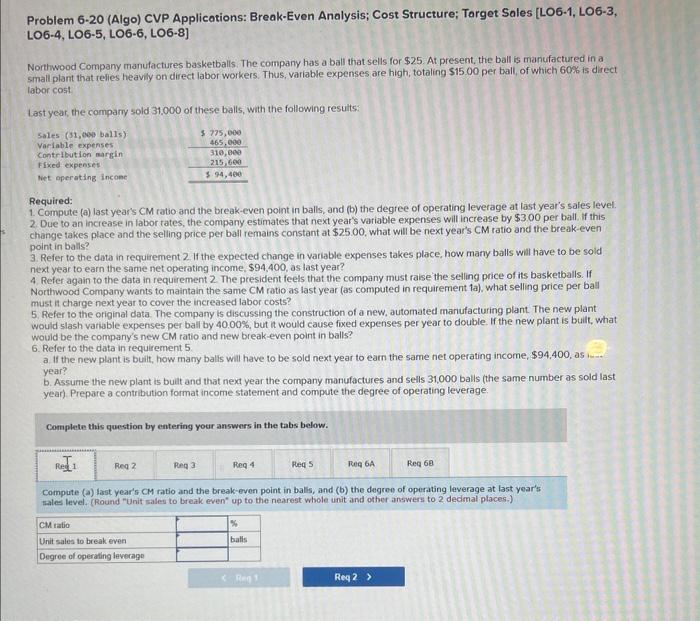
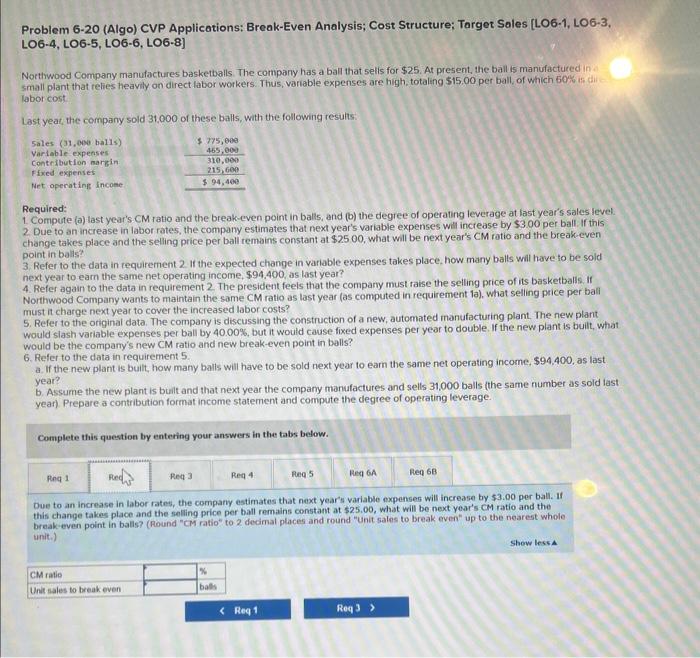
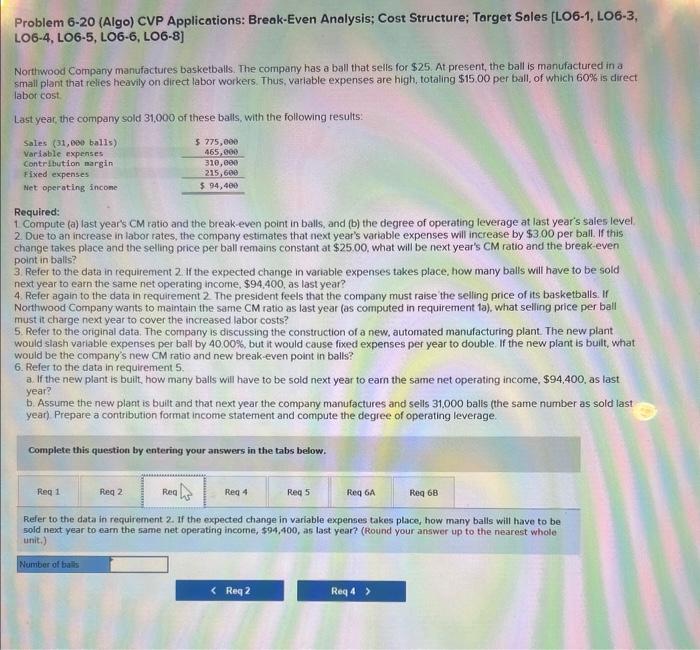
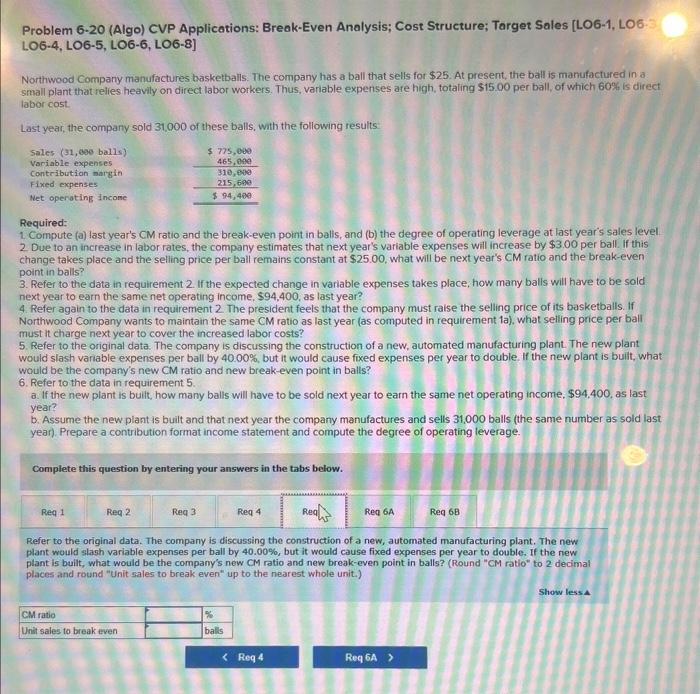
Problem 6-20 (Algo) CVP Applications: Break-Even Analysis; Cost Structure; Target Sales [LO6-1, LO6-3, LOG-4, LO6-5, LOG-6, LOG-8] Northwood Company manufactures basketbalis. The company has a ball that sells for $25. At present, the ball is manufactured in a small plant that relies heavify on direct labor workers. Thus, variable expenses are high, totaling $15.00 per ball, of which 60% is direct labor cost Last year, the company sold 31,000 of these balls, with the following results: Required: 1. Compute (a) last year's CM ratio and the break-even point in balls, and (b) the degree of operating leverage at last year's sales level. 2 Due to an increase in labor rates, the company estimates that next year's variable expenses will increase by $3.00 per ball if this change takes place and the selling price per ball remains constant at $25.00, what will be next year's CM ratio and the break-even point in balls? 3. Refer to the data in requirement 2 . If the expected change in variable expenses takes place, how many balls will have to be soid next year to earn the same net operating income, $94,400, as last year? 4. Refer again to the data in requirement 2 . The president feels that the company must raise the selling price of its basketballs. If Northwocd Company wants to maintain the same CM ratio as last year (as computed in requirement 1a), what selling price per ball must it charge next year to cover the increased labor costs? 5. Refer to the original data. The company is discussing the construction of a new, automated manufacturing plant. The new plant would slash variable expenses per ball by 40.00%, but it would cause fixed expenses per year to double. If the new plant is built, what would be the company's new CM ratio and new break even point in balls? 6. Refer to the data in requirement 5 a If the new plant is buit, how many balls will have to be sold next year to earn the same net operating income, $94.400, as is... year? b. Assume the new plant is bult and that next year the company manufactures and sells 31,000 balls ithe same number as sold last year). Prepare a contribution format income statement and compute the degree of operating leverage. Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Compute (a) last year's CM ratio and the break-even point in balis, and (b) the degren of operating leverage at last year's sales level. (Round "Enit sales to break even" up to the nearest whole unit and other answers to 2 decimal places,) Problem 6-20 (Algo) CVP Applications: Break-Even Analysis; Cost Structure; Target Sales [LO6-1, LO6-3, LO6-4, LOG-5, LOG-6, LOG-8] Northwood Company manufactures basketballs. The company has a bal that selis for $25, At present, the ball is manufactured in: small plant that relies heavily on direct labor workers. Thus, variable expenses are high, totaling $15,00 per ball, of which 50% is Iabor cost Last year, the company sold 31,000 of these balls, with the following results Required: 1 Compute (a) last year's CM ratio and the break-even point in balss, and (b) the degree of operating leverage at last year's sales level. 2 Due to an increase in labor rates, the company estimates that next year's variable expenses will increase by 53.00 per ball. If this change takes piace and the selling price per ball remains constant at $2500, what will be next year's CM ratio and the break-even point in balls? 