Problem One: Credit Analysis (8 points)
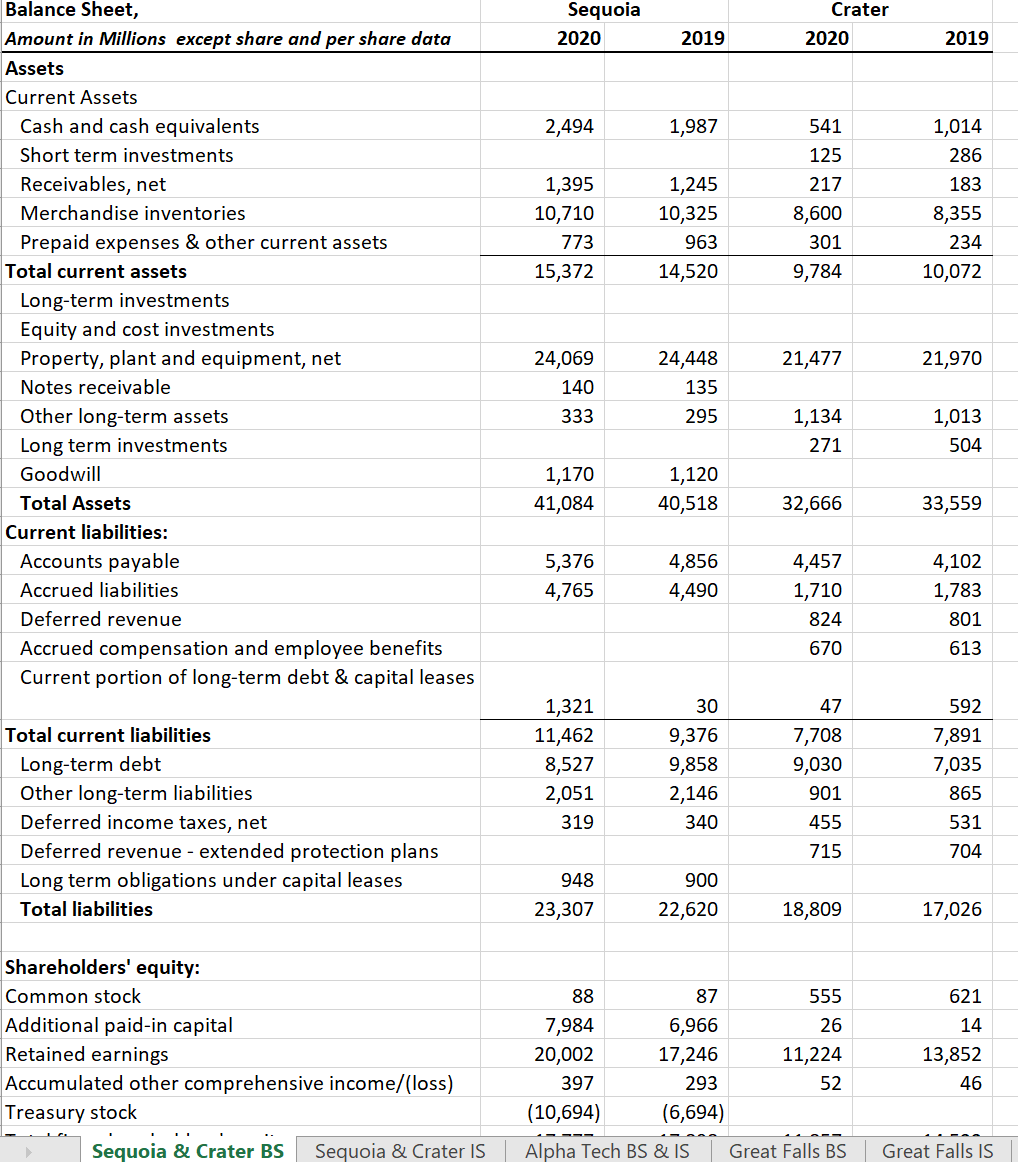
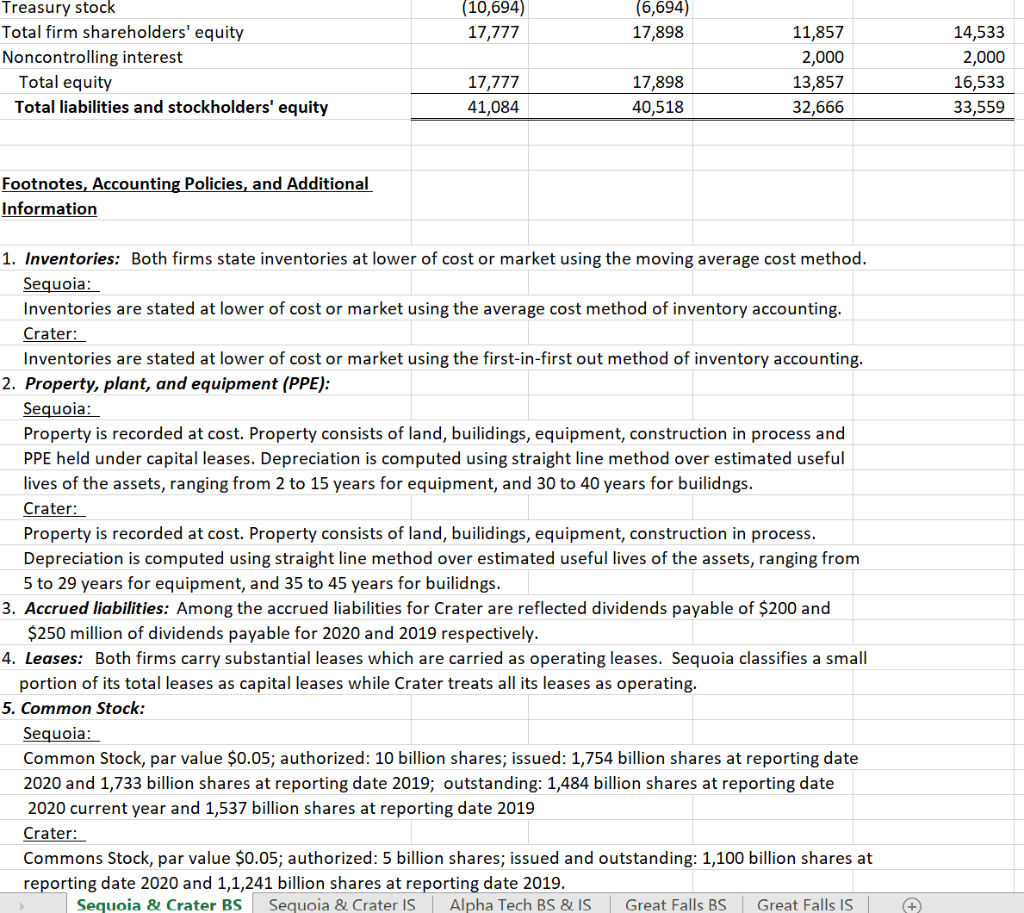
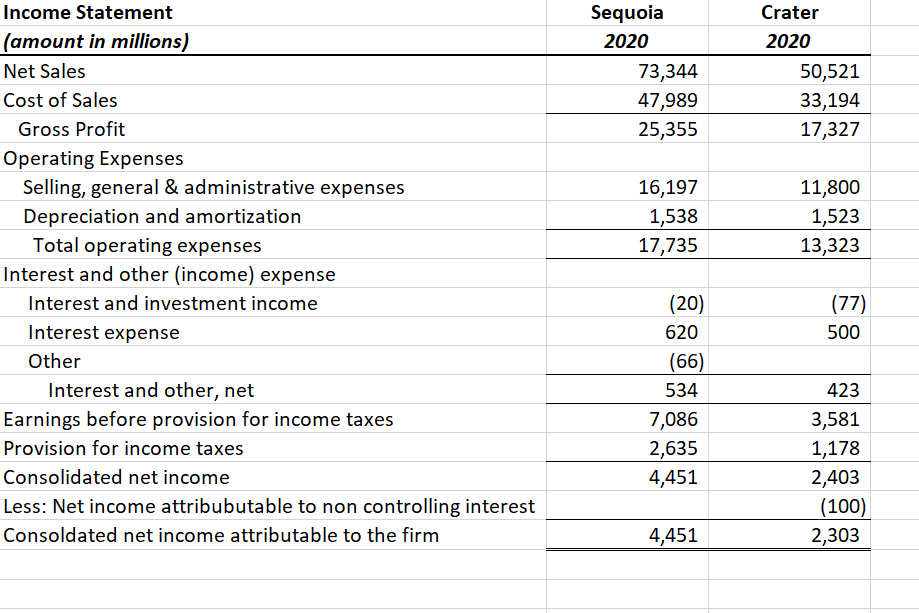
Using the financial statements and additional notes provided in the attached excel file (Final Exam, tabs Sequoia and Crater BS, and Sequoia and Crater IS), analyze the relative credit risk by computing and interpreting the results of the following metrics for both firms:
- Current and quick ratios (liquidity analysis) for 2020 and 2019 and times interest earned ratio, and the EBITDA coverage ratios for 2020. (2 points)
- Liabilities to equity and total debt to equity ratios for 2020 and 2019. (1 points)
- Altman Z-scores for the two companies for 2019. (1 points)
- The percentages of operating lease to total lease in 2019 for Sequoia vs. Crater are 30% and 70% respectively? What type of adjustments would you make to the financial statements and what potential impact may that have on your credit risk analysis? (2 points).
