Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
prepare a full case report analyzing the issues and making appropriate recommendations.Assume you are a consultant advisingDr. Frank Davis, one of CMIs radiologists partners. Write
- prepare a full case report analyzing the issues and making appropriate recommendations.Assume you are a consultant advisingDr. Frank Davis, one of CMIs radiologists partners.
- Write your group report, following the format described below.Consider both quantitative and qualitative factors.Include any appropriate tables of numbers; attach longer tables to the end of your report.
I have attached:
- Instructions on formatting your group report
Report Format
Use the following format (see Note on Report Writing in the IveyCoursepackfor examples and more explanation).
- Title page
- Table of Contents
- Introduction and problem definition
- Analysis (may require sub-sections)
- Alternatives
- Recommendations
- Implementation (if appropriate)
- Measures for control (if appropriate)
- Conclusion
- End matter (detailed tables, etc.)
Each page should bedouble-spaced and use 12-pointTimes New Roman. Number each page in the top right corner (beginning at the Introduction/Problem Definition)
Prepare a proper Accounting Report on the Community Medical Imaging case 








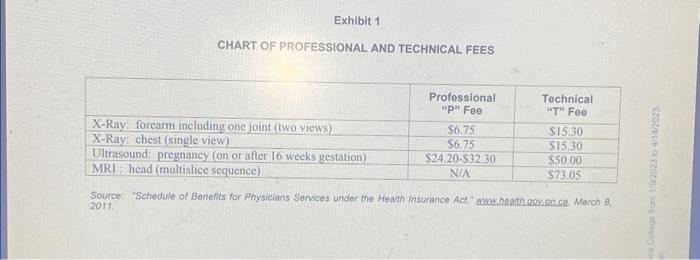
COMMUNITY MEDICAL IMAGING (CMI) History CMI was established in 1931 at one location with one radiologist. At the time, radiological caarninations were so infrequent that tbe radiologist was able to manage both his cline and all radiology at St. Michael's hospital. By 1954, CMil had fout radiologots, and the team began resdine films from a handful of hospitals in snall towns across fegion. In the decades that followed, addational clinics and plysicians were continually added and, in 2002, CMI converted the business from a film-erading centre to a state-of the-ait digital imaging centre, a six-miobth prosess. The CMI team had yrown bol4 radiologists (all partners). In recent years, a new partner was hired every three to four years Recently, CMI had been one of four finalists in the small business division of the Chamber of Commerce Busmess of the Vear. A wathds. Current Operations per idy, fivedays per week CHART OF PROFESSIONAL AND TECHNICAL FEES 2011. The digitization of medical imaging had drastically altered the dynamies of the industry, mainly due to the introduction of teleradiology. Teleradiology was "the electronic transmission of diagnostic imaging studies from one location to another for the purpose of interpretation and/or consultation." Teleradiology offered the opportunities for providing top-level service to rural and remote areas without having to recruit specialized physicians to these areas; however, elients still preferred to have a radiologist present Historically, due to the "windshield factor," radiologists had provided service only within their geographic regions and, therefore, maintained some compctitive protection from other radiologists within their area. With the ability to read images remotely, the medical imaging industry became more global, and radiologists were increasingly forced to cater to their customers' needs (such as on-call service and flexible scheduling) rather than dictate to their clients. Personal relationships and strong reputations also became more iniegral to developing partnerships between hospitals and radiology groups: Another notable trend was the increasing level of bureaucracy in the bealth-care industry. The majority of "contracts" for remote work was historically done on a handshake between physicians; however, to read innages and esim revenue RADIOLOGY History Radiology was a branch of medicine that utilized radiation for the treatment and diagnosis of disease 2 The field of radiology began with the discovery of X-riays and their analysis in 1895 . Today, ndiologists bot only read images from X-ray films but also images from ultrasound, magnetio resonance imaging (MRL). and computerized axial tomography (CT sean). These different techaigues used within medical imaging were referred to as "modalities" Radiologists were phyacians and, as a result, were requited to complete two fo four years of undergraduate sodics, four years of medical school, four to six years for their ipecialization and an optional fellowship? Whath the field of radiology, doctors onen focused on areas of specialization such as Becutoradiology. obsietrical imaging and gastrointestinal imaging The length of education was related to these specializations; for example, neuroradiology required 16 years of postisecondary education. hired statt. Now Physicians To meet the demands of the northern Ontario hospitals, there would have to bo two major changes to CMI's operatioas. First, there would be an evening shift added from 5 p.m. to 11pm, seven days