Question
Production. 1. Consider the Cobb-Douglas production function f(x,y) = 12x0.4y0.8. (A) Find the intensities (? and 1 ? ?) of the two factors of production.


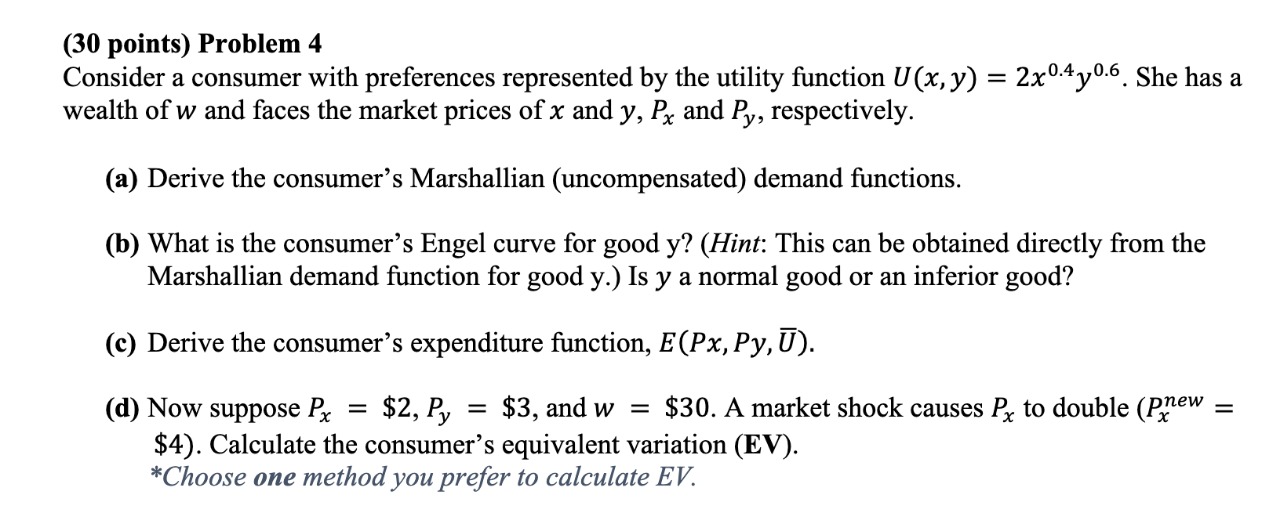

Production.
1. Consider the Cobb-Douglas production function f(x,y) = 12x0.4y0.8.
(A) Find the intensities (? and 1 ? ?) of the two factors of production. Does this firm have decreasing, increasing, or constant returns to scale? What percentage of the firm's total production costs will be spent on good x?
(B) Suppose the firm decides to increase its input bundle (x, y) by 10%. That is, it inputs 10% more units of good x and 10% more units of good y. What is the percent increase in output?
(C) Suppose the firm has a production quota of q = 1000 units, and the firm inputs x = 100 units of the first good. How many units of the second good does it need to use to meet the quota?
(D) Assume the firm has a production quota of q = 2000 units, and the input prices are (px,py) = (7,19). Find the minimized cost C(2000) and the conditional factor demands (x?,y?).
Problem 2. Consider the linear (perfect substitutes) production function f (x, y) = 12.7x + 19.4y.
(A) How many units of good y would be a perfect substitute for 1 unit of good x? What is the slope of
the firm's isoquants?
(B) Suppose the input prices are (px,py) = (5,8). What is the slope of the isocost lines? How much output does the firm get when it inputs $1 worth of good x? How much output does the firm get when it inputs $1 worth of good y?
(C) Suppose this firm has a production quota of q = 500 units. Find the minimized cost C(500) and the corresponding conditional factor demands.
(D) Draw the firm's level-500 isoquant, as well as the isocost lines. Indicate the cost minimizer on your diagram.
Problem 3. Consider the Leontiev (perfect complements) production function f (x, y) = M in x , y . 9.6 5.2
(A) How many units of good y would be a perfect complement for 1 unit of good x? What is the equation of the firm's kink line?
(B) Assume the firm has a production quota of q = 400 units. Graph the firm's level-400 isoquant. What are the coordinates of the kink?
(C) Suppose the input prices are (px,py) = (16,9). Find the minimized cost C(400). What is the cost minimizing input bundle (x?, y?)?
(D) Give a complete geometric illustration of this firm's cost minimization. On a single diagram, draw the firm's level-400 isoquant, the isocost lines, and the cost minimizing input bundle.
Problem 4. Suppose that a firm's production plan is (x, y, z) = (102, 19, 957), and the market prices are (px , py , pz ) = (10, 5, 1.25). How much profit would the firm make if it carried out this plan?
Problem 5. Suppose that a firm's production function is f(x,y) = 20x0.7y0.3. Starting from the input bundle (x, y) = (40, 60), how much extra output will the firm get if it increases x from 40 to 41? How many units of output will the firm lose if x decreases from 40 to 39?
Problem 6. Suppose that the production of airframes (for aircraft) uses two inputs: capital (good x) and labor (good y). The production function is f(x,y) = xy. Assume that the price of capital is $1 per unit, and the price of labor is $10 per unit. The manufacturer wants to make 121,000 airframes. Find the cost-minimizing combination of capital and labor inputs.
ii.
Work out the following questions with explanations.



Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


