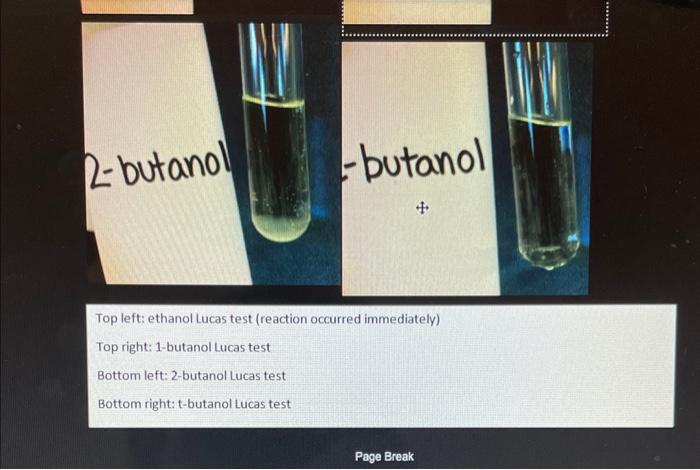
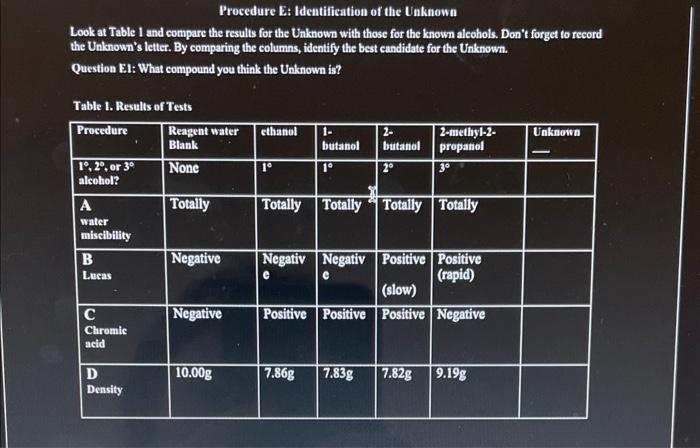
Procedure B: Lucas Test In the procedures below, you will perform the Lueas test on the known alcohols, the unknown alcohol, and a 'water blank". The water blank will not react in any tests and can be used to compare to the other results. This way, you can tell what is a reaction (a positive (+) test resulf) and what is not a reaction (a negative () test resuli). Question B1: Will the water give a positive or a negative result in all tests? The Lueas test has a negative result for 1 alcohols. The test has a rapid positive for 3 alcohols and a slower positive for 2 alcohols. Prelab Question 10: Of the alcohols below, which do you predigh will show a positive Luess test resuln? Into six 20mL labeled test tubes place about 3mL of these liquids: a water blank, ethanol, 1-butanol, 2-butanol, tbutanol, and the unknown. In the fume hood, to each add up to 5mL of Lucas reagent, ZnCl, in cone. HCl. Without shaking, wait 5min. Look for the appearance of a white solid precipitate, an insoluble chlorohydrocarbon suspended in the alcohol. Presence of the white solid is the positive ( ( ) result of the Lucas test. Compare each tube with the negative () result for the water blank. Into Table 1, record a ' + 'or ' " ' for each alcohol. 2 - butanol - butanc Top left: ethanol Lucas test (reaction occurred immediately) Top right: 1-butanol Lucas test Bottom left: 2-butanol Lucas test Bottom right: t-butanol Lucas test Procedure C: Chromic Acid Test Chromic acid is a mixture of potassium dichromate (K2Cr2O7) and concentrated sulfuric acid (H2,SO4). It is a potent oxidizing agent or oxidant. Oxidants such as chromic acid will oxidize primary alcohols to aldehydes, then finally to carboxylic acids. Secondary alcohols will be oxidized to ketones. However, tertiary alcohols, lacking the necessary H on the hydroxyl group's carbon, will not be oxidized by chromic acid. So, this test is a good way to distinguish between 3 alcohols and the others. Chromic acid has the orange dichromate color. When it oxidizes an alcohol, the reduced, green Cr(III) cation is formed. So, when there's a positive result, not only will the orange color fade, but a greenish color will appear. Prelab Question 11: Of the alcohols below, which do you predict will be oxidized by chromic acid? Into six 20mL labeled test tubes place about 3mL of these liquids: a water blank, ethanol, 1-butanol, 2-butanol, tbutanol, and the unknown. Add about 10 drops of acetone to the alcohols found to be immiscible in Procedure B. Cover each tube with Parafilm and shake until mixed. Then add about 2 drops of the chromic acid solution. Wam the solutions in your water bath at about 6070C for about 10min After 10min, remove the tubes from the bath. Allow to cool for 2min. Look for a greenish color; this is the positive (+) result of this test. Compare each tube with the orangeish, unreacted, negative ( ) result for the water blank. Into Table 1, record a " + 'or "-' for each alcohol. Nater To the left is the chromic acid test using water for the negative control. Procedure E: Identification of the Unknown Look at Table 1 and compare the results for the Unknown with those for the known alcohols. Don't forget to record the Unknown's letter. By comparing the columns, identify the best candidate for the Unknown. Question E.1: What compound you think the Unknown is? Table 1. Results of Tests