a week, in Toronto. Although CMI's team had always worked loog hours, there had never been a formal evening work shift. Second, a CMI physician would have to be present at Thunder Bay District Hospital for three out of four weeks each month. The 14 physicians would have to rotate through this responsibility in one. week intervals. CMI's directot estimated that the existing team's average workday eould increase to a high of 15 hours per day with the additional workload; consequently, she recommended that CMI hire four additiobal radiologists to make the Duunder Bay workload more manageable. This approach would also heip to spread out the physicians" day-to-day work in Toronto: however, it was untikely that additional parnen could be hited until mid-2010 because CMI had hissoncally hired focent graduates (who finished university in carly May each year) to help grow its business Financial Considerations Potential sevenue from the Thunder Bay proposal was expovied to be 5167,000 cach mooth beyaming in January 2010 The 14 exisang parners would receive ao increane in pay' for any adtitional hours uveked. however, all cash in excess of $100,000 would be evenly distributed among the parners at the end of eash. year. Alf revenue camed would take 30 days to receive and would be paid to Thunder Bay Diinct: and food - were estimated at 54,500 a week and would be minbursed by the Mumstry of Health and be received from the governakent in 30 days To provide teleradiology service, a new diagnostic suite would need to be created at the main Toronto clinic. The total cost for the renovation would be $85,000, which included the cost of the PACS workstation and installation of a secure communications line for privacy. Thunder Bay District Hospital was prepared to contribute $65,000 towards this renovation upon its completion. Although PACS technology was quite new, Davis estimated the new system would function for 10 to 15 years CONCLUSION Although Davis was proud of CMI's existing business and reputation, he knew the draw of unusual work and therefore recognized that helping an underserved arca could be difficult for the team to furn down. If they tumed down the opportunity, one of the other medical imaging companies vying for the job - many based in Calgary - would casily step in. If CMI took on the job but could not handle the increased workload, Thunder Bay District Hospital would use locunis, and CMI would be quickly phased out of the job. Regardless of their deciston, the partmers would need to act quickly but practically. per day, five days per week CMI employed a full-time director who managed all aspects of the business and advised the partisers on its future direction. Also, an extensive team of technologists and suppott staff performed many of the procedures and completed administrative duties such as scheduline and belling Partnor Physiclans Each of CMI's 14 partnets received equal pay and equal distribution of income. (Typically, 5100,000canh was kept on hand for daily business needs, and all other income was destributed) As such. the team exhibited o significant level of co-operation and a colloctive pride, both in CMI'v reputation and in its quality of woek provided for the community, therefore, when making decisions, the partien had is consides whar was in the best ingerest of the entite teams. In 2006, the partaen developed mission, visua and key valoes statements io help gaide the decisson-making prosess. CMITr misson apd vision of folver parines CMI's partners also placed a high value on being leaders in their field. This meant they would be early adopters of new technologies, be exposed to challenging and intriguing work, and maintain a sizable presence in the province. Professional autonomy was important to the partners, and an integral component of achieving this goal included their ability to lobby the Ministry of Health and Long-Term Care THE THUNDER BAY PROPOSAL. Geographic Coverage The Thunder Bay proposal would involve providing service, both on-site and through telerndiology, to 10 Northern Ontano bospitals with Thunder Bay as the main hub (sce map in Evhibit 2). As the primary lub of medicine in the north, Thunder Bay District Hespital had the very best equipunent in medical imieing A few of CMI's partners bad completed locums at the hospital on a tral basis and had found the work to be quite intriguing, for example, due to differences in living conditions atsd culture, medical conditions were otten seen in Northem Oniatio that were rare in Southem Ontatio Now Physiclans To meet the demands of the nortiem Ontario hospitals, thece woild have to be two majat changes to week intorits Radiology in Ontario Within Ontario's universal health-care systcuty, many medical procedures, including medical imaging services, were paid by the provincial governinent. Typically, patients were referred