Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
A 2D steady, incompressible and inviscid flow field is defined by the velocity vector components: i) ii) i) u=-2xy ii) v=y - x Determine

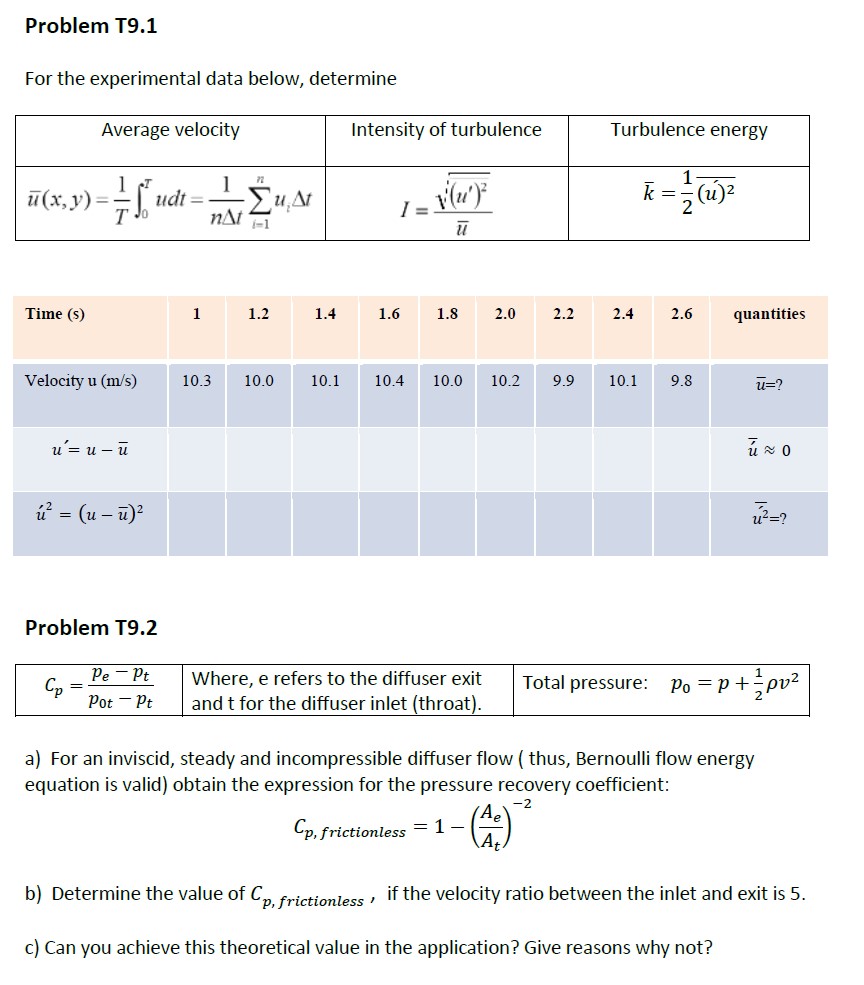

A 2D steady, incompressible and inviscid flow field is defined by the velocity vector components: i) ii) i) u=-2xy ii) v=y - x Determine if the flow is irrotational? Problem T7.2 A 2D steady, incompressible and inviscid flow field is described by the velocity potential function: d=xy Determine the velocity field (u=? and v=?) Show that the continuity is satisfied. Attempt to sketch the constant value potential lines for the flow. Hint: For any constant value of C (where i=0 to n), sketch y=/x on X-Y plane. Remember: At any point (x,y), the velocity vector is normal to the potential line passing through (x,y). Determine the velocity potential function for this flow. Let at the origin(x=0, y=0). Equations: Angular velocity: Problem: T7.1 W = w=0.0 1/dv x - Definition of the velocity potential function , Problem: T7.2 d d 11 = and W= d dz Problem T9.1 For the experimental data below, determine Average velocity 1 72 (x, y) == "undt = A -u, At Time (s) Velocity u (m/s) u= u - = (u - ) Problem T9.2 Cp = Pe - Pt Pot Pt 1 nt - 1.2 10.3 10.0 1.4 Intensity of turbulence b) Determine the value of C 1= 4(u' 1.6 1.8 Where, e refers to the diffuser exit and t for the diffuser inlet (throat). 'p, frictionless ' 2.0 10.1 10.4 10.0 10.2 9.9 2.2 Turbulence energy 2.4 1 k=(u) 2.6 10.1 9.8 Total pressure: quantities u=? 0 a) For an inviscid, steady and incompressible diffuser flow (thus, Bernoulli flow energy equation is valid) obtain the expression for the pressure recovery coefficient: -2 Cp, frictionless = 1- c) Can you achieve this theoretical value in the application? Give reasons why not? Po = P + + pv if the velocity ratio between the inlet and exit is 5. Problem T9.3 a) For a given steady flow, these are the values observed at a point in the flow. Total Acceleration in x direction= 5 (N/m) Pressure gradient in X direction= -8 (N/m) . Determine: du dt . b) At another location of the flow, if there is no acceleration, but the pressure gradient is still the same of -8 (N/m) du dt Viscous (shear) force = ? (N/m) c) Consider a), if the flow is inviscid, what is the pressure gradient (?) to achieve the same total acceleration of 5 (N/m) ? Determine: Viscous (shear) force = ? (N/m3) d) Consider the inviscid flow of c), and justify whether in the direction of flow the flow area remains constant or it is increasing or decreasing. Equations at dx + u + x +v +w n n n + Oz + oxoy z body +F bo Acceleration in X direction (N/kg) Incompressible momentum equations in X direction N/m 3
Step by Step Solution
★★★★★
3.45 Rating (148 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
The skin friction coefficient Cf for a laminar boundary ...
Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


