Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Problem 4.35E Converging duct flow is modeled by the steady, two-dimensional velocity field of Prob. 4-16. For the case in which U0 = 3.56
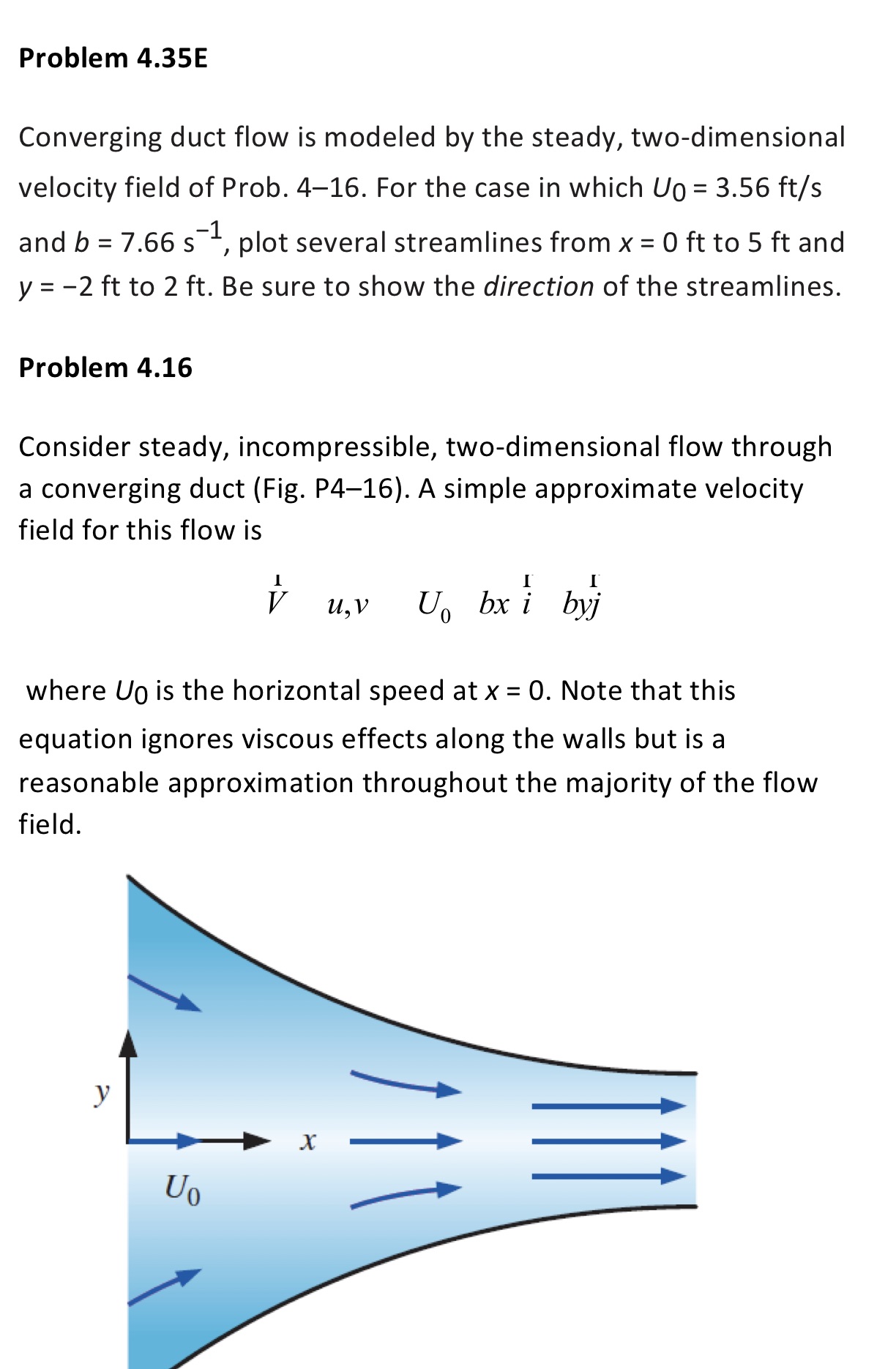
Problem 4.35E Converging duct flow is modeled by the steady, two-dimensional velocity field of Prob. 4-16. For the case in which U0 = 3.56 ft/s -1 ' and b = 7.66 s plot several streamlines from x = 0 ft to 5 ft and y = -2 ft to 2 ft. Be sure to show the direction of the streamlines. Problem 4.16 Consider steady, incompressible, two-dimensional flow through a converging duct (Fig. P4-16). A simple approximate velocity field for this flow is I V u, V U bx i byj where Uo is the horizontal speed at x = 0. Note that this equation ignores viscous effects along the walls but is a reasonable approximation throughout the majority of the flow field. y Uo X
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