3. Refer to the data in requirement 2 . If the expected change in variable expenses takes place, how many balls will have to be sold next year to eam the same net operating income, $94.400, as last year? 4. Refer again to the data in requirement 2 . The president feels that the compary must raise the selling price of its basketballs. If Northwood Company wants to maintain the same CM ratio as last year (as computed in requirement la), what selling price per bali must it charge next year to cover the increased labor costs? 5. Refer to the original data. The company is discussing the construction of a new, automated manufacturing plant. The new plant Would slash variable expenses per ball by 40.00%, but it would cause fixed expenses per year to double. If the new plant is built, what would be the company's new CM ratio and new break-even point in balls? 6. Refer to the data in requirement 5. a. If the new plant is bult, how many balls will have to be sold next year to earn the same net operating income, 594,400 , as last year? b. Assume the new plant is buit and that next year the compary manufactures and sells 31,000 balls (the same number as sold last year) Prepare a contribution format income statement and compute the degree of operating leverage. Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Due to an increase in labor rates, the company estimates that next year's variable oxpensen will increase by $3.00 per ball. If this change takes place and the folling price per ball remains constant at $25.00, what will be next year's cM ratio and the breakeeven point in balis? (Round "CM ratio" to 2 decimal places and round "Unit sales to break even" up to the nearest whole unit.) Problem 6-20 (Algo) CVP Applications: Break-Even Analysis; Cost Structure; Target Sales [LO6-1, LO6-3, LOG-4, LOG-5, LOG-6, LOG-8] Northwood Company manufactures basketballs. The company has a ball that sells for $25. At present, the ball is manufactured in a small plant that relies heavily on direct labor workers. Thus, variable expenses are high, totaling $15.00 per ball, of which 60%6 is direct laboricost. Last year, the company sold 31,000 of these balls, with the following results: Required: 1 Compute (a) last year's CM ratio and the break-even point in balls, and (b) the degree of operating leverage at last year's sales level 2 Due to an increase in labor rates, the company estimates that next year's variable expenses will increase by $3.00 per ball. If this change takes place and the selling price per ball remains constant at $25.00, what will be next year's CM ratio and the break-even point in balls? 3. Refer to the data in requirement 2 . If the expected change in variable expenses takes place, how many balls will have to be sold next year to eam the same net operating income, $94,400, as last year? 4. Refer again to the data in requirement 2 . The president feels that the company must raise the selling price of its basketballs. If Northwood Company wants to maintain the same CM ratio as last year (as computed in requirement 1a ), what selling price per ball must it charge next year to cover the increased labor costs? 5. Refer to the original data. The company is discussing the construction of a new, automated manufacturing plant. The new plant would slash variable expenses per ball by 40.00%, but it would cause fixed expenses per year to double. If the new plant is buit, what would be the company's new CM ratio and new break-even point in balls? 