Question
Preparing pro forma financial statements (requires Appendix 7.1). Problem 25 Exhibits below presents financial statements for Bullseye Corporation for its fiscal years ending December 31,
Preparing pro forma financial statements (requires Appendix 7.1). Problem 25 Exhibits below presents financial statements for Bullseye Corporation for its fiscal years ending December 31, 2011, 2012, and 2013, as well as financial statement ratios. a. Prepare a set of pro forma financial statements for Bullseye Corporation for fiscal years 2014 through 2018 using the assumptions detailed below. b. Describe actions that Bullseye might take to deal with the shortage of cash projected in part a. c. What are the likely reasons for the projected changes in the return on equity?
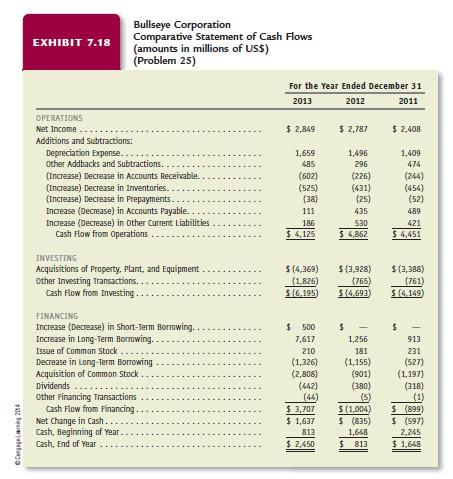
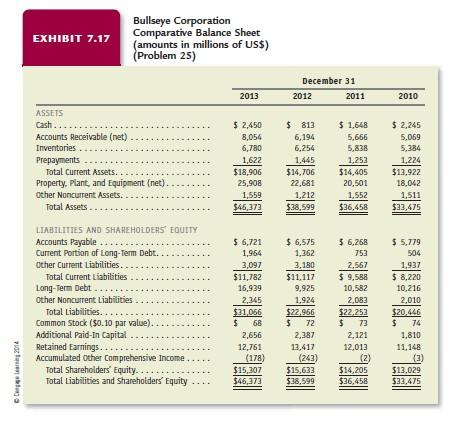
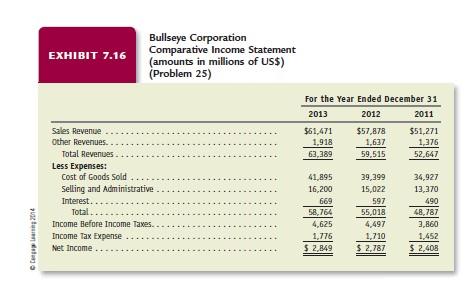
INCOME STATEMENT ASSUMPTIONS 1. Sales grew 12.2% in 2011 and 12.9% in 2012, primarily as a result of increases in the number of new stores and increases in sales of stores open more than one year. Sales grew only 6.3% in 2013 because of recession conditions. Although Bullseye Corporation will continue to increase the number of stores, economic conditions and competition will likely constrain increases in sales. Thus, assume that sales will grow 9% each year between 2014 and 2018. 2. Other revenues, representing interest on outstanding accounts receivable, have been approximately 3% of sales during the last three years. Assume that other revenues will continue at this historical rate. 3. The cost of goods sold to sales percentage increased slightly from 66.1% in 2011 to 68.2% in 2013. Assume that the cost of goods sold to sales percentage will be 68.1% for 2014 to 2018. 4. The selling and administrative expense percentage has increased slightly from 26.1% of sales in 2011 to 26.2% of sales in 2013. Bullseye will realize economies of scale as its growth rate in sales increases to 9% annually. Assume that the selling and administrative expense to sales percentage will be 26.0% for 2014 to 2018. 5. Bullseye Corporation has borrowed using long-term debt to construct new stores. The average interest rate on interest-bearing debt was approximately 4.4% during 2013. Assume this interest rate for all borrowing outstanding (long-term debt, and current portion of long-term debt) for Bullseye Corporation will be 5% for 2014 to 2018. Compute interest expense on the average amount of interest-bearing debt outstanding each year.
6. Bullseye Corporations average income tax rate as a percentage of income before income taxes has varied around 38% during the last three years. Assume an income tax rate of 38% of income before income taxes for 2014 to 2018. 7. Bullseye Corporations dividends increased at an average annual rate of 17.9% between 2011 and 2013. Assume that dividends will grow 16% each year between 2014 and 2018. BALANCE SHEET ASSUMPTIONS 8. Cash will be the amount necessary to equate total assets with total liabilities plus shareholders equity. 9. Accounts receivable will increase at the growth rate in sales. 10. Inventory will increase at the growth rate in sales. 11. Prepayments relate to ongoing operating costs, such as rent and insurance. Assume that prepayments will grow at the growth rate in sales. 12. Property, plant, and equipment grew 12.4% annually during the most recent three years. The construction of new stores will require additional investments in property, plant, and equipment, but not at the growth rate experienced in recent years. Assume that property, plant, and equipment will grow 10% each year between 2014 and 2018. 13. Other assets changed by only a small amount during the last three years. Assume that other assets will remain the same amount for 2014 to 2018 as the amount at the end of 2013. 14. The accounts payable turnover ratio increased from 5.9 in 2011 to 6.4 during 2013. Assume that Bullseye Corporation will increase its accounts payable turnover to 6.5 times per year for 2014 to 2018. 15. The notes to Bullseye Corporations financial statements indicate that current maturities of long-term debt on December 31 of each year are as follows: 2013, $1,964 (amount already appears on the December 31, 2013, balance sheet); 2014, $1,951; 2015, $1,251; 2016, $2,236; 2017, $107; 2018, $2,251. 16. Other current liabilities relate to ongoing operating activities and are expected to grow at the growth rate in sales. 17. Bullseye Corporation uses long-term debt to finance acquisitions of property, plant, and equipment. Assume that long-term debt will decrease by the amount of long-term debt reclassified as a current liability each year and then the remaining amount will increase at the growth rate in property, plant, and equipment. For example, the December 31, 2013, balance sheet of Bullseye Corporation shows the current portion of long-term debt to be $1,964. Bullseye Corporation will repay this amount during 2014. During 2014, Bullseye will reclassify $1,951 from long-term debt to current portion of long-term debt (see item 15 above). This will leave a preliminary balance in long-term debt of $14,988 (= $16,939 $1,951). Bullseye Corporation will increase this amount of long-term debt by the 10% growth rate in property, plant, and equipment. The projected amount for long-term debt on the December 31, 2014, balance sheet is $16,487 (= $14,988 1.1). 18. Other noncurrent liabilities include an amount related to retirement benefits and taxes due after more than one year. Assume that other noncurrent liabilities will increase at the growth rate in sales. 19. Assume that common stock and additional paid-in capital will not change. 20. Assume that accumulated other comprehensive income will grow at the growth rate in sales. STATEMENT OF CASH FLOW ASSUMPTIONS 21. Assume that depreciation expense will increase at the growth rate in property, plant, and equipment. 22. Assume that changes in other noncurrent liabilities and in accumulated other comprehensive income on the balance sheet are operating activities. 23. Assume that the amount for Other Financing Transactions is zero for 2014 to 2018.