- The forecasted levels of sales and cash in 2019 for company Sequoia vs. Crater are as follows: Sales for Sequoia vs. Crater are $71,000 and 54,000 respectively and the cash for Sequoia vs. Crater are $2,210 and 620. Does the forecasted cash deviate from the normal levels for both companies? and why? (2 points)
Problem Two: Forecasting Financial Statements (5 points)
Using the forecasted income statement and balance sheet and additional notes provided in the attached excel file (Final Exam, tabs Great Falls BS, and Great Falls IS), please answer the following questions:
- Prepare a forecasted statement of cash flows for the company for 2020 assuming the following assumptions.
- Assume that net sales will grow by 1.16%, 2.16%, 3.16% and 4.16% for the next five years 2020, 2021, 2022, 2023, and 2024. Use the parsimonious method of forecasting to project net operating profit after tax (NOPAT) and net operating assets (NOA) for 2020 through 2023, inclusive. (2 points)
| Depreciation expense to start of year PPE, net | 21.2% |
| Amortization expense to start of year intangible assets, net | 4.9% |
| CAPEX to total net sales | 1.8% |
| Dividends to net earnings | 33.5% |
| | |
- Describe the difference between the full forecast of financial statements and the parsimonious method. When is one preferable to the other? Please support your answer. (3 points)
Problem Three: Valuation Analysis (7 points)
As a financial analyst, after conducting a careful accounting, financial statement, and prospective analysis of a company, you are now developing an independent assessment of the value of the firm to develop an investment recommendation for your clients. Using the financial statements and additional notes provided for the firm in the attached excel file (Final Exam, tab Alpha Tech BS & IS), develop a valuation for the firm using the DCF model. Additional information and assumptions for the firm that you have made include:
- The book value of the firms debt equals its market value.
- The estimated market beta for the firm is 0.46, the expected risk free-rate is 2.5%, and the expected market premium is 5%.
- The firms stock closed at $55.85 on March 31, 2017 (fiscal year end), and the stock is currently trading at $59.50.
- The firms statutory tax rate is 37%.
- Based on a historical analysis, adjusted by a strategic and industry assessment, you have developed the following forecasts for the firm for the next four years, (2018-2021):
Sales Growth 8%
Net operating profit margin (NOPM) 6.8%
Net operating asset turnover (NOAT) 1.41
Terminal Period 1%
- Develop an Estimate for weighted average cost of capital for the firm (4 points)
- Estimate the companys average pretax borrowing cost.
- Assuming the book value of the firms debt equals its market value, estimate the firms cost of debt capital.
- Estimate the cost of equity capital for the firm.
- Based on (b) and (c) estimate the firms weighted average cost of capital (WACC)
- Estimating Valuation (3 points)
- Using the discounted cash flow model (DCF), estimate the value of a share for the firms common stock.
- Based on your valuation, provide an investment recommendation for your clients.
