PROBLEM 1014 Basic Variance Analysis Becton Labs, Inc., produces various chemical compounds for industrial use. One compound, called Fludex, is prepared using an elaborate distilling
PROBLEM 1014 Basic Variance Analysis
Becton Labs, Inc., produces various chemical compounds for industrial use. One compound, called Fludex, is prepared using an elaborate distilling process. The company has developed standard costs for one unit of Fludex, as follows:
| Standard Quantity or Hours | Standard Price or Rate | Standard Cost | |
| Direct materials | 2.5 ounces | $20.00 per ounce | $50.00 |
| Direct labor | 1.4 hours | $22.50 per hour | $31.50 |
| Variable MOH | 1.4 hours | $3.50 per hour | $4.90 |
| Total Standard Cost per Unit | $86.40 |
During November, the following activity was recorded related to the production of Fludex:
a. Materials purchased, 12,000 ounces at a cost of $225,000.
b. There was no beginning inventory of materials; however, at the end of the month, 2,500 ounces of material remained in ending inventory.
c. The company employs 35 lab technicians to work on the production of Fludex. During November, they worked an average of 160 hours at an average pay rate of $22 per hour.
d. Variable manufacturing overhead is assigned to Fludex on the basis of direct labor-hours. Variable manufacturing overhead costs during November totaled $18,200.
e. During November, the company produced 3,750 units of Fludex.
Required:
For direct materials:
a. Compute the price and quantity variances.
b. The materials were purchased from a new supplier who is anxious to enter into a long-term purchase contract. Would you recommend that the company sign the contract? Explain.
2. For direct labor:
a. Compute the rate and efficiency variances.
b. In the past, the 35 technicians employed in the production of Fludex consisted of 20 senior technicians and 15 assistants. During November, the company experimented with fewer senior technicians and more assistants in order to save costs. Would you recommend that the new labor mix be continued? Explain.
3. Compute the variable overhead rate and efficiency variances. What relation can you see between this efficiency variance and the labor efficiency variance?
PROBLEM 1015 Comprehensive Variance Analysis
Miller Toy Company manufactures a plastic swimming pool at its Westwood Plant. The plant has been experiencing problems as shown by its June contribution format income statement below:
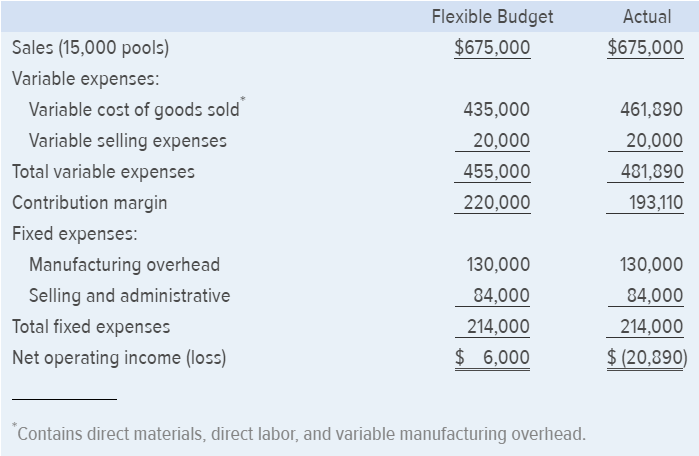 Janet Dunn, who has just been appointed general manager of the Westwood Plant, has been given instructions to get things under control. Upon reviewing the plants income statement, Ms. Dunn has concluded that the major problem lies in the variable cost of goods sold. She has been provided with the following standard cost per swimming pool:
Janet Dunn, who has just been appointed general manager of the Westwood Plant, has been given instructions to get things under control. Upon reviewing the plants income statement, Ms. Dunn has concluded that the major problem lies in the variable cost of goods sold. She has been provided with the following standard cost per swimming pool:
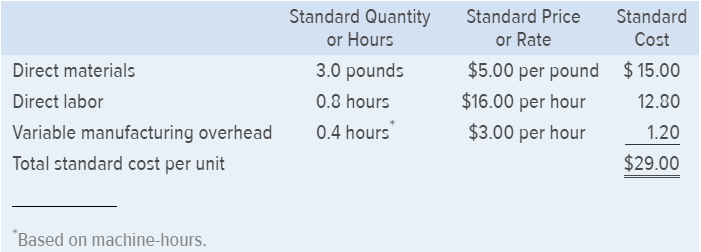 During June the plant produced 15,000 pools and incurred the following costs:
During June the plant produced 15,000 pools and incurred the following costs:
a. Purchased 60,000 pounds of materials at a cost of $4.95 per pound.
b. Used 49,200 pounds of materials in production. (Finished goods and work in process inventories are insignificant and can be ignored.)
c. Worked 11,800 direct labor-hours at a cost of $17.00 per hour.
d. Incurred variable manufacturing overhead cost totaling $18,290 for the month. A total of 5,900 machine-hours was recorded.
It is the companys policy to close all variances to cost of goods sold on a monthly basis.
Required:
Compute the following variances for June:
a. Materials price and quantity variances.
b. Labor rate and efficiency variances. c. Variable overhead rate and efficiency variances
3. Pick out the two most significant variances that you computed in (1) above. Explain to Ms. Dunn possible causes of these variances.
Actual Flexible Budget $675,000 Sales (15,000 pools) Variable expenses $675,000 435,000 20,000 455,000 220,000 461,890 20,000 481,890 193,110 Variable cost of goods sold Variable selling expenses Total variable expenses Contribution margin Fixed expenses 130,000 84,000 214,000 $6,000 Manufacturing overhead Selling and administrative 130,000 84,000 214,000 $(20,890 Total fixed expenses Net operating income (loss) Contains direct materials, direct labor, and variable manufacturing overheadStep by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