6. Refer to the data in requirement 5 . a. If the new plant is built how many balls will have to be sold next year to earn the same net operating income, $94,400, as last year? b. Assume the new plant is built and that next year the company manufactures and sells 31.000 balls (the same number as sold last year) Prepare a contribution format income statement and compute the degree of operating leverage. Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Refer to the data in requirement 2. If the expected change in variable expenses takes place, how many balls will have to be sold next year to earn the same net operating income, $94,400, ab last year? (Round your answer up to the nearest whole unit.) Problem 6-20 (Algo) CVP Applications: Break-Even Analysis; Cost Structure; Target Sales [LO6-1, LO6-3 LOG-4, LOG-5, LOG-6, LOG-8] Northwood Company manufactures basketballs. The company has a ball that sells for $25. At present, the ball is manufactured in a small plant that relies heavily on direct labor workers. Thus, variable expenses are high, totaling $15.00 per ball, of which 60% is direct labor cost. Last year, the company sold 31,000 of these balls, with the following results: Required: 1. Compute (a) last year's CM ratio and the break-even point in balls, and (b) the degree of operating leverage at last year's sales level. 2. Due to an increase in labor rates, the company estimates that next year's variable expenses will increase by $3.00 per ball. If this change takes place and the selling price per ball remains constant at $25.00, what will be next year's CM ratio and the break-even point in balls? 3. Refer to the data in requirement 2 . If the expected change in variable expenses takes place, how many balls will have to be sold next year to earn the same net operating income, $94,400, as last year? 4. Refer again to the data in requirement 2 . The president feels that the company must raise the selling price of its basketballs. If Northwood Company wants to maintain the same CM ratio as last year (as computed in requirement 1a), what selling price per ball must it charge next year to cover the increased labor costs? 5. Refer to the original data. The company is discussing the construction of a new, automated manufacturing plant. The new plant would siash variable expenses per ball by 40.00%, but it would cause fixed expenses per year to double. If the new plant is built, what would be the company's new CM ratio and new break-even point in balls? 6. Refer to the data in requirement 5 . a. If the new plant is built, how many balls will have to be sold next year to earn the same net operating income, $94,400, as last year? b. Assume the new plaat is built and that next year the company manufactures and sells 31,000 balls (the same number as sold last year). Prepare a contribution format income statement and compute the degree of operating leverage. Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Refer again to the data in requirement 2. The president feels that the company must raise the selling price of its basketballs. If Northwood Company wants to maintain the same CM ratio as last year (as computed in requirement la), what selling price per ball must it charge next year to cover the increased labor costs? (Round your answer to 2 decimal places.) Problem 6-20 (Algo) CVP Applications: Break-Even Analysis; Cost Structure; Target Sales [LO6-1, LO6LO6-4, LOG-5, LOG-6, LOG-8] Northwood Compary manufactures basketballs. The company has a ball that sells for $25. At present, the ball is manufactured in a small plant that relies heavily on direct labor workers. Thus, variable expenses are high, totaling $15.00 per ball, of which 60 \% is direct labor cost: Last year, the company sold 31,000 of these balls, with the following results Required: 1. Compute (a) last year's CM ratio and the break-even point in balis, and (b) the degree of operating leverage at last year's sales level 2 Due to an increase in labor rates, the company estimates that next year's variable expenses will increase by $3.00 per ball. If this change takes place and the selling price per ball remains constant at $25.00, what will be next year's CM ratio and the break-even point in balls? 