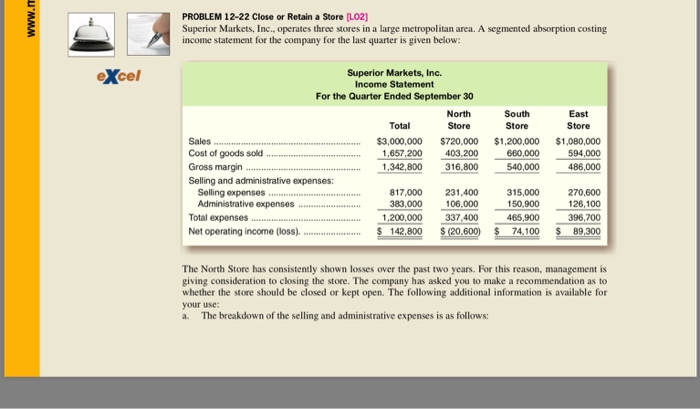
PROBLEM 12-22 Close or Retain a Store [Lo2] Superior Markets, Inc., operates three stores in a large metropolitan area. A segmented absorption costing income statement for the company for the last quarter is given below: eXcel Superior Markets, Inc. Income Statement For the Quarter Ended September 30 North Store South Store East Store Total Sales Cost of goods sold Gross margin Selling and administrative expenses: $3,000,000 $720,000 $1,200,000 $1,080,000 594,000 1,342,800 316,800 540,000 486,000 1,657,200 403.200 660,000 Selling expenses 817,000 383,000 231.400 106,000 15,000 150,900 465,900 74.100 270,600 126,100 396.700 89,300 ,200,000 337,400 Total expenses Net operating income (loss). S 142800 (20,600 74100 89.300 The North Store has consistently shown losses over the past two years. For this reason, management is giving consideration to closing the store. The company has asked you to make a recommendation as to whether the store should be closed or kept open. The following additional information is available for your use: a. The breakdown of the selling and administrative expenses is as follows: 524 Chapter 12 PROBLEM 12-23 Relevant Cost Analysis in a Variety of Situations [L02, L03, LO4] Andretti Company has a single product called a Dak. The company normally produces and sells 60,000 Daks each year at a selling price of $32 per unit. The company's unit costs at this level of activity are given below: Direct materials Direct labor Variable manufacturing overhead Fixed manufacturing overhead. $10.00 4.50 2.30 5.00 ($300,000 total) 1.20 3.50 $210,000 total) Fixed seling expenses Total cost per unit 26.50 A number of questions relating to the production and sale of Daks follow. Each question is independent. I. Assume that Andretti Company has sufficient capacity to produce 90,000 Daks each year without any increase in fixed manufacturing overhead costs. The company could increase its sales by 25% above the present 60,000 units each year if it were willing to increase the fixed selling expenses by $80,000. Would the increased fixed selling expenses be justified? Assume again that Andretti Company has sufficient capacity to produce 90,000 Daks each year. A customer in a foreign market wants to purchase 20,000 Daks. Import duties on the Daks would be $1.70 per unit, and costs for permits and licenses would be $9,000. The only selling costs that would be associated with the order would be $3.20 per unit shipping cost. Compute the per unit break-evern price on this order 2. 3. The company has 1,000 Daks on hand that have some iregularities and are therefore considered to be "seconds." Due to the irregularities, it will be impossible to sell these units at the normal price through regular distribution channels. What unit cost figure is relevant for setting a minimum selling price? 4. Due to a strike in its supplier's plant, Andretti Company is unable to purchase more material for the production of Daks. The strike is expected to last for two months. Andretti Company has enough material on hand to operate at 30% of normal levels for the two-month period. As an alternative, Andretti could close its plant down entirely for the two months. If the plant were closed, fixed manu- facturing overhead costs would continue at 60% of their normal level during the two)-month period and the fixed selling expenses would be reduced by 20%, what would be the impact on profits of closing the plant for the two-month period? An outside manufacturer has offered to produce Daks and ship them directly to Andretti's customers. If Andretti Company accepts this offer, the facilities that it uses to produce Daks would be idle: however, fixed manufacturing overhead costs would be reduced by 75%. Because the outside manu- facturer would pay for all shipping costs, the variable selling expenses wouald be only two-thirds of their present amount. Compute the unit cost that is relevant for comparison to the price quoted by the