Bullseye Corporation EXHIBIT 7.18 Comparative Statement of Cash Flows (amounts in millions of US$) (Problem 25) For the Year Ended December 31 2013 2012 2011 OPERATIONS Net Income $ 2,849 $ 2,787 $ 2,408 Additions and Subtractions: Depreciation Expense. 1,659 1,496 1,409 Other Addbacks and Subtractions. 485 296 474 (Increase) Decrease in Accounts Receivable. (602) (226) (244) (Increase) Decrease in Inventories. (525) (431) (454) (Increase) Decrease in Prepayments (38) (25) (52) Increase (Decrease) in Accounts Payable.. 111 435 489 Increase (Decrease) in other current Liabilities 186 530 421 Cash Flow from Operations. 5 4.125 $ 4,862 $ 4,451 INVESTING Acquisitions of Property. Plant, and Equipment Other Investing Transactions.. Cash Flow from Investing. $(4,369) (1,826) $16.195) $ (3,928) (765) $14.693) $(3,388) (761) $14.149) FINANCING Increase (Decrease) in Short-Term Borrowing, Increase in Long-Term Borrowing.. Issue of Common Stock .. Decrease in Long-Term Borrowing Acquisition of Common Stock Dividends .... Other Financing Transactions Cash Flow from Financing Net Change in Cash... Cash, Beginning of Year Cash, End of Year $ 500 7,617 210 (1,326) (2,808) (442) (46) $ 3,707 $ 1,637 813 $ 2,450 1,256 181 (1.155) (901) (380) (5) $(1,004) $ (835) 1,648 $ 813 913 231 (527) (1,197) (318) (1) $ (899) $ (597) 2.245 $ 1,648 CL24 EXHIBIT 7.17 Bullseye Corporation Comparative Balance Sheet (amounts in millions of US$) Problem 25) 2013 December 31 2012 2011 2010 $ 2,450 8,054 6,780 1,622 $18,906 25,908 1,559 $46,373 $ 813 6,194 6,254 1.445 $14,706 22,681 1.212 $38,599 $ 1,648 5,666 5,838 1.253 $14,405 20,501 1,552 $36.458 $ 2,245 5,069 5,384 1.224 $13,922 18,042 1.511 $33,475 ASSETS Cash.. Accounts Receivable (net) Inventories Prepayments Total Current Assets.. Property, plant, and Equipment (net) Other Noncurrent Assets. Total Assets LIABILITIES AND SHAREHOLDERS' EQUITY Accounts Payable.... Current Portion of Long-Term Debt.. Other Current Liabilities. Total Current Liabilities Long-Term Debt.... Other Noncurrent Liabilities Total Liabilities.... Common Stock ($0.10 par value). Additional Paid-In Capital ... Retained Earnings.. Accumulated other comprehensive Income Total Shareholders' Equity.. Total Liabilities and Shareholders' Equity $ 6,721 1,964 3,097 $11,782 16,939 2.345 $31,056 $ 68 2,656 12,761 (178) $15,207 $46,373 $ 6,575 1.362 3.180 $11,117 9,925 1.924 $22.966 $ 72 2,387 13,417 (243) $15,632 $38,599 5 6.268 753 2,567 $ 9,588 10,532 2,083 $22,253 $ 73 2,121 12,013 (2) $14,205 $36.458 $ 5,779 504 1,937 $ 8,220 10,216 2,010 $20.446 $ 74 1,810 11,148 (3) $13,029 $32,475 20/14 EXHIBIT 7.16 Bullseye Corporation Comparative Income Statement (amounts in millions of US$) (Problem 25) For the Year Ended December 31 2013 2012 2011 $61,471 $57,878 $51,271 1,918 1,637 1,376 63,389 59,515 52,647 Sales Revenue Other Revenues. Total Revenues Less Expenses: Cost of Goods Sold Selling and Administrative Interest. Total.. Income Before Income Taxes. Income Tax Expense Net Income pus 41.895 16,200 669 58.764 4,625 1,776 $ 2,849 39,399 15,022 597 55,018 4,497 1.710 $ 2,787 34,927 13,370 490 48,787 3,860 1.452 $2,408
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


