Problem 4-3 (LO 2) 70%, equity, beginning and ending inventory, subsidiary seller. Refer to the preceding facts for Packards acquisition of Stude common stock. On Jan- uary 1, 2016, Packard held merchandise acquired from Stude for $10,000. This beginning inventory had an applicable gross profit of 25%. During 2016, Stude sold $40,000 worth of merchandise to Packard. Packard held $6,000 of this merchandise at December 31, 2016. This ending inventory had an applicable gross profit of 30%. Packard owed Stude $11,000 on December 31 as a result of these intercompany sales. 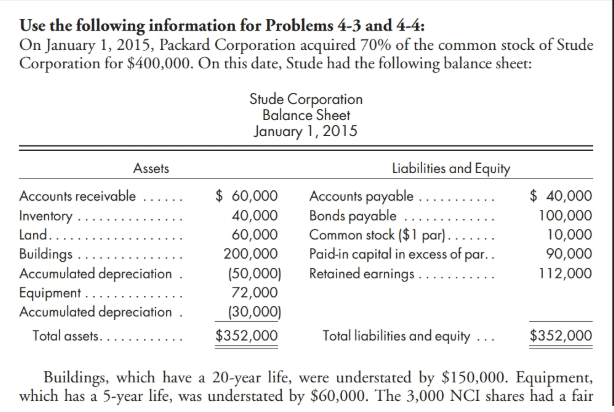
How to prepare the cost method worksheet? Use the form down there.
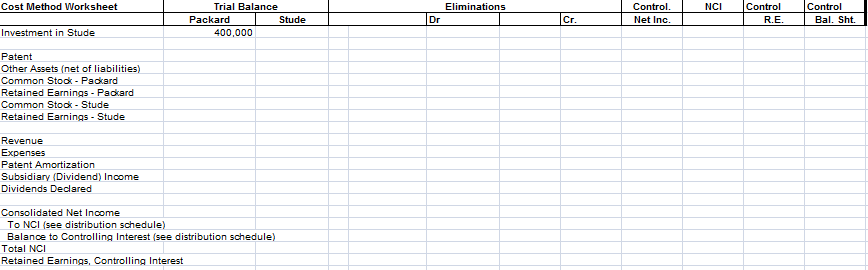
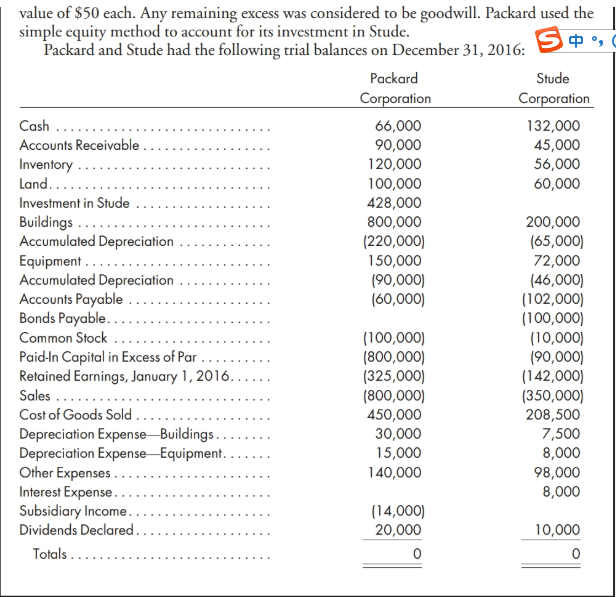
Use the following information for Problems 4-3 and 4-4: On January 1, 2015, Packard Corporation acquired 70% of the common stock of Stude Corporation for $400,000. On this date, Stude had the following balance sheet: Stude Corporation Balance Sheet January 1, 2015 Assets Accounts receivable Inventory ............... Land................... Buildings .............. Accumulated depreciation Equipment.. Accumulated depreciation Total assets............ $ 60,000 40,000 60,000 200,000 (50,000) 72,000 (30,000) $352,000 Liabilities and Equity Accounts payable ........... Bonds payable ............. Common stock ($ 1 par)....... Paid-in capital in excess of par.. Retained earnings ........... $ 40,000 100,000 10,000 90,000 112,000 Total liabilities and equity ... $352,000 Buildings, which have a 20-year life, were understated by $150,000. Equipment, which has a 5-year life, was understated by $60,000. The 3,000 NCI shares had a fair Stude value of $50 each. Any remaining excess was considered to be goodwill. Packard used the simple equity method to account for its investment in Stude. Packard and Stude had the following trial balances on December 31, 2016: Packard Corporation Corporation Cash ......... 66,000 132,000 Accounts Receivable ...... 90,000 45,000 Inventory 120,000 56,000 Land................... 100,000 60,000 Investment in Stude ....... 428,000 Buildings .............. 800,000 200,000 Accumulated Depreciation (220,000) (65,000) Equipment. 150,000 72,000 Accumulated Depreciation 190,000) (46,000) Accounts Payable (60,000) (102,000) Bonds Payable. (100,000) Common Stock (100,000) (10,000) Paid-In Capital in Excess of Par.. (800,000) 190,000) Retained Earnings, January 1, 2016.... (325,000) (142,000) (800,000) (350,000) Cost of Goods Sold ...... 450,000 208,500 Depreciation Expense Buildings........ 30,000 7,500 Depreciation Expense-Equipment..... 15,000 8,000 Other Expenses......... 140,000 98,000 Interest Expense.......... 8,000 Subsidiary Income......... (14,000) Dividends Declared...... 