for medical imaging by their family physicians and were then booked for appointments at elinics. At these climics, patients would present their provineial health cards and then have the appropriate procedure(s) completed by technologists. The technologists then uploaded the image to secure picture archiving communication systems (PACS). These images would then be read by radiologists who dictated their reports These oral reports were typed by medical transeriptionists and sent back to famaly phystcians, who in turm reported the dagnosis to patients. For emergency or acute treatment in hospitals, this process was completed entirely within the hospital Radiologists in Ontano received all their revenue from the provincial government, through standardized professional fees (P-fees) and technical fees (T-fees). Fxhibit I shows the P-fees and T-fees for a few standard procedures. P-fees were paid directly to the radiologists performing the inage readings; whereas. Thfees were paid to the clinics or to the hospitals and were intended to cover the cost of technologists. transcriptionists, imvestments in equipment and any overhcad costs. The time fequired to read an image could vary from a few minutes (for a simple break in an ams) to a few boors (for neurological images) Since revenue was received on a per-reading basis, radiologists' ability to read images quickly and reduce downtame contributed to theit financial seccess. There was great demand for radiologists actoss Ontario, especially in rumal or remote areas of the province: CMI s darector, who managed all busuness operations, estimated that she received four to five zequests every month for CMI to provide services outside of Toronto. Fo help fullil this necd, many radiologists uscd potbons of their vacation time to perform locums - short-term placements (typically one week) - in underserviced aress COMMUNITY MEDICAL IMAGING Jestice Kelly wrote this case under the supervision of Ellzobuth M.A. Grasby soley to provide mulenlar for class discurtion. . The certain names and other idenbifying informaton to protect conbdentaity. Richavd Wey School of Eusiness Foundation prahipits any form of reproduction, stonge or transmssion wincut its written Copmont 02011 . Richard hey Schod af Aueness Foundabion Vecison 20120112 It was Febriary I8, 2009, and Dr. Frank Davis, radiologist with Community Medical Imagang (CMI), in Toronto. Ontario, had just received an anxious phone call from the chief of radjology at Thunder Bary District Hospital. The Vancouver-bised company that had provided on-call serviect to Thander Bay and the sarrounding area had relocated to the United States and could no longer provide service. The chicf was hoping that Davis and his highly regarded feam at CMI could take on the extra wockload. Davis lanew the deal woald provide interesting wotk ind improve CMI's presence across the provines, but if would also place an increased demand, both professonaliy and personally, on CMI's physaciars COMMUNITY MEDICAL IMAGING (CMI) History CMI was established in 1931 at one location with one radiologist. At the time, radiological caarninations were so infrequent that tbe radiologist was able to manage both his cline and all radiology at St. Michael's hospital. By 1954, CMil had fout radiologots, and the team began resdine films from a handful of hospitals in snall towns across fegion. In the decades that followed, addational clinics and plysicians were continually added and, in 2002, CMI converted the business from a film-erading centre to a state-of the-ait digital imaging centre, a six-miobth prosess. The CMI team had yrown bol4 radiologists (all partners). In recent years, a new partner was hired every three to four years Recently, CMI had been one of four finalists in the small business division of the Chamber of Commerce Busmess of the Vear. A wathds. Current Operations per idy, fivedays per week CHART OF PROFESSIONAL AND TECHNICAL FEES 2011. The digitization of medical imaging had drastically altered the dynamies of the industry, mainly due to the introduction of teleradiology. Teleradiology was "the electronic transmission of diagnostic imaging studies from one location to another for the purpose of interpretation and/or consultation." Teleradiology offered the opportunities for providing top-level service to rural and remote areas without having to recruit specialized physicians to these areas; however, elients still preferred to have a radiologist present Historically, due to the "windshield factor," radiologists had provided service only within their geographic regions and, therefore, maintained some compctitive protection from other radiologists within their area. With the ability to read images remotely, the medical imaging industry became more global, and radiologists were increasingly forced to cater to their customers' needs (such