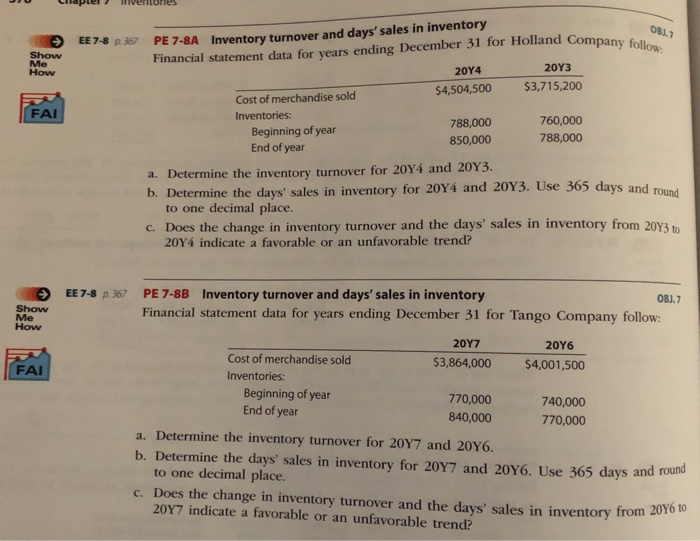
Practice Exercises Example Exercises PE 7-1A Cost flow methods EE 7-1 p 349 B.2 The following three identical units of Item A are purchased during April: Show Me How Item A Units Cost p. 2 Purchase 1 $68 14 Purchase 73 28 Purchase 1 75 Total $216 Average cost per unit $72 ($216+3 units) Assume that one unit is sold on April 30 for $118. Determine the gross profit for April and ending inventory on April 30 using the (a) first-in, first-out (FIFO); (b) last-in, first-out (LIFO); and (c) weighted average cost methods. BJ. 2 Cost flow methods PE 7-1B EE 7-1 p. 349 The following three identical units of Item Beta are purchased during June: Show Me How Units Cost Item Beta $ 50 Purchase 1 2 June 60 Purchase 1 12 70 Purchase 1 23 $180 Total $ 60 ($180+3 units) Average cost per unit Assume that one unit is sold on June 27 for $110. Determine the gross profit for June and ending inventory on June 30 using the (a) first-in, first-out (FIFO); (b) last-in, first-out (LIFO); and (c) weighted average cost methods BI.3 PE 7-2A Perpetual inventory using FIFO Beginning inventory, purchases, and sales for Item Widget are as follows: EE 7-2 p. 351 Show Me How 200 units at $8 Inventory Sale Mar. 1 175 units Purchase 160 units at 9 13 Sale 150 units 25 Assuming a perpetual inventory system and using the first-in, first-out (FIFO) method, de- termine (a) the cost of merchandise sold on March 25 and (b) the inventory on March 31, 76 Chapter 7 Inventories Beginning inventory, purchases, and sales for Item Delta are as follows Inventory Sale Purchase Perpetual inventory using FIFO EE 7-2 p 35 PE 7-2B Show Me How 50 units at $1S July 1 44 units 7 90 units at $18 40 units 15 Sales 24 Assuming a perpetual inventory system and using the first-in, first-out (FIFO) method, determine (a) the cost of merchandise sold on July 24 and (b) the inventory on July O8.3 Perpetual inventory using LIFO PE 7-3A EE 7-3p353 Beginning inventory, purchases, and sales for Item Gidget are as follows: Inventory Sale Show Me How 80 units at $175 Sept 1 65 units 10 75 units at $180 Purchase 18 Sale 70 units 27 Assuming a perpetual inventory system and using the last-in, first-out (LIFO) method determine (a) the cost of merchandise sold on September 27 and (b) the inventory on September 30. PE 7-38 Perpetual inventory using LIFO Beginning inventory, purchases, and sales for Item Foxtrot are as follows: OBJ.3 EE 7-3 p.353 Show Me How 270 units at $18 Mar. 1 Inventory Sale 225 units 8 Purchase 375 units at $20 15 240 units 27 Sale Assuming a perpetual inventory system and using the last-in, first-out (LIFO) method, de termine (a) the cost of merchandise sold on March 27 and (b) the inventory on March 31. PE 7-4A Perpetual inventory using weighted average Beginning inventory, purchases, and sales for Meta-B1 are as follows: EE 7-4 p354 08J.3 Show Me How July 1 Inventory 100 units at $400 12 Sale 70 units 23 Purchase 120 units at $450 110 units 26 Sale Assuming a perpetual inventory system and using the weighted average method, deter- mine (a) the weighted average unit cost after the July 23 purchase, (b) the cost of the merchandise sold on July 26, and (c) the inventory on July 31. EE 7-4 p354 PE 7-48 Perpetual inventory using weighted average Beginning inventory, purchases, and sales for WCS12 are as follows: OBJ.3 Show Me How Oct. 1 Inventory 300 units at $8 13 Sale 175 units 22 Purchase 375 units at $10 29 Sale 280 units Assuming a perpetual inventory system and using the weighted average method, del mine (a) the weighted average unit cost after the October 22 purchase, (b) the cost of the merchandise sold on October 29, and (c) the inventory on October 31. Chapter 7 Inventories 377 PE 7-SA Periodic inventory using FIFO, LIF0, and weighted average cost methods os The units of an item available