20,000 10,000 Totals Sales Cost Method Worksheet NCI Trial Balance Packard Stude 400,000 Eliminations Inr Control. Net Inc. Control R.E. Control Bal. Sht. Cr. Investment in Stude Patent Other Assets (net of liabilities) Common Stock - Packard Retained Earnings - Packard Common Stock - Stude Retained Earnings - Stude Revenue Expenses Patent Amortization Subsidiary (Dividend) Income Dividends Declared Consolidated Net Income To NCI (see distribution schedule) Balance to Controlling Interest (see distribution schedule) Total NCI Retained Earnings, Controlling Interest Use the following information for Problems 4-3 and 4-4: On January 1, 2015, Packard Corporation acquired 70% of the common stock of Stude Corporation for $400,000. On this date, Stude had the following balance sheet: Stude Corporation Balance Sheet January 1, 2015 Assets Accounts receivable Inventory ............... Land................... Buildings .............. Accumulated depreciation Equipment.. Accumulated depreciation Total assets............ $ 60,000 40,000 60,000 200,000 (50,000) 72,000 (30,000) $352,000 Liabilities and Equity Accounts payable ........... Bonds payable ............. Common stock ($ 1 par)....... Paid-in capital in excess of par.. Retained earnings ........... $ 40,000 100,000 10,000 90,000 112,000 Total liabilities and equity ... $352,000 Buildings, which have a 20-year life, were understated by $150,000. Equipment, which has a 5-year life, was understated by $60,000. The 3,000 NCI shares had a fair Stude value of $50 each. Any remaining excess was considered to be goodwill. Packard used the simple equity method to account for its investment in Stude. Packard and Stude had the following trial balances on December 31, 2016: Packard Corporation Corporation Cash ......... 66,000 132,000 Accounts Receivable ...... 90,000 45,000 Inventory 120,000 56,000 Land................... 100,000 60,000 Investment in Stude ....... 428,000 Buildings .............. 800,000 200,000 Accumulated Depreciation (220,000) (65,000) Equipment. 150,000 72,000 Accumulated Depreciation 190,000) (46,000) Accounts Payable (60,000) (102,000) Bonds Payable. (100,000) Common Stock (100,000) (10,000) Paid-In Capital in Excess of Par.. (800,000) 190,000) Retained Earnings, January 1, 2016.... (325,000) (142,000) (800,000) (350,000) Cost of Goods Sold ...... 450,000 208,500 Depreciation Expense Buildings........ 30,000 7,500 Depreciation Expense-Equipment..... 15,000 8,000 Other Expenses......... 140,000 98,000 Interest Expense.......... 8,000 Subsidiary Income......... (14,000) Dividends Declared...... 20,000 10,000 Totals Sales Cost Method Worksheet NCI Trial Balance Packard Stude 400,000 Eliminations Inr Control. Net Inc. Control R.E. Control Bal. Sht. Cr. Investment in Stude Patent Other Assets (net of liabilities) Common Stock - Packard Retained Earnings - Packard Common Stock - Stude Retained Earnings - Stude Revenue Expenses Patent Amortization Subsidiary (Dividend) Income Dividends Declared Consolidated Net Income To NCI (see distribution schedule) Balance to Controlling Interest (see distribution schedule) Total NCI Retained Earnings, Controlling Interest









