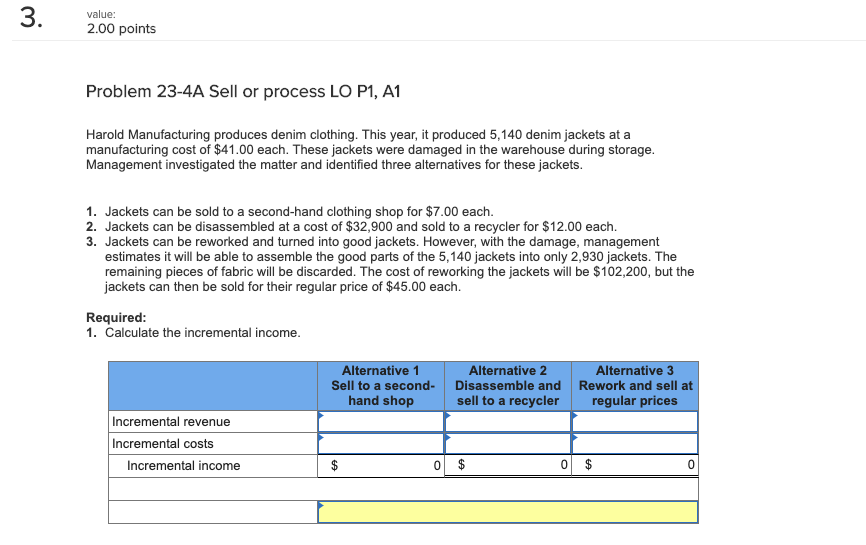
Problem 23-4A Sell or process LO P1, A1
| Harold Manufacturing produces denim clothing. This year, it produced 5,140 denim jackets at a manufacturing cost of $41.00 each. These jackets were damaged in the warehouse during storage. Management investigated the matter and identified three alternatives for these jackets. |
| 1. | Jackets can be sold to a second-hand clothing shop for $7.00 each. |
| 2. | Jackets can be disassembled at a cost of $32,900 and sold to a recycler for $12.00 each. |
| 3. | Jackets can be reworked and turned into good jackets. However, with the damage, management estimates it will be able to assemble the good parts of the 5,140 jackets into only 2,930 jackets. The remaining pieces of fabric will be discarded. The cost of reworking the jackets will be $102,200, but the jackets can then be sold for their regular price of $45.00 each. |
| Required: |
| 1. | Calculate the incremental income. |
Problem 23-5A Analysis of sales mix strategies LO A1
| Edgerron Company is able to produce two products, G and B, with the same machine in its factory. The following information is available. |
| | Product G | Product B |
| Selling price per unit | | | $ | 210 | | | | | $ | 240 | | |
| Variable costs per unit | | | | 90 | | | | | | 144 | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Contribution margin per unit | | | $ | 120 | | | | | $ | 96 | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Machine hours to produce 1 unit | | 0.4 | hours | | | | 1.0 | hours | | |
| Maximum unit sales per month | | 650 | units | | | | 250 | units | | |
| |
| The company presently operates the machine for a single eight-hour shift for 22 working days each month. Management is thinking about operating the machine for two shifts, which will increase its productivity by another eight hours per day for 22 days per month. This change would require $12,000 additional fixed costs per month. (Round hours per unit answers to 1 decimal place. Enter operating losses, if any, as negative values.)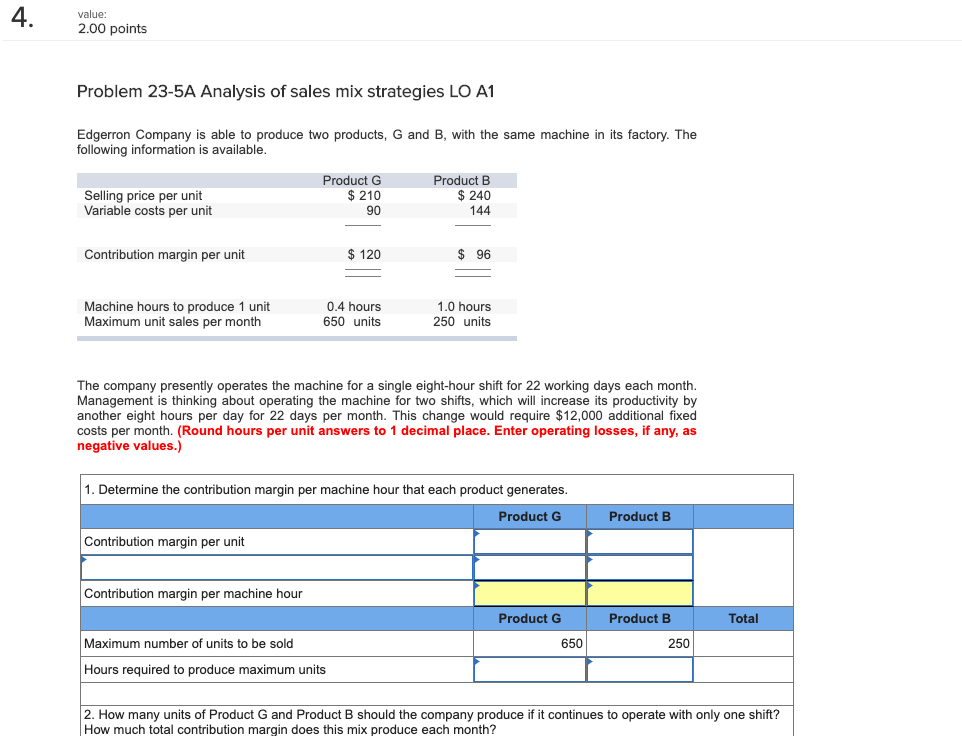 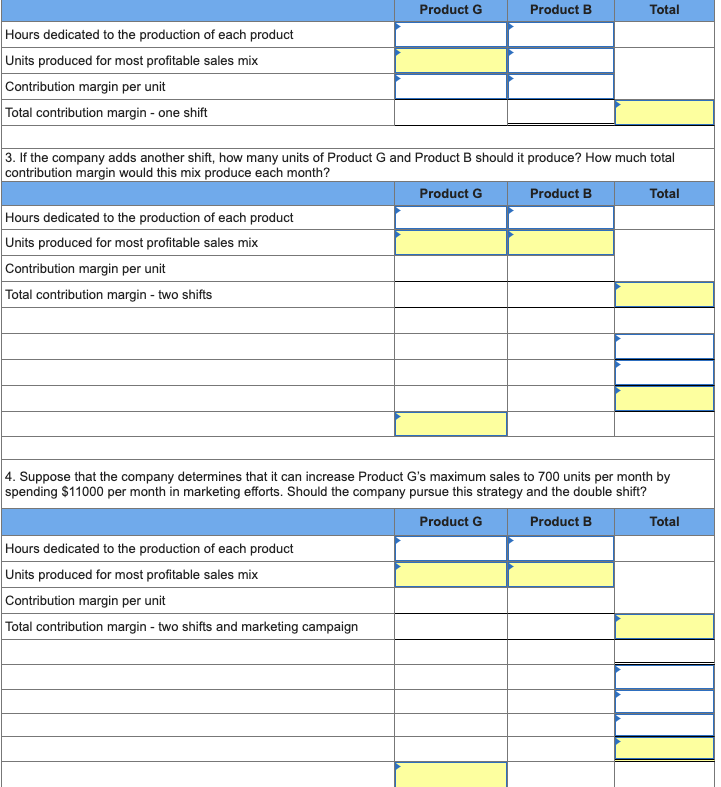 |
3. value: 2.00 points Problem 23-4A Sell or process LO P1, A1 Harold Manufacturing produces denim clothing. This year, it produced 5,140 denim jackets at a manufacturing cost of $41.00 each. These jackets were damaged in the warehouse during storage. Management investigated the matter and identified three alternatives for these jackets. 