Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Problem 3. Heat exchange in a blood warmer You are asked to design a blood warmer to be used during the transfusion of blood
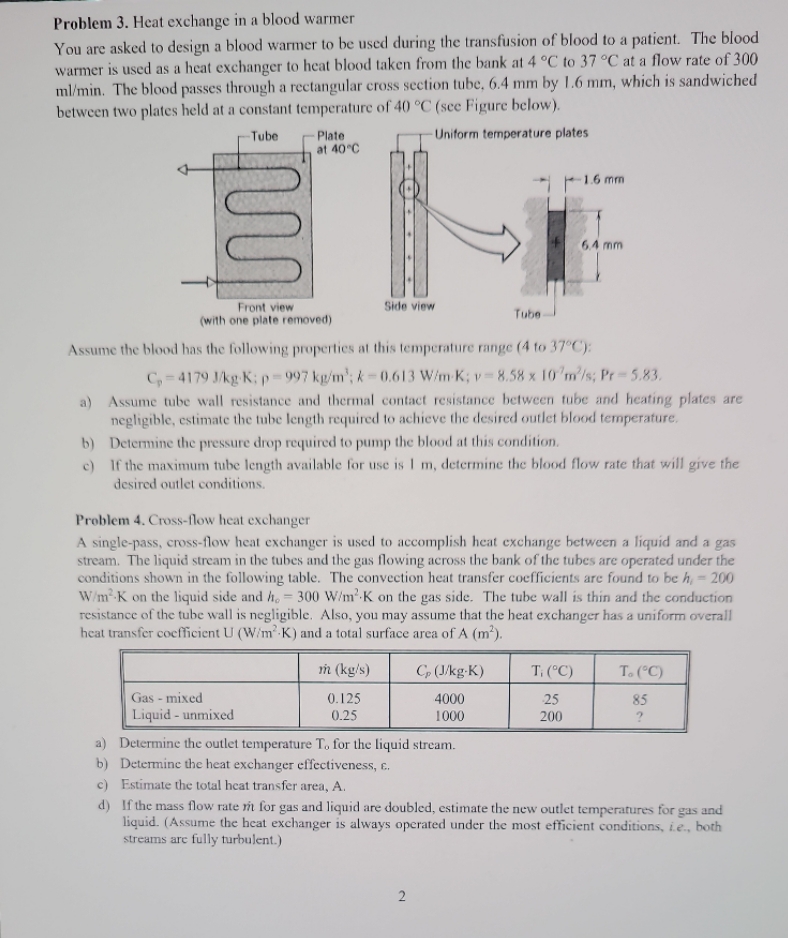
Problem 3. Heat exchange in a blood warmer You are asked to design a blood warmer to be used during the transfusion of blood to a patient. The blood warmer is used as a heat exchanger to heat blood taken from the bank at 4 C to 37 C at a flow rate of 300 ml/min. The blood passes through a rectangular cross section tube, 6.4 mm by 1.6 mm, which is sandwiched between two plates held at a constant temperature of 40 C (see Figure below). Plate Tube at 40C Uniform temperature plates 1.6 mm 6.4 mm Front view (with one plate removed) Side view Tube- Assume the blood has the following properties at this temperature range (4 to 37C): C-4179 J/kg K; p=997 kg/m; k-0.613 W/m-K; v 8.58 x 10 m/s; Pr-5.83. a) Assume tube wall resistance and thermal contact resistance between tube and heating plates are negligible, estimate the tube length required to achieve the desired outlet blood temperature. b) Determine the pressure drop required to pump the blood at this condition. c) If the maximum tube length available for use is 1 m, determine the blood flow rate that will give the desired outlet conditions. Problem 4. Cross-flow heat exchanger A single-pass, cross-flow heat exchanger is used to accomplish heat exchange between a liquid and a gas stream. The liquid stream in the tubes and the gas flowing across the bank of the tubes are operated under the conditions shown in the following table. The convection heat transfer coefficients are found to be h,- 200 W/mK on the liquid side and h. 300 W/mK on the gas side. The tube wall is thin and the conduction resistance of the tube wall is negligible. Also, you may assume that the heat exchanger has a uniform overall heat transfer coefficient U (W/mK) and a total surface area of A (m). = Gas - mixed Liquid - unmixed m (kg/s) 0.125 0.25 Cp (J/kg-K) T: (C) T. (C) 4000 25 85 1000 200 ? a) Determine the outlet temperature To for the liquid stream. b) Determine the heat exchanger effectiveness, c. c) Estimate the total heat transfer area, A. d) If the mass flow rate m for gas and liquid are doubled, estimate the new outlet temperatures for gas and liquid. (Assume the heat exchanger is always operated under the most efficient conditions, ie., both streams are fully turbulent.) 2
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