outside manufacturer 5. PROBLEM 12-22 Close or Retain a Store [Lo2] Superior Markets, Inc., operates three stores in a large metropolitan area. A segmented absorption costing income statement for the company for the last quarter is given below: eXcel Superior Markets, Inc. Income Statement For the Quarter Ended September 30 North Store South Store East Store Total Sales Cost of goods sold Gross margin Selling and administrative expenses: $3,000,000 $720,000 $1,200,000 $1,080,000 594,000 1,342,800 316,800 540,000 486,000 1,657,200 403.200 660,000 Selling expenses 817,000 383,000 231.400 106,000 15,000 150,900 465,900 74.100 270,600 126,100 396.700 89,300 ,200,000 337,400 Total expenses Net operating income (loss). S 142800 (20,600 74100 89.300 The North Store has consistently shown losses over the past two years. For this reason, management is giving consideration to closing the store. The company has asked you to make a recommendation as to whether the store should be closed or kept open. The following additional information is available for your use: a. The breakdown of the selling and administrative expenses is as follows: 524 Chapter 12 PROBLEM 12-23 Relevant Cost Analysis in a Variety of Situations [L02, L03, LO4] Andretti Company has a single product called a Dak. The company normally produces and sells 60,000 Daks each year at a selling price of $32 per unit. The company's unit costs at this level of activity are given below: Direct materials Direct labor Variable manufacturing overhead Fixed manufacturing overhead. $10.00 4.50 2.30 5.00 ($300,000 total) 1.20 3.50 $210,000 total) Fixed seling expenses Total cost per unit 26.50 A number of questions relating to the production and sale of Daks follow. Each question is independent. I. Assume that Andretti Company has sufficient capacity to produce 90,000 Daks each year without any increase in fixed manufacturing overhead costs. The company could increase its sales by 25% above the present 60,000 units each year if it were willing to increase the fixed selling expenses by $80,000. Would the increased fixed selling expenses be justified? Assume again that Andretti Company has sufficient capacity to produce 90,000 Daks each year. A customer in a foreign market wants to purchase 20,000 Daks. Import duties on the Daks would be $1.70 per unit, and costs for permits and licenses would be $9,000. The only selling costs that would be associated with the order would be $3.20 per unit shipping cost. Compute the per unit break-evern price on this order 2. 3. The company has 1,000 Daks on hand that have some iregularities and are therefore considered to be "seconds." Due to the irregularities, it will be impossible to sell these units at the normal price through regular distribution channels. What unit cost figure is relevant for setting a minimum selling price? 4. Due to a strike in its supplier's plant, Andretti Company is unable to purchase more material for the production of Daks. The strike is expected to last for two months. Andretti Company has enough material on hand to operate at 30% of normal levels for the two-month period. As an alternative, Andretti could close its plant down entirely for the two months. If the plant were closed, fixed manu- facturing overhead costs would continue at 60% of their normal level during the two)-month period and the fixed selling expenses would be reduced by 20%, what would be the impact on profits of closing the plant for the two-month period? An outside manufacturer has offered to produce Daks and ship them directly to Andretti's customers. If Andretti Company accepts this offer, the facilities that it uses to produce Daks would be idle: however, fixed manufacturing overhead costs would be reduced by 75%. Because the outside manu- facturer would pay for all shipping costs, the variable selling expenses wouald be only two-thirds of their present amount. Compute the unit cost that is relevant for comparison to the price quoted by the outside manufacturer 5