Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Problem 15-41 Cost-Plus Pricing vs. Target Costing (LO 15-1, 15-3, 15-5, 15-6, 15-8) [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.] For many years,
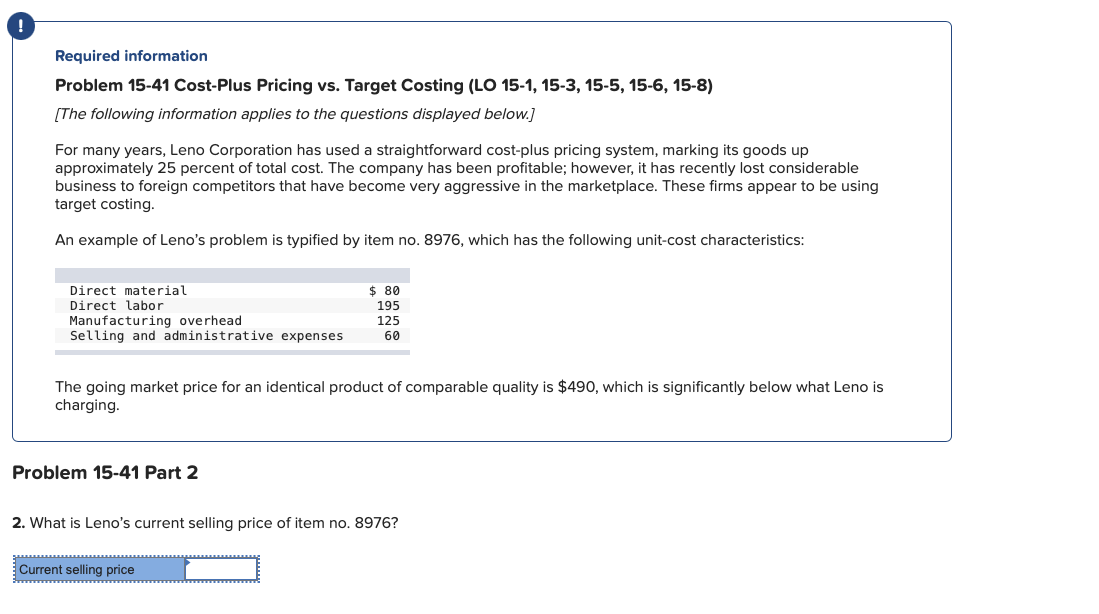

 Problem 15-41 Cost-Plus Pricing vs. Target Costing (LO 15-1, 15-3, 15-5, 15-6, 15-8) [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.] For many years, Leno Corporation has used a straightforward cost-plus pricing system, marking its goods up approximately 25 percent of total cost. The company has been profitable; however, it has recently lost considerable business to foreign competitors that have become very aggressive in the marketplace. These firms appear to be using target costing. An example of Leno's problem is typified by item no. 8976, which has the following unit-cost characteristics: The going market price for an identical product of comparable quality is $490, which is significantly below what Leno is charging. Problem 15-41 Part 2 2. What is Leno's current selling price of item no. 8976 ? Required information Problem 15-41 Cost-Plus Pricing vs. Target Costing (LO 15-1, 15-3, 15-5, 15-6, 15-8) [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.] For many years, Leno Corporation has used a straightforward cost-plus pricing system, marking its goods up approximately 25 percent of total cost. The company has been profitable; however, it has recently lost considerable business to foreign competitors that have become very aggressive in the marketplace. These firms appear to be using target costing. An example of Leno's problem is typified by item no. 8976, which has the following unit-cost characteristics: The going market price for an identical product of comparable quality is $490, which is significantly below what Leno is charging. oblem 15-41 Part 3 Leno used target costing for item no. 8976, what must happen to costs if the company desires to meet the market price and ntain its current rate of profit on sales? By how much? Required information Problem 15-41 Cost-Plus Pricing vs. Target Costing (LO 15-1, 15-3, 15-5, 15-6, 15-8) [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.] For many years, Leno Corporation has used a straightforward cost-plus pricing system, marking its goods up approximately 25 percent of total cost. The company has been profitable; however, it has recently lost considerable business to foreign competitors that have become very aggressive in the marketplace. These firms appear to be using target costing. An example of Leno's problem is typified by item no. 8976, which has the following unit-cost characteristics: The going market price for an identical product of comparable quality is $490, which is significantly below what Leno is charging. Problem 15-41 Part 4 4. Would the identification of value-added and non-value-added costs assist Leno in this situation? Required information Problem 15-41 Cost-Plus Pricing vs. Target Costing (LO 15-1, 15-3, 15-5, 15-6, 15-8) [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.] For many years, Leno Corporation has used a straightforward cost-plus pricing system, marking its goods up approximately 25 percent of total cost. The company has been profitable; however, it has recently lost considerable business to foreign competitors that have become very aggressive in the marketplace. These firms appear to be using target costing. An example of Leno's problem is typified by item no. 8976, which has the following unit-cost characteristics: The going market price for an identical product of comparable quality is $490, which is significantly below what Leno is charging. Problem 15-41 Part 5 5. Suppose that by previous cost-cutting drives, costs had already been "pared to the bone" on item no. 8976. What might Leno be orced to do with its markup on cost to remain competitive? By how much? (Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your percentage answer to 2 decimal places (i.e., .1234 should be entered as 12.34).) Required information Problem 15-41 Cost-Plus Pricing vs. Target Costing (LO 15-1, 15-3, 15-5, 15-6, 15-8) [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.] For many years, Leno Corporation has used a straightforward cost-plus pricing system, marking its goods up approximately 25 percent of total cost. The company has been profitable; however, it has recently lost considerable business to foreign competitors that have become very aggressive in the marketplace. These firms appear to be using target costing. An example of Leno's problem is typified by item no. 8976, which has the following unit-cost characteristics: The going market price for an identical product of comparable quality is $490, which is significantly below what Leno is charging. Problem 15-41 Part 6 6. In many industries, prices are the result of an interaction between market forces and costs. True or False
