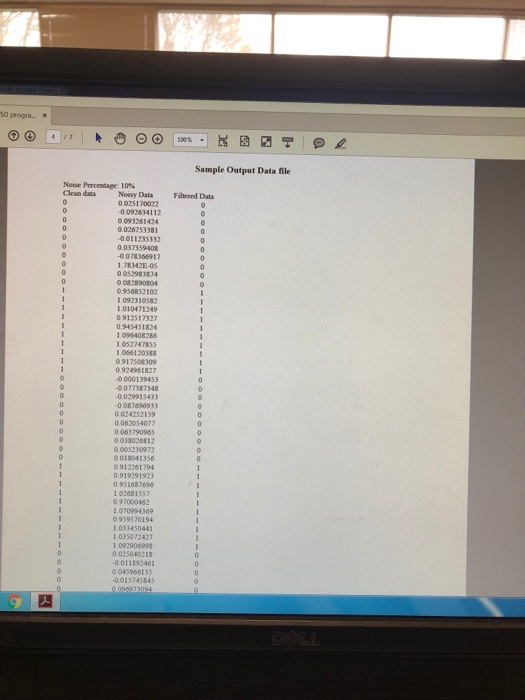
progra. X Data Communications and Computer Networks (CSCI 3150) Programming project Simulation of Nolse and Noise Filtering in Data Communication Devices Noise is often defined as unwanted di ality of signals or data. In digital data communication systems such as computer networks, digital signals could be affected by various types of noise. One of the more common types of noise in digital data communications is white noise. White noise is also called thermal or Gaussian noise is relatively contimuous noise and always present to some degree in electronic devices. The temperature rises in electronie devices increases the amount of white noise in signals (for more information about this noise read Chapter 6 of your textbook). All digital data communication devices such as hubs and switches are capable of filtering out thermal noise (if it is not too much) and restoring the digital signals back to their nominal values. In this project. you will develop a Java computer program to simulate a clean digital square wave signal and then add Gaussian noise to the signal as a percentage of the maximum signal strength. The square wave signal has two values of Os and 1s (see figure 6-1 of Chapter 6 of the textbook). Assume the duration of zeros or ones is equal to one millisecond (for simplicity you may assiume every 10 zeroes or 10 ones generated by program is one millisecond). The total simulation time is 10 milliseconds. The program should prompt the aser to enter the noise percentage and then it adds the noise to the signal. The Gaussian noise could be generated using the function NextGaussian0 in java. The NextGaussa random normal numbers with mean 0 and standard deviation of 1 (note that you need to have the libeary import java.a 99.7% of all random numbers are within 3 standard deviation, we need to normalize the wnil. Random; in the program). Since in Gaussian distribution aumbers to be between -1 and I by dividing the NextGmussian over 3. Thus, the following equation should be used in the progranm Noise amount Noise percent ((1/3) NextGuassain0) The noisy data in the program is obtained as follows: Noisy data Clean data + Noise amount Next, the program simulates the function of a hub switch to filter out the noise from the signal This could be easily accomplished by an "If statement. For example, if the value of the noise data is greater than one or greater than 0.31 then the filtered data is set to 1 otherwise, the value is set to 0 The program should output the clean data, noisy data, and the filtered data into a text file in You need t progra. X Data Communications and Computer Networks (CSCI 3150) Programming project Simulation of Nolse and Noise Filtering in Data Communication Devices Noise is often defined as unwanted di ality of signals or data. In digital data communication systems such as computer networks, digital signals could be affected by various types of noise. One of the more common types of noise in digital data communications is white noise. White noise is also called thermal or Gaussian noise is relatively contimuous noise and always present to some degree in electronic devices. The temperature rises in electronie devices increases the amount of white noise in signals (for more information about this noise read Chapter 6 of your textbook). All digital data communication devices such as hubs and switches are capable of filtering out thermal noise (if it is not too much) and restoring the digital signals back to their nominal values. In this project. you will develop a Java computer program to simulate a clean digital square wave signal and then add Gaussian noise to the signal as a percentage of the maximum signal strength. The square wave signal has two values of Os and 1s (see figure 6-1 of Chapter 6 of the textbook). Assume the duration of zeros or ones is equal to one millisecond (for simplicity you may assiume every 10 zeroes or 10 ones generated by program is one millisecond). The total simulation time is 10 milliseconds. The program should prompt the aser to enter the noise percentage and then it adds the noise to the signal. The Gaussian noise could be generated using the function NextGaussian0 in java. The NextGaussa random normal numbers with mean 0 and standard deviation of 1 (note that you need to have the libeary import java.a 99.7% of all random numbers are within 3 standard deviation, we need to normalize the wnil. Random; in the program). Since in Gaussian distribution aumbers to be between -1 and I by dividing the NextGmussian over 3. Thus, the following equation should be used in the progranm Noise amount Noise percent ((1/3) NextGuassain0) The noisy data in the program is obtained as follows: Noisy data Clean data + Noise amount Next, the program simulates the function of a hub switch to filter out the noise from the signal This could be easily accomplished by an "If statement. For example, if the value of the noise data is greater than one or greater than 0.31 then the filtered data is set to 1 otherwise, the value is set to 0 The program should output the clean data, noisy data, and the filtered data into a text file in You need t