for sale during the year were as follows EE7-5 eow Jan 1 Inventory Purchase 12 units at $5,400 $ 64800 18 units at $6,000 Aug. 7 Dec. 11 108.000 Purchase 15 units at 56,480 45 units 97200 Available for sale $270,000 There are 14 units of the item in the physical inventory at December 31. The periodic in- ventory system is used. Determine the inventory cost using (a) the first-in, first-out (FIFO) method; (b) the last-in, first-out (LIFO) method; and (c) the weighted average cost method. E 7-5 p 358 PE 7-5B Periodic inventory using FIFO, LIFO, and weighted average cost methods osJ.4 The units of an item available for sale during the year were as follows: Show Jan. 1 How Inventory 20 units at $360 7,200 Aug. 13 Purchase 260 units at $342 88.920 Nov. 30 Purchase 40 units at $357 14,280 Available for sale $110,400 320 units There are 57 units of the item in the physical inventory at December 31. The periodic in- ventory system is used. Determine the inventory cost using (a) the first-in, first-out (FIFO) method; (b) the last-in, first-out (LIFO) method; and (c) the weighted average cost method. OBJ. Lower-of-cost-or-market method PE 7-6A EE 7-6 p 36 On the basis of the following data, determine the value of the inventory at the lower of cost or market. Apply lower of cost or market to each inventory item, as shown in Exhibit 9. Show Me How Market Value per Unit (Net Realizable Value) Cost per Unit Inventory Quantity Item $112 $115 1,200 Raven 10 22 17 6,500 Dove 23 OBJ. 6 PE 7-68 Lower-of-cost-or-market method On the basis of the following data, determine the value of the inventory at the lower of cost or market. Apply lower of cost or market to each inventory item, as shown in Exhibit 9. EE 7-6 p 361 Show Me How Market Value per Unit (Net Realizable Value) $11 Cost per Unit Inventory Quantity Item $10 6,330 JFW1 34 36 1,140 SAW9 OBJ. 6 EE 7-7 p365s PE 7-7A Effect of inventory errors Show Me How During the taking of its physical inventory on August 31, 2019, Kate Interiors Company incorrectly counted its inventory as $366,900 instead of the correct amount of $378,500 Indicate the effect of the misstatement on Kate Interiors' August 31, 2019, balance sheet and income statement for the year ended August 31, 2019. OBJ. 6 During the taking of its physical inventory on December 31, 2019, Waterjet Bath Company incorrectly counted its inventory as $728,660 instead of the correct amount of $719,880. Indicate the effect of the misstatement on Waterjet Bath's December 31, 2019, balance sheet and income statement for the year ended December 31, 2019, Effect of inventory errors EE 7-7 p 365 PE 7-7B Show Me Haw PE 7-8A Inventory turnover and days' sales in inventory Financial statement data for years ending December 31 for Holland Company follow: OBJ.7 EE 7-8 p 367 Show Me How 203 204 $3,715,200 $4,504,500 Cost of merchandise sold FAI Inventories: 760,000 788,000 Beginning of year End of year 788,000 850,000 a. Determine the inventory turnover for 20Y4 and 20Y3. b. Determine the days' sales in inventory for 20Y4 and 20Y3. Use 365 days and round to one decimal place. c. Does the change in inventory turnover and the days' sales in inventory from 20Y3 to 20Y4 indicate a favorable or an unfavorable trend? EE 7-8 p 367 PE 7-8B Inventory turnover and days' sales in inventory Financial statement data for years ending December 31 for Tango Company follow OBJ.7 Show Me How 207 20Y6 Cost of merchandise sold $3,864,000 $4,001,500 FAI Inventories: Beginning of year End of year 770,000 740,000 840,000 770,000 a. Determine the inventory turnover for 20Y7 and 20Y6 b. Determine the days' sales in inventory for 20Y7 and 20Y6. Use 365 days and round to one decimal place. c. Does the change in inventory turnover and the days' sales in inventory from 20Y6 to 20Y7 indicate a favorable or an unfavorable trend? Practice