
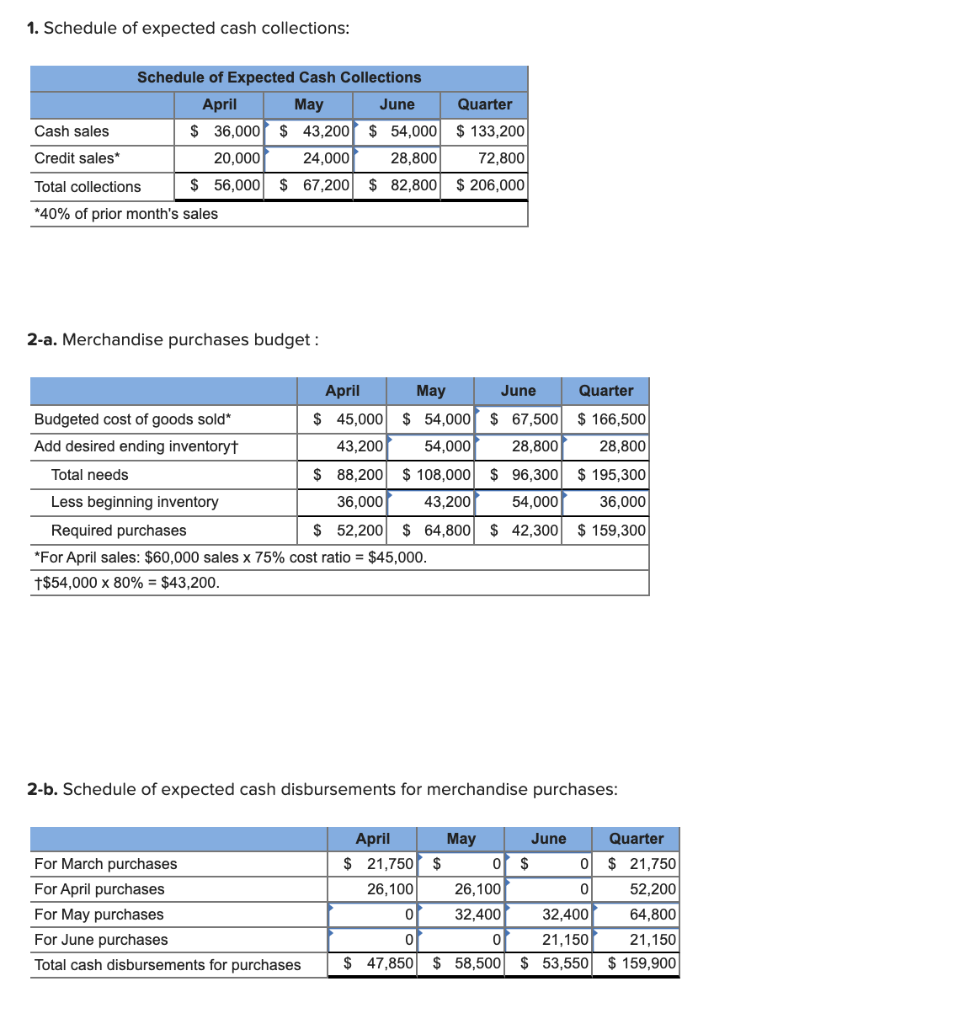
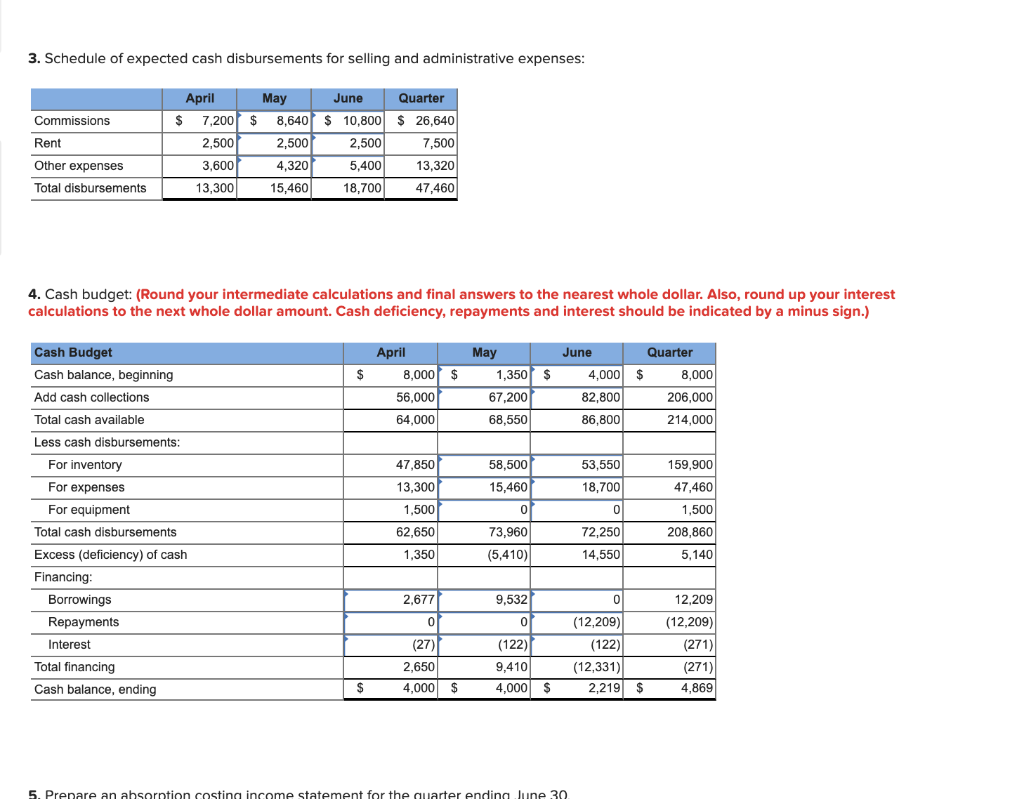
Problem 9-20 Completing a Master Budget (LO2] The following data relate to the operations of Soper Company, a wholesale distributor of consumer goods as of March 31: Cash Accounts receivable Inventory Building and equipment, net Accounts payable Common shares Retained earnings $ 8,000 20,000 36,000 120,000 21,750 150,000 12,250 a. The gross margin is 25% of sales. b. Actual and budgeted sales data are as follows: March (actual) April May June July $50,000 $ 60,000 $72,000 $ 90,000 $ 48,000 c. Sales are 60% for cash and 40% on credit. Credit sales are collected in the month following sale. The accounts receivable at March 31 are a result of March credit sales. d. Each month's ending inventory should equal 80% of the following month's budgeted cost of goods sold. e. One-half of a month's inventory purchases is paid for in the month of purchase; the other half is paid for in the following month. The accounts payable at March 31 are the result of March purchases of inventory. f. Monthly expenses are as follows: commissions, 12% of sales; rent, $2,500 per month; other expenses (excluding depreciation), 6% of sales. Assume that these expenses are paid monthly. Depreciation is $900 per month (includes depreciation on new assets). g. Equipment costing $1,500 will be purchased for cash in April. h. The company must maintain a minimum cash balance of $4,000. An open line of credit is available at a local bank. All borrowing is done at the beginning of a month, and all repayments are made at the end of a month. The monthly interest rate is 1%. Interest must be paid at the end of each month based on the total loans outstanding for that month. Required: Using the data above, complete the following statements and schedules for the second quarter: 1. Schedule of expected cash collections: Schedule of Expected Cash Collections April May June Quarter Cash sales $ 36,000 $ 43,200 $ 54,000 $ 133,200 Credit sales* 20,000 24,000| 28,800 72,800 Total collections $ 56,000 $ 67,200 $ 82,800 $ 206,000 *40% of prior month's sales 2-a. Merchandise purchases budget : April May June Budgeted cost of goods sold" $ 45,000 $ 54,000 $ 67,500 Add desired ending inventoryt 43,200 54,000 28,800 Total needs | $ 88,200 $ 108,000 $ 96,300 Less beginning inventory 36,000 43,200 54,000 Required purchases $ 52,200 $ 64,800 $ 42,300 *For April sales: $60,000 sales x 75% cost ratio = $45,000. +$54,000 x 80% = $43,200. Quarter $ 166,500 28,800 $ 195,300 36,000 $ 159,300 2-b. Schedule of expected cash disbursements for merchandise purchases: For March purchases For April purchases For May purchases For June purchases Total cash disbursements for purchases April $ 21,750 26,100 0 May $ 0 26,100 32,400 0 $ 58,500 June Quarter $ 0 $ 21,750 0 52,200 32,400 64,800 21.150 21,150 $ 53,550 $ 159,900 $ 47,850 3. Schedule of expected cash disbursements for selling and administrative expenses: May $ 8,640 Commissions Rent Other expenses Total disbursements April $ 7,200 2,5001 3,600 13,300 June $ 10,800 2,500 5,400 18,700 Quarter $ 26,640 7,500 13,320 47,460 4,320 15,460 4. Cash budget: (Round your intermediate calculations and final answers to the nearest whole dollar. Also, round up your interest calculations to the next whole dollar amount. Cash deficiency, repayments and interest should be indicated by a minus sign.) $ $ $ April 8,000 56,000 64,000 May 1,350 67,200 68,550 June 4,000 82,800 86,800 Quarter $ 8,000 206,000 214,000 Cash Budget Cash balance, beginning Add cash collections Total cash available Less cash disbursements: For inventory For expenses For equipment Total cash disbursements Excess (deficiency) of cash Financing: Borrowings Repayments Interest Total financing Cash balance, ending 47,850 13,300 1,500 62,650 1,350 58,500 15,460 0 73,960 (5,410) 53,550 18,700 0 72,250 14,550 159,900 47,460 1,500 208,860 5,140 2,677 of (27) 2,650 4,000 9,532 0p (122) 9,410 4,000 0 (12,209) (122) (12,331) 2,219 12,209 (12,209) (271) (271) 4,869 $ $ $ $ 5. Prenare an absorption costing income statement for the quarter ending June 30 5. Prepare an absorption costing income statement for the quarter ending June 30. SOPER COMPANY Income Statement For the Quarter Ended June 30 Sales Cost of goods sold: Operating expenses: $ 0 6. Prepare a balance sheet as of June 30. SOPER COMPANY Balance Sheet June 30 Assets Current assets: Total current assets 0 Total assets $ Liabilities and Stockholders' Equity Stockholders' equity: Total liabilities and stockholders' equity $