3. Refer to the data in requirement 2 . If the expected change in variable expenses takes place, how many balls will have to be sold next year to earn the same net operating income, $94,400, as last year? 4. Refer again to the data in requirement 2 The president feels that the company must raise the selling price of its basketballs. If Northwood Company wants to maintain the same CM ratio as last year (as computed in requirement 1a ), what selling price per ball must it charge next year to cover the increased labor costs? 5. Refer to the original data. The company is discussing the construction of a new, automated manufacturing plant. The new plant would slash variable expenses per ball by 4000%, but it would cause fixed expenses per year to double. If the new plant is built, what would be the company's new CM ratio and new break-even point in balls? 6. Refer to the data in requirement 5 . a. If the new plant is buit, how many balis will have to be sold next year to earn the same net operating income, $94,400, as last year? b. Assume the new plant is buil and that next year the company manufactures and sells 31,000 balls (the same number as sold last. year). Prepare a contribution format income statement and compute the degree of operating leverage. Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Refer to the original data. The company is discussing the construction of a new, automated manufacturing plant. The new plant would slagh variable expenses per ball by 40.00%, but it would cause fixed expenses per year to double. If the new plant is built, what would be the company's new CM ratio and new break-even point in balls? (Round "CM ratio" to 2 decimal places and round "Unit sales to break even" up to the nearest whole unit.) Problem 6-20 (Algo) CVP Applications: Break-Even Analysis; Cost Structure; Target Sales [LO6-1, LO6-3. LOG-4, LOG-5, LOG-6, LOG-8] Northwood Company manufactures basketballs. The company has a ball that sells for $25. At present, the ball is manufactured in a small plant that relies heavily on direct labor workers. Thus, variable expenses are high, totaling $15. 00 per ball, of which 60 \% is direct kabor cost Last year, the company sold 31,000 of these balls, with the following results: Required: 1. Compute (a) last year's CM fatio and the break-even point in balls, and (b) the degree of operating leverage at last year's sales level 2. Due to an increase in labor rates, the company estimates that next year's variable expenses will increase by $3.00 per ball, If this change takes place and the seling price per ball remains constant at $25.00, what will be next year's CM ratio and the break-even point in balls? 3. Refer to the data in requirement 2 . If the expected change in variable expenses takes place, how many balls will have to be sold next year to earn the same net operating income, $94.400, as last year? 4. Refer again to the data in requirement 2 . The president fecls that the company must raise the selling price of its basketballs. If Northwood Company wants to maintain the same CM ratio as last year (as computed in requirement la), what selling price per ball must it charge next year to cover the increased labor costs? 