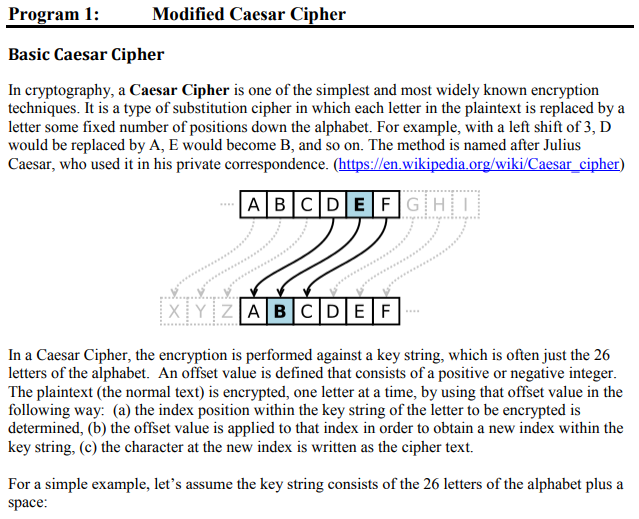



Program 1: Modified Caesar Cipher Basic Caesar Cipher In cryptography, a Caesar Cipher is one of the simplest and most widely known encryption techniques. It is a type of substitution cipher in which each letter in the plaintext is replaced by a letter some fixed number of positions down the alphabet. For example, with a left shift of 3, D would be replaced by A, E would become B, and so on. The method is named after Julius Caesar, who used it in his private correspondence. (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Caesar cipher) ABIC DIEF G HiI In a Caesar Cipher, the encryption is performed against a key string, which is often just the 26 letters of the alphabet. An offset value is defined that consists of a positive or negative integer The plaintext (the normal text) is encrypted, one letter at a time, by using that offset value in the following way: (a) the index position within the key string of the letter to be encrypted is determined, (b) the offset value is applied to that index in order to obtain a new index within the key string, (c) the character at the new index is written as the cipher text. For a simple example, let's assume the key string consists of the 26 letters of the alphabet plus a space: 0 2 345 6 90 23456 7 A B Here we have the 26 letters of the English alphabet plus a space with their index positions listed above. (To simplify, we'll stick with all caps for the moment.) We want to encrypt the phrase "I LOVE TO FLY" using a fixed offset of +5. We get the following Plain text: Cipher text: I LOVE TO FLY NEQT JEYTEKQC Note that 'T' has an index of 8 within the key string. When we add 5 we get an index of 13, which corresponds to the letter N', also within the key string. We then write down that letter as the first character of the encrypted text. Similarly, the letter 'Y' has an index of 24. When we add 5 we get 29, but since that index doesn't exist within the array, we "wrap around" and replace the 'Y' with a 'C. (Note that the "10 is not counted.) To decrypt a message, we apply the offset value in reverse. If the offsets were added to produce the cipher text, they should be subtracted to reconstitute the plaintext. Cipher text: Plain text: NEQT JEYTEKQC I LOVE TO FLY Here the plaintext is obtained from the cipher text by subtracting a constant offset of 5. Note that with this technique, spaces are treated just like any other character. Note also that we did not access the ASCII table in any way. All offsets are calculated within the key string only Modification of the Caesar Cipher The basic Caesar Cipher has a characteristic that makes it relatively easy to break: every character in the plain text is encoded with the same character in the cipher text. In the above example, every space is encoded with an "E'. Since the space is the most commonly used character, an observant reader could assume that a space is represented by an 'E' and determine the offset value from that. A variation on the basic Caesar Cipher uses a variable offset, one that is different for each character encoded. In this algorithm, the first character of the plain text will be encoded by some firstOffset as above, the next character is encoded by (firstOffset+1), the next by (firstOffset+2) etc. As you can see, the offsets grow sequentially from the first character of the plain text to the last. This ensures that instances of a character in the plain text will be represented by different characters in the cipher text. Here is the above string encoded with a sequential offset that begins with 5. Notice that the "I" is still encoded by "N", which represents an offset of 5. But all other characters are encoded by different and sequential offsets Plain text Cipher text: I LOVE TO FLY NESWDOKEANUAO Here the "" is encoded with an offset of 5, yielding a cipher text character "N". The first space is encoded with an offset of 6, yielding a cipher text character of "F". The "L" is encoded with an offset of 7, yielding a cipher text character of "S", and so forth. Each character is encoded by an offset 1 larger than the preceding character until the end of the plain text is reached. Let's apply the modified Caesar Cipher described above to a more complicated example. What follows is the key string you can use to decrypt the cipher text. Key Strin,g "hXTFexn39AJ6cmCYgktNuUwBdlKL04R1DSQrH y5q8VpjIZMGivEfasowOb72zP" The only characters in the key string are lower case alpha characters, upper case alpha characters, digits from 0 to 9, and a space. Those characters have been jumbled up to make the problem more difficult. The double quotes are used to mark the ends of the key string, they are not part of it. The cipher text that you need to decrypt against that key string is Ciper text Of necessity, all characters in the cipher text are contained within the key string. The sequential offset values used to encrypt the plain text are positive and can begin with any number between1 and 60. You should, therefore, apply negative sequential offsets to decrypt the cipher text Assignment Your task is to determine the initial offset value that will correctly decrypt the cipher text above and apply the modified Caesar Cipher algorithm to it to decrypt the string. When you find the correct initial offset, you will be able to read the string. If you do what the decrypted string says, you can have 5 extra bonus points. In order to determine the initial offset value, your program should calculate all possible initial offsets from 1 to 60. Your output should look like the following, where "Offset" means "Initial Offset" Cipher Text: "qf5wlpIe760jTmr eKLbKVzmIcCniJofnBVWH1q2hPRD2Xuxclu8s0" Offset: 1 Result: 5vHtu y7vX2Df PuUv99yxuyfuivBupduHf3uPvXuwuvEXtHuKyDfX Offset: 2; Result: yrkNH bihI1E2Nu133 eN ENGgNVBNrEnNzhNUNVhkrNI1EhH Offset: 3 Result: GOgtrHOGPjRv2tNGnnHFtHvtMG5t8wtQvxt2GPtutGiPgQtdHRvPr Offset: Result: HMSYkrWMzp4i7ktMxxrTkrikZMykqUkSiek7MzkNkMGzYSkBr4izo Offset:5Result: r2DCgSQo22v0GbgkZeeQXgQGgI2 g5ugDGFgb22gtg2M2CDgwQ0G2S Offset: 6 Result: . Make sure these results are lined up and neat, as it makes the analysis much easier. Remember that since the cipher text was encrypted with positive offsets, you will decrypt with negative offsets. These are actual data, so you can use these to check your program. After the full list is generated, you will be able to visually scan through it and determine the offset and the plain text. Hints The following functions would be useful to your solution. I suggest writing them from scratch for practice, although C versions exist. We will discuss the C versions when we get to that part of the course. 1. A function to determine the length of a C-string. Note that the "0 is not included in the length calculation. a. int strlen (char * Kstring.h>) 2. A function to locate a character within a C-string and return its index value. a. This function can be used to find a given character within the key string. Finally, you can initialize a C-string with the key string and cipher text specified above by copy/pasting those strings into your code, but here is an important point: never copy/paste from a non-text file, like a PDF for example, directly into your code. Instead, copy/paste the text into Notepad or Notepad++ first, then copy/paste into your code. This eliminates most of the problems caused by hidden formatting characters and other issues