1. Jackets can be sold to a second-hand clothing shop for $7.00 each. 2. Jackets can be disassembled at a cost of $32,900 and sold to a recycler for $12.00 each. 3. Jackets can be reworked and turned into good jackets. However, with the damage, management estimates it will be able to assemble the good parts of the 5,140 jackets into only 2,930 jackets. The remaining pieces of fabric will be discarded. The cost of reworking the jackets will be $102,200, but the jackets can then be sold for their regular price of $45.00 each. Required: 1. Calculate the incremental income. Alternative 1 Alternative 2 Alternative 3 Sell to a second- Disassemble and Rework and sell at hand shop sell to a recycler regular prices Incremental revenue Incremental costs Incremental income $ 0 $ 0 $ 4. value: 2.00 points Problem 23-5A Analysis of sales mix strategies LO A1 Edgerron Company is able to produce two products, G and B, with the same machine in its factory. The following information is available. Selling price per unit Variable costs per unit Product G $ 210 90 Product B $ 240 144 Contribution margin per unit $ 120 $ 96 Machine hours to produce 1 unit Maximum unit sales per month 0.4 hours 650 units 1.0 hours 250 units The company presently operates the machine for a single eight-hour shift for 22 working days each month. Management is thinking about operating the machine for two shifts, which will increase its productivity by another eight hours per day for 22 days per month. This change would require $12,000 additional fixed costs per month. (Round hours per unit answers to 1 decimal place. Enter operating losses, if any, as negative values.) 1. Determine the contribution margin per machine hour that each product generates. Product G Contribution margin per unit Product B Contribution margin per machine hour Product G Product B Total 650 250 Maximum number of units to be sold Hours required to produce maximum units 2. How many units of Product G and Product B should the company produce if it continues to operate with only one shift? How much total contribution margin does this mix produce each month? Product G Product B Total Hours dedicated to the production of each product Units produced for most profitable sales mix Contribution margin per unit Total contribution margin-one shift 3. If the company adds another shift, how many units of Product G and Product B should it produce? How much total contribution margin would this mix produce each month? Product G Product B Total Hours dedicated to the production of each product Units produced for most profitable sales mix Contribution margin per unit Total contribution margin-two shifts 4. Suppose that the company determines that it can increase Product G's maximum sales to 700 units per month by spending $11000 per month in marketing efforts. Should the company pursue this strategy and the double shift? Product G Product B Total Hours dedicated to the production of each product Units produced for most profitable sales mix Contribution margin per unit Total contribution margin-two shifts and marketing campaign









