Question
Problem Develop a Java application that provides a GUI that contains -a single-selection list box , LB1 -a second list box, LB2 -a label ----->
Problem
Develop a Java application that provides a GUI that contains
-a single-selection list box, LB1
-a second list box, LB2
-a label "----->" that indicates the direction of movement of items between the list boxes, namely, from LB1 to LB2
-a command button Exit with legend "Exit"
When your application begins it must do the following initialization
-Load LB1 with items shown in the Sample Program Dialogue. (Note The items contains the course numbers for undergraduate Computer Science courses, one course-number-string per file record).
-Empty (clear the contents of) LB2.
When your application is running it must respond to the following GUI events
-Double-left-clicking on an item in LB1 causes that item to be moved from LB1 to LB2. (Note A move copies the item from LB1 to LB2 then deletes the item from LB1.)
-Typing Shift+M after selecting exactly one item in LB1 causes the selected item to be moved from LB1 to LB2. Note Shift+M keyboard events must be ignored when no item is selected in LB1.
-Single-left-clicking the Exit command button causes the application to normally terminate.
PLEASE take screenshot of GUI when completefd
//---------------------------------------------------------
// Chapter #14, Problem #2
// Problem2.java
//---------------------------------------------------------
import javax.swing.*;
public class Problem2
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
GUI gui = new GUI();
// *NOTE* Dr. Hanna experimented with several other layout managers; perhaps you should too?!
// GUI2 gui = new GUI2(); // FlowLayout
// GUI3 gui = new GUI3(); // BorderLayout
// GUI4 gui = new GUI4(); // GridLayout
gui.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
gui.setSize(760,600);
gui.setVisible(true);
}
}
//---------------------------------------------------------
// Class GUI for Chapter #14, Problem #2
// GUI.java
//---------------------------------------------------------
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
import javax.swing.*;
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
//---------------------------------------------------------
public class GUI extends JFrame
//---------------------------------------------------------
{
private Font font = new Font("Courier",Font.PLAIN,12);
private DefaultListModel LB1List;
private JList LB1;
private DefaultListModel LB2List;
private JList LB2;
private JLabel arrow;
private JButton Exit;
//----------------------------------------------------
public GUI()
//----------------------------------------------------
{
super("Chapter #14, Problem #2 (absolute layout)");
// Use *NO* layout manager (absolute layout)
setLayout( null );
// LB1 list box
LB1List = new DefaultListModel();
LB1 = new JList(LB1List);
LB1.setSelectionMode(ListSelectionModel.SINGLE_SELECTION);
LB1.setBounds(10,30,200,500);
LB1.setFont(font);
Input records from text file "Problem2.in" and use each record as a single string to initialize
the contents of LB1. Hints (1) Study sequential file input in Section 17.4; and (2) use the
DefaultListModel method addElement().
Place LB1 into the GUI
Define a mouseClicked event handler to handle a double-left-click event for LB1. Note JList does not
provide any special event handling of multiple (2 or more) mouse clicks, so you have to provide
logic that distinguishes between one-click and double-click events. To handle a multi-click mouse
event, add a MouseListener. Hints Use (1) the MouseEvent method getClickCount(); (2) the
DefaultListModel methods getElementAt(), addElement(), and removeElementAt(); and (3) the JList
methods getSelectedIndex() and clearSelection().
Define keyTyped event handler to handle the typing of Shift+M event. Hints Use (1) theKeyEventmethod
getKeyChar(); (2) the DefaultListModel methods getElementAt(), addElement(), andremoveElementAt();
and (3) the JList methods getSelectedIndex() and clearSelection(). Note getSelectedIndex() returns -1
when no item is selected.
// "----->" label
arrow = new JLabel("----->");
Place arrow label into the GUI
// LB2 list box
LB2List = new DefaultListModel();
LB2 = new JList(LB2List);
LB2.setBounds(330,30,200,500);
LB2.setFont(font);
add(LB2);
// "Exit" command button
Exit = new JButton("Exit");
Exit.setBounds(540,510,100,20);
Exit.setFont(font);
// The event handler for the Exit command button (defined below) is coded as an anonymous inner class!
Exit.addActionListener
(
new ActionListener()
{
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent event)
{
System.exit(0);
}
}
);
add(Exit);
}
}
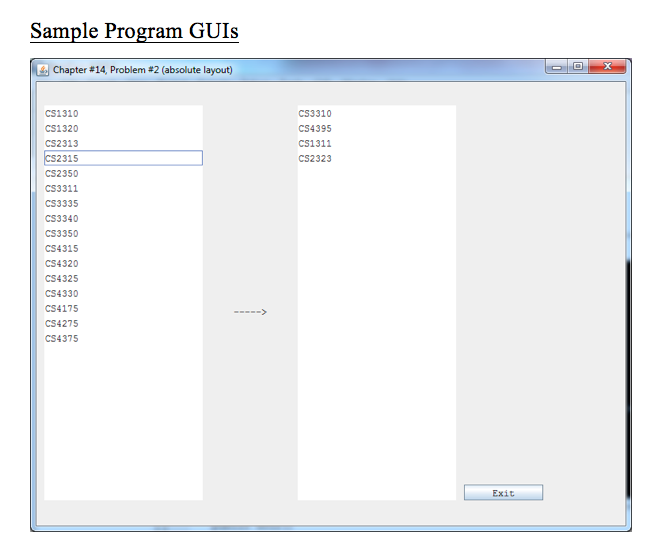
Sample Program GUIs Chapter #14, Problem #2 (absolute layout) CS1310 CS1320 CS2313 2315 CS2350 CS3311 CS3335 CS3340 CS3350 CS4315 CS4320 CS4325 CS4330 CS4175 CS4275 CS4375 CS3310 CS4395 CS1311 CS2323 ExitStep by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


