Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Problem 1. Consider an NACA2412 airfoil, Figure 1 shows the sectional lift coefficient C, the moment coefficient relative to the quarter-chord Cm/4, and the
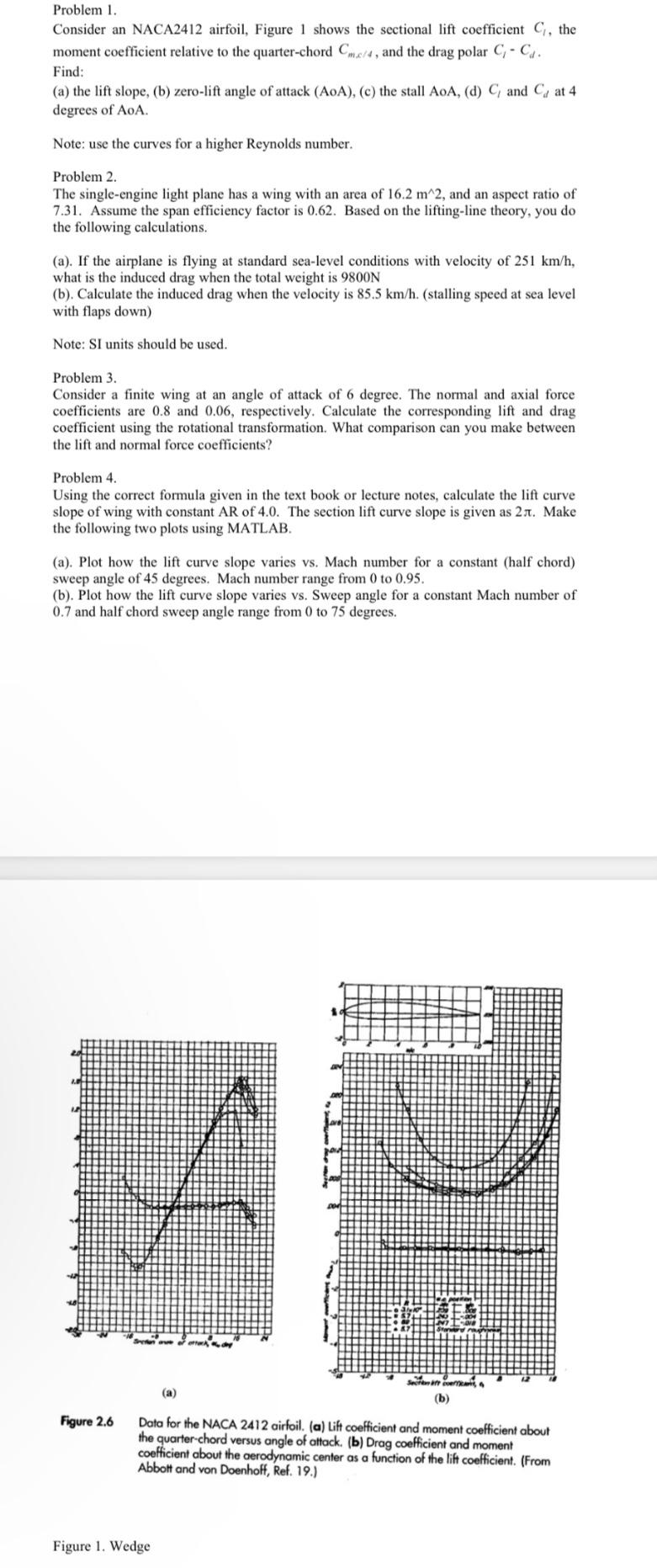
Problem 1. Consider an NACA2412 airfoil, Figure 1 shows the sectional lift coefficient C, the moment coefficient relative to the quarter-chord Cm/4, and the drag polar C- Ca. Find: (a) the lift slope, (b) zero-lift angle of attack (AOA), (c) the stall AoA, (d) C, and C at 4 degrees of AoA. Note: use the curves for a higher Reynolds number. Problem 2. The single-engine light plane has a wing with an area of 16.2 m^2, and an aspect ratio of 7.31. Assume the span efficiency factor is 0.62. Based on the lifting-line theory, you do the following calculations. (a). If the airplane is flying at standard sea-level conditions with velocity of 251 km/h, what is the induced drag when the total weight is 9800N (b). Calculate the induced drag when the velocity is 85.5 km/h. (stalling speed at sea level with flaps down) Note: SI units should be used. Problem 3. Consider a finite wing at an angle of attack of 6 degree. The normal and axial force coefficients are 0.8 and 0.06, respectively. Calculate the corresponding lift and drag coefficient using the rotational transformation. What comparison can you make between the lift and normal force coefficients? Problem 4. Using the correct formula given in the text book or lecture notes, calculate the lift curve slope of wing with constant AR of 4.0. The section lift curve slope is given as 2. Make the following two plots using MATLAB. (a). Plot how the lift curve slope varies vs. Mach number for a constant (half chord) sweep angle of 45 degrees. Mach number range from 0 to 0.95. (b). Plot how the lift curve slope varies vs. Sweep angle for a constant Mach number of 0.7 and half chord sweep angle range from 0 to 75 degrees. Figure 2.6 (a) (b) Data for the NACA 2412 airfoil. (a) Lift coefficient and moment coefficient about the quarter-chord versus angle of attack. (b) Drag coefficient and moment coefficient about the aerodynamic center as a function of the lift coefficient. (From Abbott and von Doenhoff, Ref. 19.) Figure 1. Wedge
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