Exercises Example Exercises PE 7-1A Cost flow methods EE 7-1 p 349 B.2 The following three identical units of Item A are purchased during April: Show Me How Item A Units Cost p. 2 Purchase 1 $68 14 Purchase 73 28 Purchase 1 75 Total $216 Average cost per unit $72 ($216+3 units) Assume that one unit is sold on April 30 for $118. Determine the gross profit for April and ending inventory on April 30 using the (a) first-in, first-out (FIFO); (b) last-in, first-out (LIFO); and (c) weighted average cost methods. BJ. 2 Cost flow methods PE 7-1B EE 7-1 p. 349 The following three identical units of Item Beta are purchased during June: Show Me How Units Cost Item Beta $ 50 Purchase 1 2 June 60 Purchase 1 12 70 Purchase 1 23 $180 Total $ 60 ($180+3 units) Average cost per unit Assume that one unit is sold on June 27 for $110. Determine the gross profit for June and ending inventory on June 30 using the (a) first-in, first-out (FIFO); (b) last-in, first-out (LIFO); and (c) weighted average cost methods BI.3 PE 7-2A Perpetual inventory using FIFO Beginning inventory, purchases, and sales for Item Widget are as follows: EE 7-2 p. 351 Show Me How 200 units at $8 Inventory Sale Mar. 1 175 units Purchase 160 units at 9 13 Sale 150 units 25 Assuming a perpetual inventory system and using the first-in, first-out (FIFO) method, de- termine (a) the cost of merchandise sold on March 25 and (b) the inventory on March 31, 76 Chapter 7 Inventories Beginning inventory, purchases, and sales for Item Delta are as follows Inventory Sale Purchase Perpetual inventory using FIFO EE 7-2 p 35 PE 7-2B Show Me How 50 units at $1S July 1 44 units 7 90 units at $18 40 units 15 Sales 24 Assuming a perpetual inventory system and using the first-in, first-out (FIFO) method, determine (a) the cost of merchandise sold on July 24 and (b) the inventory on July O8.3 Perpetual inventory using LIFO PE 7-3A EE 7-3p353 Beginning inventory, purchases, and sales for Item Gidget are as follows: Inventory Sale Show Me How 80 units at $175 Sept 1 65 units 10 75 units at $180 Purchase 18 Sale 70 units 27 Assuming a perpetual inventory system and using the last-in, first-out (LIFO) method determine (a) the cost of merchandise sold on September 27 and (b) the inventory on September 30. PE 7-38 Perpetual inventory using LIFO Beginning inventory, purchases, and sales for Item Foxtrot are as follows: OBJ.3 EE 7-3 p.353 Show Me How 270 units at $18 Mar. 1 Inventory Sale 225 units 8 Purchase 375 units at $20 15 240 units 27 Sale Assuming a perpetual inventory system and using the last-in, first-out (LIFO) method, de termine (a) the cost of merchandise sold on March 27 and (b) the inventory on March 31. PE 7-4A Perpetual inventory using weighted average Beginning inventory, purchases, and sales for Meta-B1 are as follows: EE 7-4 p354 08J.3 Show Me How July 1 Inventory 100 units at $400 12 Sale 70 units 23 Purchase 120 units at $450 110 units 26 Sale Assuming a perpetual inventory system and using the weighted average method, deter- mine (a) the weighted average unit cost after the July 23 purchase, (b) the cost of the merchandise sold on July 26, and (c) the inventory on July 31. EE 7-4 p354 PE 7-48 Perpetual inventory using weighted average Beginning inventory, purchases, and sales for WCS12 are as follows: OBJ.3 Show Me How Oct. 1 Inventory 300 units at $8 13 Sale 175 units 22 Purchase 375 units at $10 29 Sale 280 units Assuming a perpetual inventory system and using the weighted average method, del mine (a) the weighted average unit cost after the October 22 purchase, (b) the cost of the merchandise sold on October 29, and (c) the inventory on October 31. Chapter 7 Inventories 377 PE 7-SA Periodic inventory using FIFO, LIF0, and weighted average cost methods os The units of an item available for sale during the year were as follows EE7-5 