Sequoia 2020 Crater 2020 2019 2019 2,494 1,987 1,395 10,710 773 15,372 1,245 10,325 963 14,520 541 125 217 8,600 301 9,784 1,014 286 183 8,355 234 10,072 Balance Sheet, Amount in Millions except share and per share data Assets Current Assets Cash and cash equivalents Short term investments Receivables, net Merchandise inventories Prepaid expenses & other current assets Total current assets Long-term investments Equity and cost investments Property, plant and equipment, net Notes receivable Other long-term assets Long term investments Goodwill Total Assets Current liabilities: Accounts payable Accrued liabilities Deferred revenue Accrued compensation and employee benefits Current portion of long-term debt & capital leases 21,477 21,970 24,069 140 24,448 135 333 295 1,134 271 1,013 504 1,170 41,084 1,120 40,518 32,666 33,559 5,376 4,765 4,856 4,490 4,457 1,710 824 670 4,102 1,783 801 613 592 1,321 11,462 8,527 2,051 319 30 9,376 9,858 2,146 340 Total current liabilities Long-term debt Other long-term liabilities Deferred income taxes, net Deferred revenue - extended protection plans Long term obligations under capital leases Total liabilities 47 7,708 9,030 901 7,891 7,035 865 455 531 715 704 948 23,307 900 22,620 18,809 17,026 621 Shareholders' equity: Common stock Additional paid-in capital Retained earnings Accumulated other comprehensive income/(loss) Treasury stock Sequoia & Crater BS Sequoia & Crater IS 88 87 555 7,984 6,966 26 20,002 17,246 11,224 397 293 52 (10,694) (6,694) Alpha Tech BS & IS Great Falls BS 14 13,852 46 Great Falls IS (10,694) 17,777 (6,694) 17,898 Treasury stock Total firm shareholders' equity Noncontrolling interest Total equity Total liabilities and stockholders' equity 11,857 2,000 13,857 32,666 14,533 2,000 16,533 33,559 17,777 41,084 17,898 40,518 Footnotes, Accounting Policies, and Additional Information 1. Inventories: Both firms state inventories at lower of cost or market using the moving average cost method. Sequoia: Inventories are stated at lower of cost or market using the average cost method of inventory accounting. Crater: Inventories are stated at lower of cost or market using the first-in-first out method of inventory accounting. 2. Property, plant, and equipment (PPE): Sequoia: Property is recorded at cost. Property consists of land, builidings, equipment, construction in process and PPE held under capital leases. Depreciation is computed using straight line method over estimated useful lives of the assets, ranging from 2 to 15 years for equipment, and 30 to 40 years for builidngs. Crater: Property is recorded at cost. Property consists of land, builidings, equipment, construction in process. Depreciation is computed using straight line method over estimated useful lives of the assets, ranging from 5 to 29 years for equipment, and 35 to 45 years for builidngs. 3. Accrued liabilities: Among the accrued liabilities for Crater are reflected dividends payable of $200 and $250 million of dividends payable for 2020 and 2019 respectively. 4. Leases: Both firms carry substantial leases which are carried as operating leases. Sequoia classifies a small portion of its total leases as capital leases while Crater treats all its leases as operating. 5. Common Stock: Sequoia: Common Stock, par value $0.05; authorized: 10 billion shares, issued: 1,754 billion shares at reporting date 2020 and 1,733 billion shares at reporting date 2019; outstanding: 1,484 billion shares at reporting date 2020 current year and 1,537 billion shares at reporting date 2019 Crater: Commons Stock, par value $0.05; authorized: 5 billion shares; issued and outstanding: 1,100 billion shares at reporting date 2020 and 1,1,241 billion shares at reporting date 2019. Sequoia & Crater BS Sequoia & Crater IS Alpha Tech BS & IS Great Falls BS Great Falls IS Sequoia 2020 73,344 47,989 25,355 Crater 2020 50,521 33,194 17,327 16,197 1,538 17,735 11,800 1,523 13,323 Income Statement (amount in millions) Net Sales Cost of Sales Gross Profit Operating Expenses Selling, general & administrative expenses Depreciation and amortization Total operating expenses Interest and other (income) expense Interest and investment income Interest expense Other Interest and other, net Earnings before provision for income taxes Provision for income taxes Consolidated net income Less: Net income attribubutable to non controlling interest Consoldated net income attributable to the firm (77) 500 (20) 620 (66) 534 7,086 2,635 4,451 423 3,581 1,178 2,403 (100) 2,303 4,451 Sequoia 