Question
Program Purpose - Check relational expressions for correctness. The program should accept relational expressions input from the standard input device (using cin) in the format
Program Purpose - Check relational expressions for correctness.
The program should accept relational expressions input from the standard input device (using cin) in the format
integer arithmetic-operator integer less-than-or-greater-than-symbol integer
Assume that the user will input expressions in this format, entering only integer values for the numbers, and single characters for the arithmetic and relational operators.
If the arithmetic operator entered is not a valid C++ arithmetic operator (+, -, *, /, %) the program should output Unrecognized arithmetic operator followed by the character input where an arithmetic operator was expected (see examples below).
If the relational operator entered is not , the program should output Unrecognized relational operator followed by the character input where a relational operator was expected (see examples below).
The program should determine if the expression entered is a true statement. If the expression is a true statement, output the relational expression followed by - Correct. If the expression is a false statement, output the relational expression followed by - Incorrect.
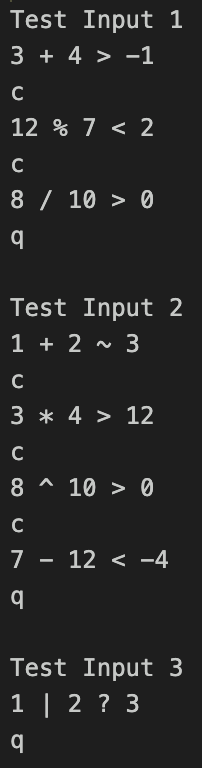
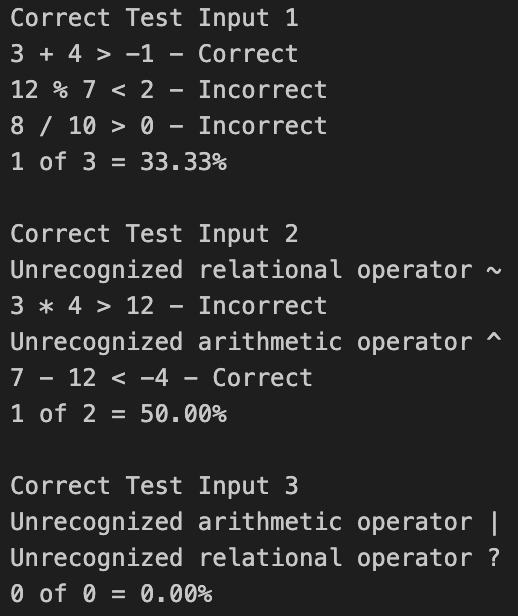
Example input/output pairs Input: 3 + 4 > -1 Output: 3 + 4 > -1 Correct
Input: 12 % 7Input: 2 ^ 5 > 28 Output: Unrecognized arithmetic operator ^Input: 3 7 * 3 Output: Unrecognized relational operator *After each relational expression entered, the user will input c to continue (to enter another relational expression) or q to quit. The program should read each input relational expression and produce the corresponding output as described above until the user enters q.After the user enters q, the program should output a summary of the results in the format:number-correct of total-number-of-expressions = percent-correct% The percent correct should display with two places following the decimal.
Specifications- All output should be directed to the standard output device using cout. - All input should be accepted from the standard input device using cin.
- Do not prompt for input. - All of your source code for the program must be contained in a single file named program1.cc - You will submit program1.cc to the assignment in Blackboard. - Programs must compile and run on a computer of the instructors choosing in the Linux lab (see your course syllabus for additional details). - Be sure to review the program expectations section of the course syllabus.
Testing
Text files containing sample input and the corresponding expected output are attached to the program assignment. A makefile has been included to run your program with the sample input and compare the results to the expected output. In order to use the makefile, ensure that your program1.cc and all of the files attached to the assignment (checkit.cc, correct-test1.txt, correct-test2.txt, correct-test3.txt, test1-input.txt, test2-input.txt, test3-input.txt) are in the same directory. The commands to run the tests are given below:make test1 make test2 make test3Your program will be graded using this same method with different input/output file pairs.Note: Differences in capitalization or spacing (including extra whitespace at the end of the output) and prompts for input will cause the tests to fail. The tests will display your output up to the first character that doesnt match the expected output. You can view your full output in the student- test#.txt file and compare it to the corresponding expected output in the correct-test#.txt file.
Grade Breakdown Style: 1 point Documentation: 1 point Clean compilation: 2 points Runs correctly with instructors test data set 1: 2 points Runs correctly with instructors test data set 2: 2 points Runs correctly with instructors test data set 3: 2 pointsMakefile
program1 : program1.cc
g++ -Wall -std=c++17 program1.cc -o program1
checkit : checkit.cc
g++ -Wall -std=c++17 checkit.cc -o checkit
test1 : program1 checkit test1-input.txt correct-test1.txt
./program1 student-test1.txt
./checkit 0
test2 : program1 checkit test2-input.txt correct-test2.txt
./program1 student-test2.txt
./checkit 1
test3 : program1 checkit test3-input.txt correct-test3.txt
./program1 student-test3.txt
./checkit 2
clean :
rm student* checkit program1
checkit.cc
// Copyright 2023 bhipp #includeusing std::ifstream; #include using std::cout; using std::endl; using std::cin; #include using std::string; #include int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { // executable must be called with a test number 0-2 if ( argc != 2 || argv[1][0] '2' ) { cout
Test Input 1 3+4>1 c 12%70 q Test Input 2 1+23 c 34>12 c 810>0 c 7121 Correct 12%70 Incorrect 1 of 3=33.33% Correct Test Input 2 Unrecognized relational operator 34>12 Incorrect Unrecognized arithmetic operator 712
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started