as on-call service and flexible scheduling) rather than dictate to their clients. Personal relationships and strong reputations also became more iniegral to developing partnerships between hospitals and radiology groups: Another notable trend was the increasing level of bureaucracy in the bealth-care industry. The majority of "contracts" for remote work was historically done on a handshake between physicians; however, to read innages and esim revenue RADIOLOGY History Radiology was a branch of medicine that utilized radiation for the treatment and diagnosis of disease 2 The field of radiology began with the discovery of X-riays and their analysis in 1895 . Today, ndiologists bot only read images from X-ray films but also images from ultrasound, magnetio resonance imaging (MRL). and computerized axial tomography (CT sean). These different techaigues used within medical imaging were referred to as "modalities" Radiologists were phyacians and, as a result, were requited to complete two fo four years of undergraduate sodics, four years of medical school, four to six years for their ipecialization and an optional fellowship? Whath the field of radiology, doctors onen focused on areas of specialization such as Becutoradiology. obsietrical imaging and gastrointestinal imaging The length of education was related to these specializations; for example, neuroradiology required 16 years of postisecondary education. hired statt. Now Physicians To meet the demands of the northern Ontario hospitals, there would have to bo two major changes to CMI's operatioas. First, there would be an evening shift added from 5 p.m. to 11pm, seven days a week, in Toronto. Although CMI's team had always worked loog hours, there had never been a formal evening work shift. Second, a CMI physician would have to be present at Thunder Bay District Hospital for three out of four weeks each month. The 14 physicians would have to rotate through this responsibility in one. week intervals. CMI's directot estimated that the existing team's average workday eould increase to a high of 15 hours per day with the additional workload; consequently, she recommended that CMI hire four additiobal radiologists to make the Duunder Bay workload more manageable. This approach would also heip to spread out the physicians" day-to-day work in Toronto: however, it was untikely that additional parnen could be hited until mid-2010 because CMI had hissoncally hired focent graduates (who finished university in carly May each year) to help grow its business Financial Considerations Potential sevenue from the Thunder Bay proposal was expovied to be 5167,000 cach mooth beyaming in January 2010 The 14 exisang parners would receive ao increane in pay' for any adtitional hours uveked. however, all cash in excess of $100,000 would be evenly distributed among the parners at the end of eash. year. Alf revenue camed would take 30 days to receive and would be paid to Thunder Bay Diinct: and food - were estimated at 54,500 a week and would be minbursed by the Mumstry of Health and be received from the governakent in 30 days To provide teleradiology service, a new diagnostic suite would need to be created at the main Toronto clinic. The total cost for the renovation would be $85,000, which included the cost of the PACS workstation and installation of a secure communications line for privacy. Thunder Bay District Hospital was prepared to contribute $65,000 towards this renovation upon its completion. Although PACS technology was quite new, Davis estimated the new system would function for 10 to 15 years CONCLUSION Although Davis was proud of CMI's existing business and reputation, he knew the draw of unusual work and therefore recognized that helping an underserved arca could be difficult for the team to furn down. If they tumed down the opportunity, one of the other medical imaging companies vying for the job - many based in Calgary - would casily step in. If CMI took on the job but could not handle the increased workload, Thunder Bay District Hospital would use locunis, and CMI would be quickly phased out of the job. Regardless of their deciston, the partmers would need to act quickly but practically. per day, five days per week CMI employed a full-time director who managed all aspects of the business and advised the partisers on its future direction. Also, an extensive team of technologists and suppott staff performed many of the procedures and completed administrative duties such as scheduline and belling Partnor Physiclans Each of CMI's 14 partnets received equal pay and equal distribution of income. (Typically, 5100,000canh was kept on hand for daily business needs, and all other income was destributed) As such. the team exhibited o significant level of co-operation and a colloctive pride, both in CMI'v reputation and in its quality of woek provided for the