Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
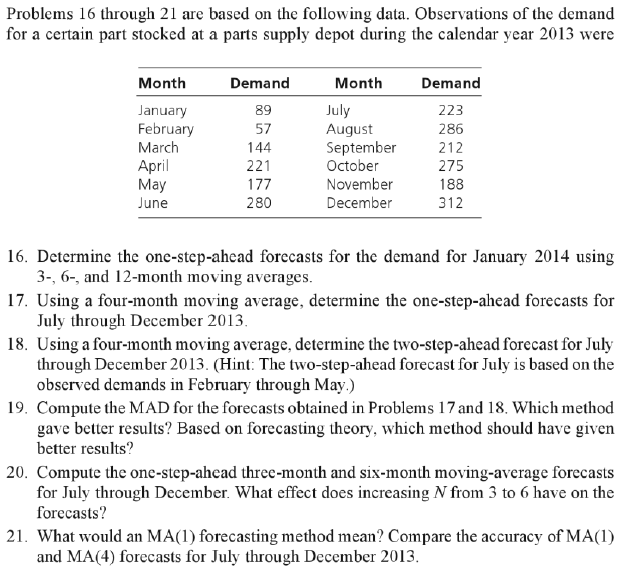
Problems on Moving Averages Problems 16 through 21 are based on the following data. Observations of the demand for a certain part stocked at a
Problems on Moving Averages
Problems 16 through 21 are based on the following data. Observations of the demand for a certain part stocked at a parts supply depot during the calendar year 2013 were Demand 89 57 Month January February March April May June 144 221 177 280 Month July August September October November December Demand 223 286 212 275 188 312 16. Determine the one-step-ahead forecasts for the demand for January 2014 using 3-, 6-, and 12-month moving averages. 17. Using a four-month moving average, determine the one-step-ahead forecasts for July through December 2013. 18. Using a four-month moving average, determine the two-step-ahead forecast for July through December 2013. (Hint: The two-step-ahead forecast for July is based on the observed demands in February through May.) 19. Compute the MAD for the forecasts obtained in Problems 17 and 18. Which method gave better results? Based on forecasting theory, which method should have given better results? 20. Compute the one-step-ahead three-month and six-month moving-average forecasts for July through December. What effect does increasing N from 3 to 6 have on the forecasts? 21. What would an MA(1) forecasting method mean? Compare the accuracy of MA(1) and MA(4) forecasts for July through December 2013. Problems 16 through 21 are based on the following data. Observations of the demand for a certain part stocked at a parts supply depot during the calendar year 2013 were Demand 89 57 Month January February March April May June 144 221 177 280 Month July August September October November December Demand 223 286 212 275 188 312 16. Determine the one-step-ahead forecasts for the demand for January 2014 using 3-, 6-, and 12-month moving averages. 17. Using a four-month moving average, determine the one-step-ahead forecasts for July through December 2013. 18. Using a four-month moving average, determine the two-step-ahead forecast for July through December 2013. (Hint: The two-step-ahead forecast for July is based on the observed demands in February through May.) 19. Compute the MAD for the forecasts obtained in Problems 17 and 18. Which method gave better results? Based on forecasting theory, which method should have given better results? 20. Compute the one-step-ahead three-month and six-month moving-average forecasts for July through December. What effect does increasing N from 3 to 6 have on the forecasts? 21. What would an MA(1) forecasting method mean? Compare the accuracy of MA(1) and MA(4) forecasts for July through December 2013Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


