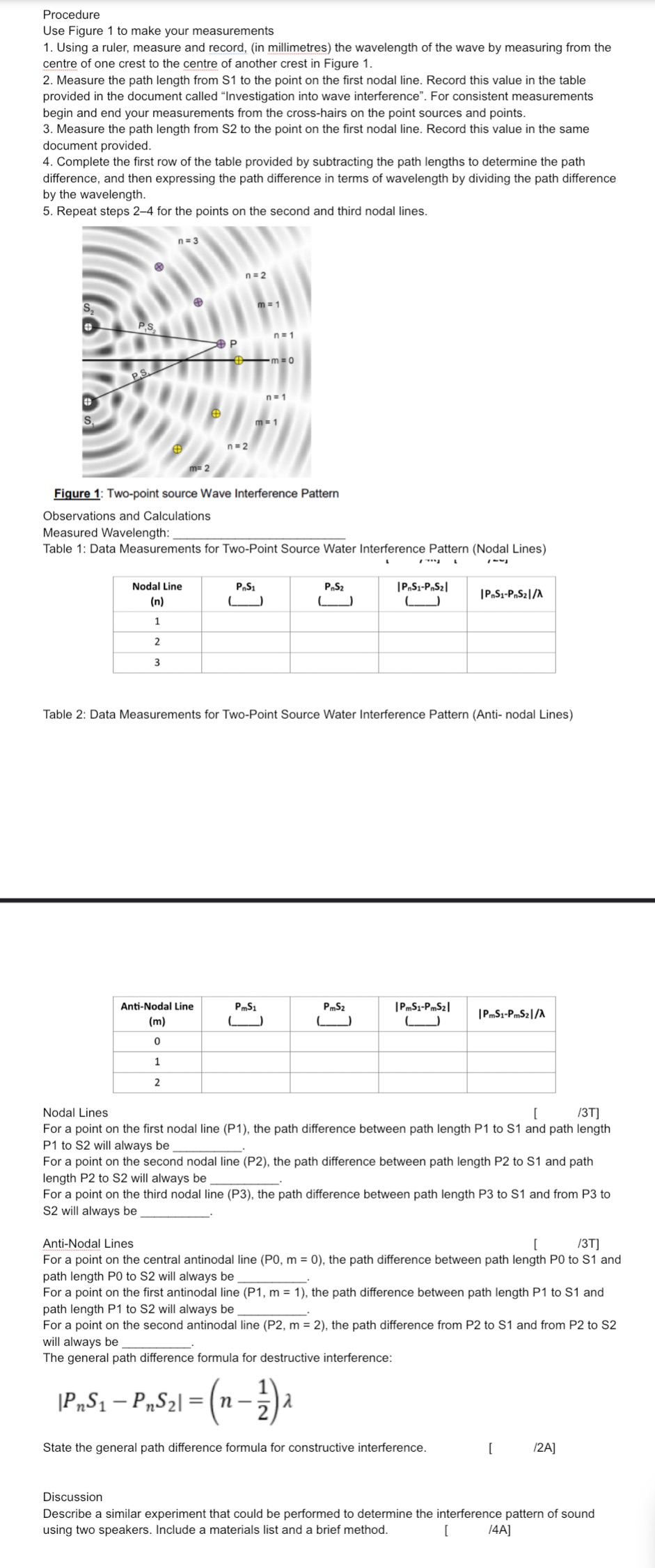
Procedure Use Figure 1 to make your measurements 1. Using a ruler, measure and record, (in millimetres) the wavelength of the wave by measuring from the centre of one crest to the centre of another crest in Figure 1. 2. Measure the path length from S1 to the point on the rst nodal line. Record this value in the table provided in the document called "Investigation into wave interference\". For consistent measurements begin and end your measurements from the cross~hairs on the point sources and points. 3. Measure the path length from 32 to the point on the rst nodal line. Record this value in the same document provided. 4. Complete the rst row of the table provided by subtracting the path lengths to determine the path difference, and then expressing the path difference in terms of wavelength by dividing the path difference by the wavelength. 5. Repeat steps 24 for the points on the second and third nodal lines. Flaug 1: Two-point source Wave Interference Pattern Observations and Calculations Measured Wavelength: Table 1.' Data Measurements for Two-Point Source Water Interference Pattern [Nodal Lines) - r ---n I I--I Nodal Llne PA; PJ; IFnSI'FnSII in) i , |p..s.-n.s:llrt ' . l l 2 i i 3 l l Table 2: Data Measurements for Two-Point Source Water Interference Pattern [Anti- nodal Lines) Anti-Nodal Llne ' PMS. I 9min - tFmsI-Pmiul lml l.__J L__J L__l 0 . . 1 2 IPMSI'PMSI Ill l l l l Nodal Lines [ 131'] For a point on the firstnodal line (P1). the path difference between path length P1 to 81 and path length P1 to 82 vaII always be For a point on the second nodal line (P2) the path difference between path length P2 to S1 and path length P2 to 32 will always be For a point on the third nodal line (P3), the path difference between path length P3 to 51 and from P3 to 52 will always be Anti-Nodal Lines I 131'] For a point on the central antinodal lIne (P0. rn = D), the path difference between path length P0 to 31 and path length P0 to 52 will always be For a point on the first antinodal line (P1, m " 1) the path difference between path length P1 to $1 and path length P1 to 52 will always be For a point on the second antinodal line (P2 m= 2) the path difference from P2 to S1 and from P2 to 82 will always be The general path difference fon'nula for destructive interference. iPnSI PnSZI = 71; A State the general path d'rfference formula for constructive interference. [ [2A] Discussion Describe a similar experiment that could be performed to detennine the interference pattern of sound using two Speakers. Include a materials list and a brief method. [ 14A]