Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Problem 1. (a) Beginning with the full constitutive equation in your class notes or the textbook( Eq.4.13 in the lecture note or Equation 4.55

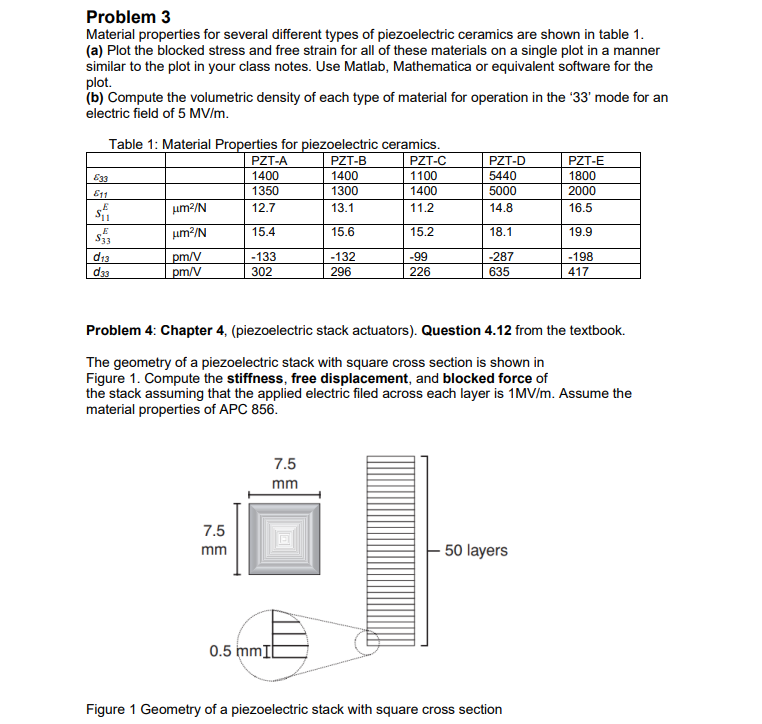
Problem 1. (a) Beginning with the full constitutive equation in your class notes or the textbook( Eq.4.13 in the lecture note or Equation 4.55 in the textbook), write the constitutive relationships for a piezoelectric material with an electric field applied in the direction of polarization( the 3 direction). Assume that the applied stress is zero except for the "1" and "2" material directions. (b) Compute the strain vector for the system described above in problem (a) when the applied field is equal to 0.5 MV/m and the applied stress in the "1" and "2" directions is 6 MPa. Assume the materials properties of APC 856. (c) Considering problem (a), compute the stress vector for APC 856 material if we assume that the strain in the "1" and "2" directions are constrained to be zero. Problem 2 A piezoelectric sensor has a stress applied in the direction of polarization equal to 10 MPa. Stress values of 8 MPa are applied in the two directions normal to the polarization vector. (a) Compute the electric field vector produced by the applied stress assuming that the electric displacement is held equal to zero. Assume the material properties of PZT-5H. Comment about the result. Page 1 of 2 (b) Compute the electric displacement in the polarization direction assuming that the electric field is held equal to zero. Comment about the result. Problem 3 Material properties for several different types of piezoelectric ceramics are shown in table 1. (a) Plot the blocked stress and free strain for all of these materials on a single plot in a manner similar to the plot in your class notes. Use Matlab, Mathematica or equivalent software for the plot. (b) Compute the volumetric density of each type of material for operation in the '33' mode for an electric field of 5 MV/m. Table 1: Material Properties for piezoelectric ceramics. PZT-A PZT-B PZT-C PZT-D PZT-E 533 1400 1400 1100 5440 1800 611 1350 1300 1400 5000 2000 E um2/N 12.7 13.1 11.2 14.8 16.5 E $33 m2/N 15.4 15.6 15.2 18.1 19.9 d13 pm/V -133 -132 -99 -287 -198 d33 pm/V 302 296 226 635 417 Problem 4: Chapter 4, (piezoelectric stack actuators). Question 4.12 from the textbook. The geometry of a piezoelectric stack with square cross section is shown in Figure 1. Compute the stiffness, free displacement, and blocked force of the stack assuming that the applied electric filed across each layer is 1MV/m. Assume the material properties of APC 856. 7.5 mm 7.5 mm 0.5 mmIt 50 layers Figure 1 Geometry of a piezoelectric stack with square cross section
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


