Question
Patty Corporation acquired a 75% of Sue Corporation for $300,000 on January 1, 2009, when Sues equity consisted of $150,000 capital stockand $50,000 retained earnings.
Patty Corporation acquired a 75% of Sue Corporation for $300,000 on January 1, 2009, when Sue’s equity consisted of $150,000 capital stockand $50,000 retained earnings. The fari value of Sue’s assetsa and liabilities were equal to their book value on t his date, any goodwill is not amortized. Patty uses the equity method of accounting for Sue.
During 2009, Patty sold inventory items to Sue for $80,000, and at December 31, 2009, Sue’s inventory included items on which there were $10,000 unrealized profits. During 2010, Patty sold inventory items fo Sue for $130,000, and at December 31, 2010, Sue’s inventory included items on which were $20,000 unrealized profits.
On December 31, 2010, Sue owed $15,000 on account for merchandise purchases to Patty. The financial. Statements of Patty and Sue Corporations at and for the year ended December 31, 2010 are summarized as follows (in thousands):
Instructions
Prepare consolidation working papers for Patty Corporation and Subsidiary for the year ended December 31, 2010
Problem 2
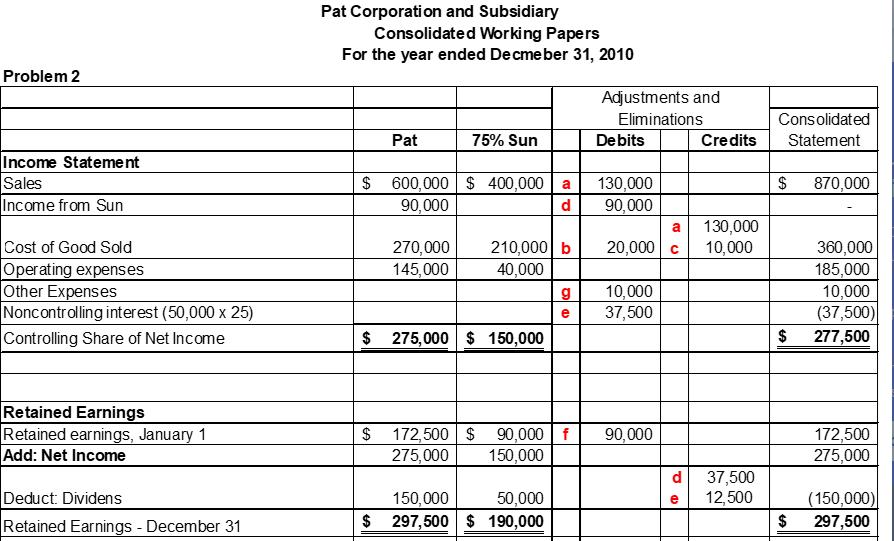
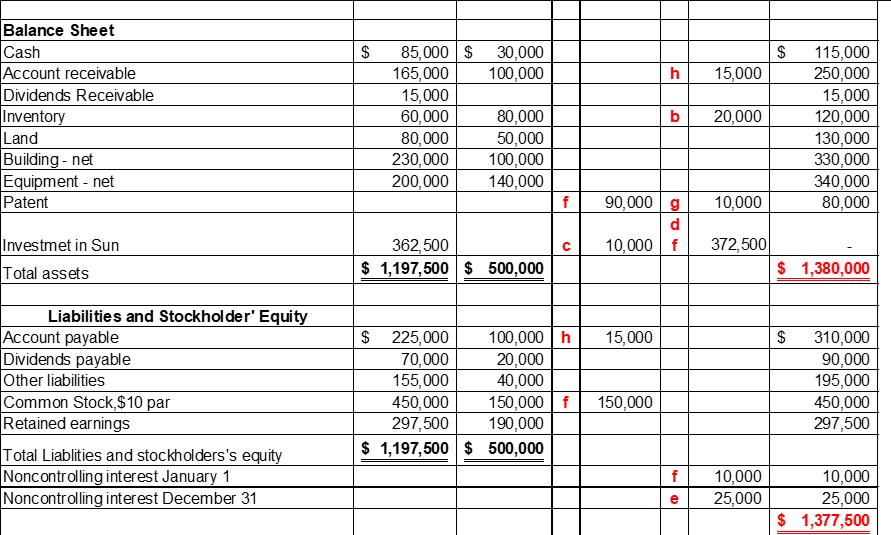
Pat Corporation acquired a 75% interest in Sun Corporation for $300,000 on January 1, 2009, when Sun’s equity consisted of $150,000 capital stock and $50,000 retained earnings. The fair values of Sun’s assets and liabilities were equal to their book values on this date. The excess purchase price was allocated to an unrecorded patent, which ha a remaining life of 10 years. Pat uses the equity method of accounting for Sun.
