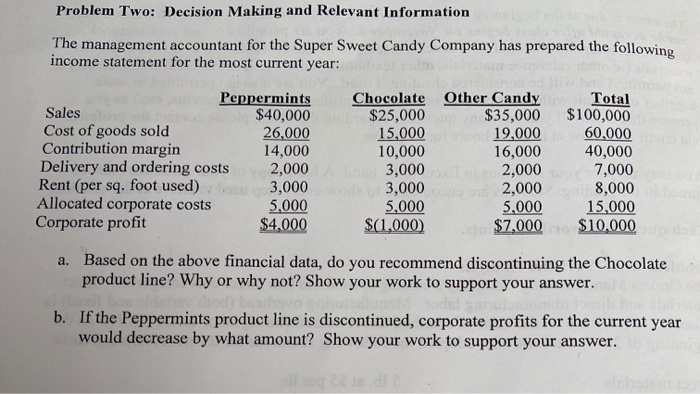
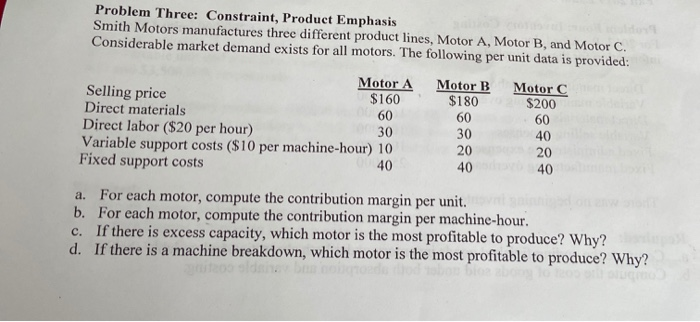
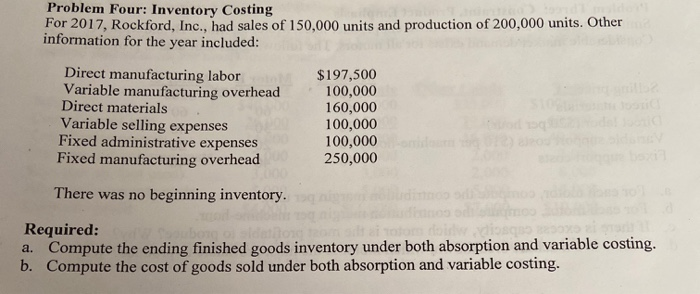
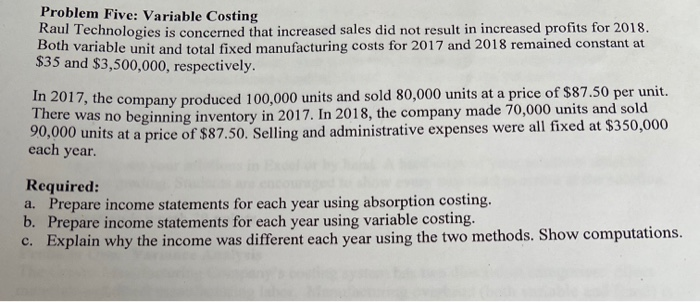
Problem One: Variance Analysis The Graves Manufacturing Company's costing system has two direct-cost categories: direct materials and direct manufacturing labor. Manufacturing overhead (both variable and fixed) is allocated to products on the basis of standard direct manufacturing labor-hours (DLH). At the beginning of 2017, the controller adopted the following standards for its manufacturing costs: 5 lb. at $5 per lb. 3 hrs. at $15 per hr. Direct materials Direct manufacturing labor Manufacturing overhead: Variable Fixed $7 per DLH $8 per DLH The flexible budget for January was based on 25,000 direct labor hours. The records for January indicated the following: Direct materials purchased 38,300 lb. at $4.00 per lb. Direct materials used 38,000 lb. Direct manufacturing labor 23,400 hrs. at $16.25 per hr. Total actual manufacturing overhead (variable and fixed) $390,000 Actual production 8,000 output units Required: For the month of January 2014, compute the following variances, indicating whether each is favorable (F) or unfavorable (U): a. Direct materials price variance, based on purchases. b. Direct materials efficiency variance c. Direct manufacturing labor price variance. d. Direct manufacturing labor efficiency variance. e. Total manufacturing overhead spending variance. f. Variable manufacturing overhead efficiency variance. g. Production-volume variance. Problem Two: Decision Making and Relevant Information The management accountant for the Super Sweet Candy Company has prepared the following income statement for the most current year: Peppermints Sales $40,000 Cost of goods sold 26,000 Contribution margin 14,000 Delivery and ordering costs 2,000 Rent (per sq. foot used) 3,000 Allocated corporate costs 5,000 Corporate profit $4,000 Chocolate $25,000 15,000 10,000 3,000 3,000 5,000 $(1.000) Other Candy $35.000 19,000 16,000 2,000 2,000 5,000 $7,000 Total $100,000 60,000 40,000 7,000 8,000 15,000 $10,000 a. Based on the above financial data, do you recommend discontinuing the Chocolate product line? Why or why not? Show your work to support your answer. b. If the Peppermints product line is discontinued, corporate profits for the current year would decrease by what amount? Show your work to support your answer. Problem Three: Constraint, Product Emphasis Smith Motors manufactures three different product lines, Motor A, Motor B, and Motor C. Considerable market demand exists for all motors. The following per unit data is provided: Motor B $180 Motor C $200 60 60 Motor A Selling price $160 Direct materials 60 Direct labor ($20 per hour) 30 Variable support costs ($10 per machine-hour) 10 Fixed support costs 30 40 20 40 40 40 a. For each motor, compute the contribution margin per unit. b. For each motor, compute the contribution margin per machine-hour. c. If there is excess capacity, which motor is the most profitable to produce? Why? d. If there is a machine breakdown, which motor is the most profitable to produce? Why? Problem Four: Inventory Costing For 2017, Rockford, Inc., had sales of 150,000 units and production of 200,000 units. Other information for the year included: Direct manufacturing labor Variable manufacturing overhead Direct materials Variable selling expenses Fixed administrative expenses Fixed manufacturing overhead $197,500 100,000 160,000 100,000 100,000 250,000 There was no beginning inventory. Required: a. Compute the ending finished goods inventory under both absorption and variable costing. b. Compute the cost of goods sold under both absorption and variable costing. Problem Five: Variable Costing Raul Technologies is concerned that increased sales did not result in increased profits for 2018. both variable unit and total fixed manufacturing costs for 2017 and 2018 remained constant at $35 and $3,500,000, respectively. In 2017, the company produced 100,000 units and sold 80,000 units at a price of $87.50 per unit. There was no beginning inventory in 2017. In 2018, the company made 70,000 units and sold 90,000 units at a price of $87.50. Selling and administrative expenses were all fixed at $350,000 each year. Required: a. Prepare income statements for each year using absorption costing. b. Prepare income statements for each year using variable costing. c. Explain why the income was different each year using the two methods. Show computations