Question
Problem 4-23 (Algorithmic) EZ-Windows, Inc., manufactures replacement windows for the home remodeling business. In January, the company produced 15,500 windows and ended the month with
Problem 4-23 (Algorithmic)
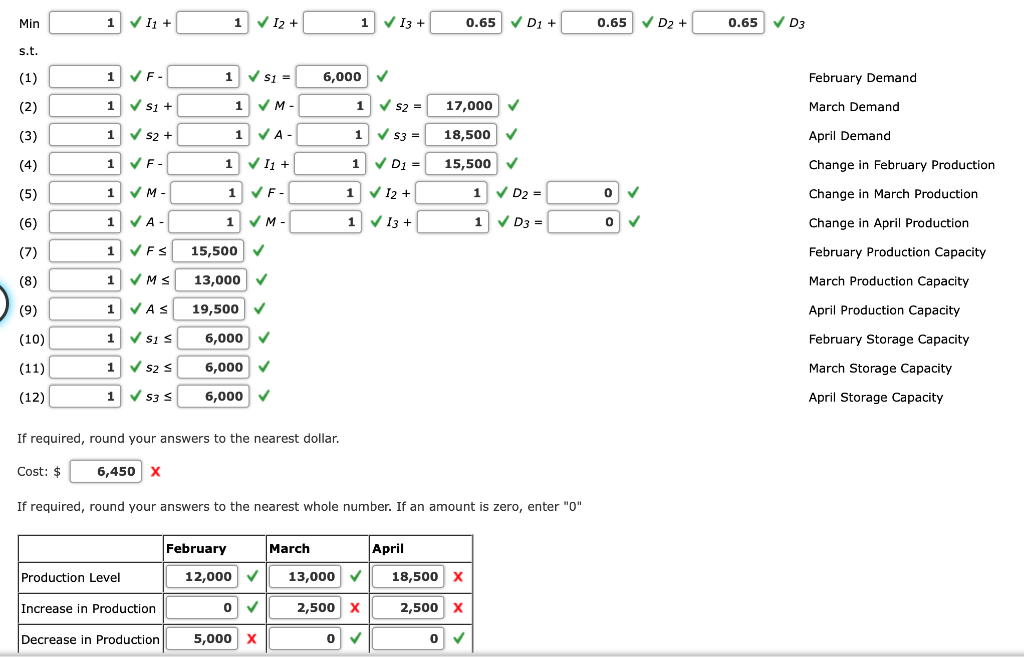
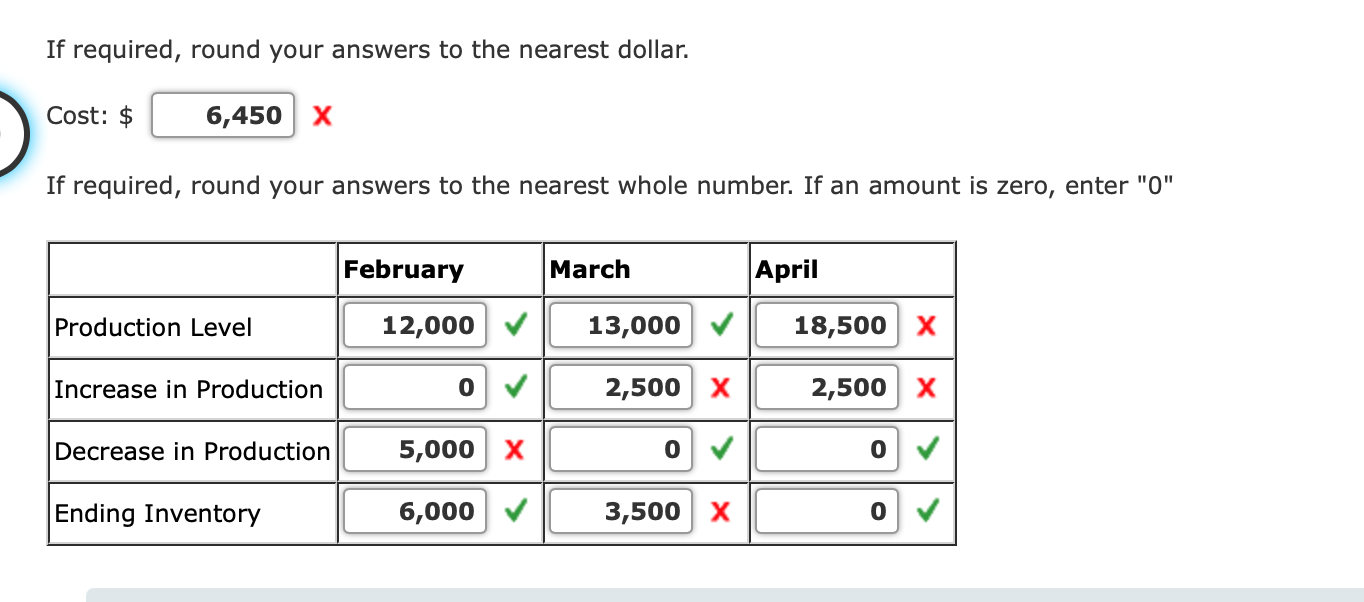
EZ-Windows, Inc., manufactures replacement windows for the home remodeling business. In January, the company produced 15,500 windows and ended the month with 9,500 windows in inventory. EZ-Windows management team would like to develop a production schedule for the next three months. A smooth production schedule is obviously desirable because it maintains the current workforce and provides a similar month-to-month operation. However, given the sales forecasts, the production capacities, and the storage capabilities as shown, the management team does not think a smooth production schedule with the same production quantity each month is possible.
| February | March | April | |
| Sales forecast | 15,500 | 17,000 | 18,500 |
| Production capacity | 15,500 | 13,000 | 19,500 |
| Storage capacity | 6,000 | 6,000 | 6,000 |
The companys cost accounting department estimates that increasing production by one window from one month to the next will increase total costs by $1.00 for each unit increase in the production level. In addition, decreasing production by one unit from one month to the next will increase total costs by $0.65 for each unit decrease in the production level. Ignoring production and inventory carrying costs, formulate and solve a linear programming model that will minimize the cost of changing production levels while still satisfying the monthly sales forecasts. If required, round your answers to two decimal places. If an amount is zero, enter "0".
Let:
F = number of windows manufactured in February
M = number of windows manufactured in March
A = number of windows manufactured in April
Im = increase in production level necessary during month m
Dm = decrease in production level necessary during month m
sm = ending inventory in month m
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