During 2009, Pat sold inventory items to Sun for $80,000, and at December 31, 2009, Sun’s inventory included items in which there were $10,000 unrealized profits. During 2010, Pat sold inventory items to Sun for $130,000, and at December 31, 2010, Sun’s inventory included items on which there were $20,000 unrealized profits.
On December 31, 2010, Sun owed Pat $15,000 on account for merchandise purchases. The financial statements of Pat and Sun Corporations at and for the year ended December 31, 2010, are summarized as follows:
Instructions
Prepare consolidation working papers for Pat Corporation and Subsidiary for the year ended December 31, 2010.
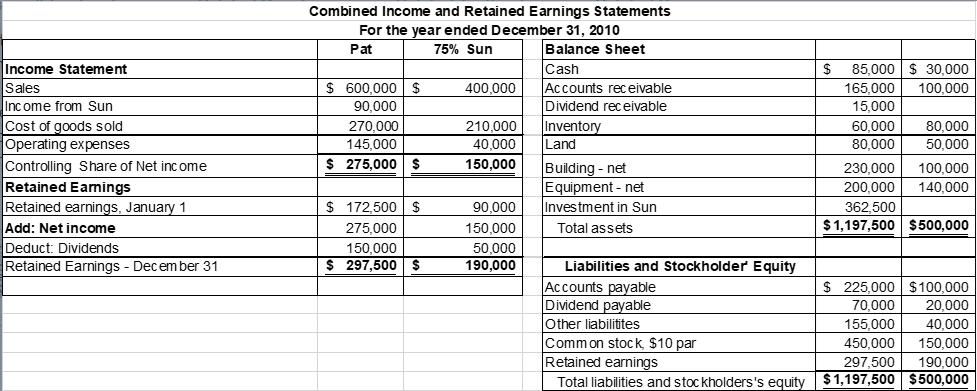
Income Statement Sales Income from Sun Cost of goods sold Operating expenses Controlling Share of Net income Retained Earnings Retained earnings, January 1 Add: Net income Deduct: Dividends Retained Earnings - December 31 Combined Income and Retained Earnings Statements For the year ended December 31, 2010 Pat 75% Sun Balance Sheet $ 600,000 $ 90,000 270,000 145,000 $ 275,000 $ $ 172,500 $ 275.000 150,000 $ 297,500 $ 400,000 210,000 40,000 150,000 90,000 150,000 50,000 190,000 Cash Accounts receivable Dividend receivable Inventory Land Building - net Equipment - net Investment in Sun Total assets Liabilities and Stockholder Equity Accounts payable Dividend payable Other liabilitites $ 85,000 $30,000 165,000 100,000 15,000 Common stock, $10 par Retained earnings 60,000 80,000 80,000 50,000 100,000 140,000 230,000 200,000 362,500 $1,197,500 $500,000 $225,000 $100,000 70,000 20,000 155,000 40,000 450,000 150,000 297,500 190,000 Total liabilities and stockholders's equity $1,197,500 $500,000
Step by Step Solution
3.61 Rating (169 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
Patty Corporation and Subsidiary Consolidation Working Papers December 31 2010 Elimination Entries Accounts Debit Credit Investment in Sue 300000 Controlling interest in Sues net assets 300000 Unreali...
Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