eow Jan 1 Inventory Purchase 12 units at $5,400 $ 64800 18 units at $6,000 Aug. 7 Dec. 11 108.000 Purchase 15 units at 56,480 45 units 97200 Available for sale $270,000 There are 14 units of the item in the physical inventory at December 31. The periodic in- ventory system is used. Determine the inventory cost using (a) the first-in, first-out (FIFO) method; (b) the last-in, first-out (LIFO) method; and (c) the weighted average cost method. E 7-5 p 358 PE 7-5B Periodic inventory using FIFO, LIFO, and weighted average cost methods osJ.4 The units of an item available for sale during the year were as follows: Show Jan. 1 How Inventory 20 units at $360 7,200 Aug. 13 Purchase 260 units at $342 88.920 Nov. 30 Purchase 40 units at $357 14,280 Available for sale $110,400 320 units There are 57 units of the item in the physical inventory at December 31. The periodic in- ventory system is used. Determine the inventory cost using (a) the first-in, first-out (FIFO) method; (b) the last-in, first-out (LIFO) method; and (c) the weighted average cost method. OBJ. Lower-of-cost-or-market method PE 7-6A EE 7-6 p 36 On the basis of the following data, determine the value of the inventory at the lower of cost or market. Apply lower of cost or market to each inventory item, as shown in Exhibit 9. Show Me How Market Value per Unit (Net Realizable Value) Cost per Unit Inventory Quantity Item $112 $115 1,200 Raven 10 22 17 6,500 Dove 23 OBJ. 6 PE 7-68 Lower-of-cost-or-market method On the basis of the following data, determine the value of the inventory at the lower of cost or market. Apply lower of cost or market to each inventory item, as shown in Exhibit 9. EE 7-6 p 361 Show Me How Market Value per Unit (Net Realizable Value) $11 Cost per Unit Inventory Quantity Item $10 6,330 JFW1 34 36 1,140 SAW9 OBJ. 6 EE 7-7 p365s PE 7-7A Effect of inventory errors Show Me How During the taking of its physical inventory on August 31, 2019, Kate Interiors Company incorrectly counted its inventory as $366,900 instead of the correct amount of $378,500 Indicate the effect of the misstatement on Kate Interiors' August 31, 2019, balance sheet and income statement for the year ended August 31, 2019. OBJ. 6 During the taking of its physical inventory on December 31, 2019, Waterjet Bath Company incorrectly counted its inventory as $728,660 instead of the correct amount of $719,880. Indicate the effect of the misstatement on Waterjet Bath's December 31, 2019, balance sheet and income statement for the year ended December 31, 2019, Effect of inventory errors EE 7-7 p 365 PE 7-7B Show Me Haw PE 7-8A Inventory turnover and days' sales in inventory Financial statement data for years ending December 31 for Holland Company follow: OBJ.7 EE 7-8 p 367 Show Me How 203 204 $3,715,200 $4,504,500 Cost of merchandise sold FAI Inventories: 760,000 788,000 Beginning of year End of year 788,000 850,000 a. Determine the inventory turnover for 20Y4 and 20Y3. b. Determine the days' sales in inventory for 20Y4 and 20Y3. Use 365 days and round to one decimal place. c. Does the change in inventory turnover and the days' sales in inventory from 20Y3 to 20Y4 indicate a favorable or an unfavorable trend? EE 7-8 p 367 PE 7-8B Inventory turnover and days' sales in inventory Financial statement data for years ending December 31 for Tango Company follow OBJ.7 Show Me How 207 20Y6 Cost of merchandise sold $3,864,000 $4,001,500 FAI Inventories: Beginning of year End of year 770,000 740,000 840,000 770,000 a. Determine the inventory turnover for 20Y7 and 20Y6 b. Determine the days' sales in inventory for 20Y7 and 20Y6. Use 365 days and round to one decimal place. c. Does the change in inventory turnover and the days' sales in inventory from 20Y6 to 20Y7 indicate a favorable or an unfavorable trend
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