community, therefore, when making decisions, the partien had is consides whar was in the best ingerest of the entite teams. In 2006, the partaen developed mission, visua and key valoes statements io help gaide the decisson-making prosess. CMITr misson apd vision of folver parines CMI's partners also placed a high value on being leaders in their field. This meant they would be early adopters of new technologies, be exposed to challenging and intriguing work, and maintain a sizable presence in the province. Professional autonomy was important to the partners, and an integral component of achieving this goal included their ability to lobby the Ministry of Health and Long-Term Care THE THUNDER BAY PROPOSAL. Geographic Coverage The Thunder Bay proposal would involve providing service, both on-site and through telerndiology, to 10 Northern Ontano bospitals with Thunder Bay as the main hub (sce map in Evhibit 2). As the primary lub of medicine in the north, Thunder Bay District Hespital had the very best equipunent in medical imieing A few of CMI's partners bad completed locums at the hospital on a tral basis and had found the work to be quite intriguing, for example, due to differences in living conditions atsd culture, medical conditions were otten seen in Northem Oniatio that were rare in Southem Ontatio Now Physiclans To meet the demands of the nortiem Ontario hospitals, thece woild have to be two majat changes to week intorits Radiology in Ontario Within Ontario's universal health-care systcuty, many medical procedures, including medical imaging services, were paid by the provincial governinent. Typically, patients were referred for medical imaging by their family physicians and were then booked for appointments at elinics. At these climics, patients would present their provineial health cards and then have the appropriate procedure(s) completed by technologists. The technologists then uploaded the image to secure picture archiving communication systems (PACS). These images would then be read by radiologists who dictated their reports These oral reports were typed by medical transeriptionists and sent back to famaly phystcians, who in turm reported the dagnosis to patients. For emergency or acute treatment in hospitals, this process was completed entirely within the hospital Radiologists in Ontano received all their revenue from the provincial government, through standardized professional fees (P-fees) and technical fees (T-fees). Fxhibit I shows the P-fees and T-fees for a few standard procedures. P-fees were paid directly to the radiologists performing the inage readings; whereas. Thfees were paid to the clinics or to the hospitals and were intended to cover the cost of technologists. transcriptionists, imvestments in equipment and any overhcad costs. The time fequired to read an image could vary from a few minutes (for a simple break in an ams) to a few boors (for neurological images) Since revenue was received on a per-reading basis, radiologists' ability to read images quickly and reduce downtame contributed to theit financial seccess. There was great demand for radiologists actoss Ontario, especially in rumal or remote areas of the province: CMI s darector, who managed all busuness operations, estimated that she received four to five zequests every month for CMI to provide services outside of Toronto. Fo help fullil this necd, many radiologists uscd potbons of their vacation time to perform locums - short-term placements (typically one week) - in underserviced aress COMMUNITY MEDICAL IMAGING Jestice Kelly wrote this case under the supervision of Ellzobuth M.A. Grasby soley to provide mulenlar for class discurtion. . The certain names and other idenbifying informaton to protect conbdentaity. Richavd Wey School of Eusiness Foundation prahipits any form of reproduction, stonge or transmssion wincut its written Copmont 02011 . Richard hey Schod af Aueness Foundabion Vecison 20120112 It was Febriary I8, 2009, and Dr. Frank Davis, radiologist with Community Medical Imagang (CMI), in Toronto. Ontario, had just received an anxious phone call from the chief of radjology at Thunder Bary District Hospital. The Vancouver-bised company that had provided on-call serviect to Thander Bay and the sarrounding area had relocated to the United States and could no longer provide service. The chicf was hoping that Davis and his highly regarded feam at CMI could take on the extra wockload. Davis lanew the deal woald provide interesting wotk ind improve CMI's presence across the provines, but if would also place an increased demand, both professonaliy and personally, on CMI's physaciars 










Make sure to have
an introduction
problem definition
background summary
analysis both qualitative and quantitative
alternatives
recommendations
and finally a conclusion
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