2020 Crater 2020 2019 2019 2,494 1,987 1,395 10,710 773 15,372 1,245 10,325 963 14,520 541 125 217 8,600 301 9,784 1,014 286 183 8,355 234 10,072 Balance Sheet, Amount in Millions except share and per share data Assets Current Assets Cash and cash equivalents Short term investments Receivables, net Merchandise inventories Prepaid expenses & other current assets Total current assets Long-term investments Equity and cost investments Property, plant and equipment, net Notes receivable Other long-term assets Long term investments Goodwill Total Assets Current liabilities: Accounts payable Accrued liabilities Deferred revenue Accrued compensation and employee benefits Current portion of long-term debt & capital leases 21,477 21,970 24,069 140 24,448 135 333 295 1,134 271 1,013 504 1,170 41,084 1,120 40,518 32,666 33,559 5,376 4,765 4,856 4,490 4,457 1,710 824 670 4,102 1,783 801 613 592 1,321 11,462 8,527 2,051 319 30 9,376 9,858 2,146 340 Total current liabilities Long-term debt Other long-term liabilities Deferred income taxes, net Deferred revenue - extended protection plans Long term obligations under capital leases Total liabilities 47 7,708 9,030 901 7,891 7,035 865 455 531 715 704 948 23,307 900 22,620 18,809 17,026 621 Shareholders' equity: Common stock Additional paid-in capital Retained earnings Accumulated other comprehensive income/(loss) Treasury stock Sequoia & Crater BS Sequoia & Crater IS 88 87 555 7,984 6,966 26 20,002 17,246 11,224 397 293 52 (10,694) (6,694) Alpha Tech BS & IS Great Falls BS 14 13,852 46 Great Falls IS (10,694) 17,777 (6,694) 17,898 Treasury stock Total firm shareholders' equity Noncontrolling interest Total equity Total liabilities and stockholders' equity 11,857 2,000 13,857 32,666 14,533 2,000 16,533 33,559 17,777 41,084 17,898 40,518 Footnotes, Accounting Policies, and Additional Information 1. Inventories: Both firms state inventories at lower of cost or market using the moving average cost method. Sequoia: Inventories are stated at lower of cost or market using the average cost method of inventory accounting. Crater: Inventories are stated at lower of cost or market using the first-in-first out method of inventory accounting. 2. Property, plant, and equipment (PPE): Sequoia: Property is recorded at cost. Property consists of land, builidings, equipment, construction in process and PPE held under capital leases. Depreciation is computed using straight line method over estimated useful lives of the assets, ranging from 2 to 15 years for equipment, and 30 to 40 years for builidngs. Crater: Property is recorded at cost. Property consists of land, builidings, equipment, construction in process. Depreciation is computed using straight line method over estimated useful lives of the assets, ranging from 5 to 29 years for equipment, and 35 to 45 years for builidngs. 3. Accrued liabilities: Among the accrued liabilities for Crater are reflected dividends payable of $200 and $250 million of dividends payable for 2020 and 2019 respectively. 4. Leases: Both firms carry substantial leases which are carried as operating leases. Sequoia classifies a small portion of its total leases as capital leases while Crater treats all its leases as operating. 5. Common Stock: Sequoia: Common Stock, par value $0.05; authorized: 10 billion shares, issued: 1,754 billion shares at reporting date 2020 and 1,733 billion shares at reporting date 2019; outstanding: 1,484 billion shares at reporting date 2020 current year and 1,537 billion shares at reporting date 2019 Crater: Commons Stock, par value $0.05; authorized: 5 billion shares; issued and outstanding: 1,100 billion shares at reporting date 2020 and 1,1,241 billion shares at reporting date 2019. Sequoia & Crater BS Sequoia & Crater IS Alpha Tech BS & IS Great Falls BS Great Falls IS Sequoia 2020 73,344 47,989 25,355 Crater 2020 50,521 33,194 17,327 16,197 1,538 17,735 11,800 1,523 13,323 Income Statement (amount in millions) Net Sales Cost of Sales Gross Profit Operating Expenses Selling, general & administrative expenses Depreciation and amortization Total operating expenses Interest and other (income) expense Interest and investment income Interest expense Other Interest and other, net Earnings before provision for income taxes Provision for income taxes Consolidated net income Less: Net income attribubutable to non controlling interest Consoldated net income attributable to the firm (77) 500 (20) 620 (66) 534 7,086 2,635 4,451 423 3,581 1,178 2,403 (100) 2,303 4,451