5. Refer to the original data. The company is discussing the construction of a new, automated manufacturing plant The new plant would slash variable expenses per ball by 40.00%, but it would cause fixed expenses per year to double. If the new plant is buit, what would be the company's new CM ratio and new break-even point in balls? 6. Refer to the data in requirement 5 . - If the new plant is buit, how many balls will have to be sold next year to earn the same net operating income, $94,400, as last year? b. Assume the new plant is built and that next year the company manufactures and sells 31,000 balls (the same number as sold last year). Prepare a contribution format income statement and compute the degree of operating leverage Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Refer to the data in requirement 5. If the new plant is built, how many balls will have to be sold next year to earn the same net operating income, $94,400, as last year? (Round your aniwer up to the nearest whole unit.) Problem 6-20 (Algo) CVP Applications: Break-Even Analysis; Cost Structure; Target Sales [LO6-1, LO6-3, LO6-4, LO6-5, LO6-6, LO6-8] Northwood Compary manufactures basketballs. The company has a balf that sells for $25, At present, the ball is manufactured in a small plant that relies heavily on direct labor workers Thus, variable expenses are high, totaling $15 o0 per ball, of which 60% is direct labor cost. Last yeat, the compary sold 31000 of these balls, with the following resuits: Required: 1. Compute (a) last year's CM ratio and the break-even point in balls, and (b) the degree of operating leverage at last year's sales level. 2. Due to an increase in labor rates, the company estimates that next year's variable expenses will increase by $3.00 per ball. If this change takes place and the selling price per ball remains constant at $25.00, what will be next year's CM ratio and the break-even point in baits? 3. Refer to the data in requirement 2 . If the expected change in variable expenses takes place, how many balls will have fo be sold next year to earn the same net operating income, $94,400, as last year? 4. Refer again to the data in requirement 2 . The president feels that the company must raise the selling price of its basketbalis. If Northwood Company wants to maintain the same CM ratio as last year (as computed in requirement 1a), what selling price per ball must it charge next year to cover the increased labor costs? 5. Refer to the original data. The company is discussing the construction of a new, automated manufacturing plant. The new plant would slash variable expenses per ball by 4000%, but it would cause foxed expenses per year to double. If the new piant is bult; what would be the company's new CM ratio and new break-even point in balls? 6. Refer to the data in requirement 5 . a. If the new plant is built, how many balls will have to be sold next year to earn the same net operating income, $94,400, as last year? b. Assume the new plant is built and that next year the compary manufactures and sells 31,000 bails (the same number as sold iast year). Prepare a contribution format income statement and compute the degree of operating leverage. Cornplete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Refer to the data in requirement 5 . Assume the new plant is bult and that next year the company manufactures and selis 31,000 balis (the same number as sold last year). Prepare a contribution format incomo statement and compute the degree of operating leverage. (Round "Degree of operating leverage" to 2 decimal places.)