Problem 15-41 Cost-Plus Pricing vs. Target Costing (LO 15-1, 15-3, 15-5, 15-6, 15-8) [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.] For many years, Leno Corporation has used a straightforward cost-plus pricing system, marking its goods up approximately 25 percent of total cost. The company has been profitable; however, it has recently lost considerable business to foreign competitors that have become very aggressive in the marketplace. These firms appear to be using target costing. An example of Leno's problem is typified by item no. 8976, which has the following unit-cost characteristics: The going market price for an identical product of comparable quality is $490, which is significantly below what Leno is charging. Problem 15-41 Part 2 2. What is Leno's current selling price of item no. 8976 ? Required information Problem 15-41 Cost-Plus Pricing vs. Target Costing (LO 15-1, 15-3, 15-5, 15-6, 15-8) [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.] For many years, Leno Corporation has used a straightforward cost-plus pricing system, marking its goods up approximately 25 percent of total cost. The company has been profitable; however, it has recently lost considerable business to foreign competitors that have become very aggressive in the marketplace. These firms appear to be using target costing. An example of Leno's problem is typified by item no. 8976, which has the following unit-cost characteristics: The going market price for an identical product of comparable quality is $490, which is significantly below what Leno is charging. oblem 15-41 Part 3 Leno used target costing for item no. 8976, what must happen to costs if the company desires to meet the market price and ntain its current rate of profit on sales? By how much? Required information Problem 15-41 Cost-Plus Pricing vs. Target Costing (LO 15-1, 15-3, 15-5, 15-6, 15-8) [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.] For many years, Leno Corporation has used a straightforward cost-plus pricing system, marking its goods up approximately 25 percent of total cost. The company has been profitable; however, it has recently lost considerable business to foreign competitors that have become very aggressive in the marketplace. These firms appear to be using target costing. An example of Leno's problem is typified by item no. 8976, which has the following unit-cost characteristics: The going market price for an identical product of comparable quality is $490, which is significantly below what Leno is charging. Problem 15-41 Part 4 4. Would the identification of value-added and non-value-added costs assist Leno in this situation? Required information Problem 15-41 Cost-Plus Pricing vs. Target Costing (LO 15-1, 15-3, 15-5, 15-6, 15-8) [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.] For many years, Leno Corporation has used a straightforward cost-plus pricing system, marking its goods up approximately 25 percent of total cost. The company has been profitable; however, it has recently lost considerable business to foreign competitors that have become very aggressive in the marketplace. These firms appear to be using target costing. An example of Leno's problem is typified by item no. 8976, which has the following unit-cost characteristics: The going market price for an identical product of comparable quality is $490, which is significantly below what Leno is charging. Problem 15-41 Part 5 5. Suppose that by previous cost-cutting drives, costs had already been "pared to the bone" on item no. 8976. What might Leno be orced to do with its markup on cost to remain competitive? By how much? (Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your percentage answer to 2 decimal places (i.e., .1234 should be entered as 12.34).) Required information Problem 15-41 Cost-Plus Pricing vs. Target Costing (LO 15-1, 15-3, 15-5, 15-6, 15-8) [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.] For many years, Leno Corporation has used a straightforward cost-plus pricing system, marking its goods up approximately 25 percent of total cost. The company has been profitable; however, it has recently lost considerable business to foreign competitors that have become very aggressive in the marketplace. These firms appear to be using target costing. An example of Leno's problem is typified by item no. 8976, which has the following unit-cost characteristics: The going market price for an identical product of comparable quality is $490, which is significantly below what Leno is charging. Problem 15-41 Part 6 6. In many industries, prices are the result of an interaction between market forces and costs. True or False Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


