Question
public class Entry { K key; // the key V value; // the value int index; // position of the element in the array Entry



public class Entry{ K key; // the key V value; // the value int index; // position of the element in the array Entry associate; // reference to the associate element in the other heap /** * Returns the key stored in this entry. * @return the entry's key */ K getKey() { return key; } /* getKey */ /** * Returns the value stored in this entry. * @return the entry's value */ V getValue() { return value; } /* getValue */ public Entry( K k, V v ) { key = k; value = v; } public void setIndex(int i) { index= i; } public int getIndex() { return index; } public void setAssociate(Entry e) { associate= e; } public Entry getAssociate() { return associate; } }
public class HeapPriorityQueue
private Entry [] storage; //The Heap itself in array form private int tail; //Index of last element in the heap public HeapPriorityQueue() {this(100);} public HeapPriorityQueue( int size ) { storage = new Entry [ size ]; tail = -1;} public int size() {return tail + 1;} public Entry
Entry
Entry
if( tail == 0 ) { tail = -1; storage [ 0 ] = null; return ret; } private void upHeap( int location ) { if( location == 0 ) return;
int parent = parent ( location );
if( storage [ parent ].key.compareTo ( storage [ location ].key ) > 0 ) { swap ( location, parent ); upHeap ( parent ); } } private void downHeap( int location ) { int left = (location * 2) + 1; int right = (location * 2) + 2;
//Both children null or out of bound if( left > tail ) return;
//left in right out; if( left == tail ) { if( storage [ location ].key.compareTo ( storage [ left ].key ) > 0 ) swap ( location, left ); return; }
int toSwap = (storage [ left ].key.compareTo ( storage [ right ].key )
if( storage [ location ].key.compareTo ( storage [ toSwap ].key ) > 0 ) { swap ( location, toSwap ); downHeap ( toSwap ); } } private int parent( int location ) { return (location - 1) / 2; } private void swap( int location1, int location2 ) { Entry
public class HeapPriorityQueueTest {
static String alpha = "abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyzABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ"; public static void main( String [] args ) {
Random rng = new Random(12345); // do not change the seed
// A min-heap HeapPriorityQueue
System.out.println();System.out.println();
// removeMin for( int i = 0; i e = pq.removeMin(); System.out.print ( "(" + e.key.toString() + "," + e.value.toString() + ":" + e.index + "), " ); }
System.out.println();System.out.println(); // removeMax /* for( int i = 0; i e = pq.removeMax(); System.out.print ( "(" + e.key.toString() + "," + e.value.toString() + ":" + e.index + "), " ); } */
System.out.println();System.out.println(); // removeMin for( int i = 0; i e = pq.removeMin(); System.out.print ( "(" + e.key.toString() + "," + e.value.toString() + ":" + e.index + "), " ); }
System.out.println();System.out.println(); // removeMax /* for( int i = 0; i e = pq.removeMax(); System.out.print ( "(" + e.key.toString() + "," + e.value.toString() + ":" + e.index + "), " ); } */ } }
public interface PriorityQueue{
int size();
boolean isEmpty();
Entryinsert( K key, V value ) throws IllegalArgumentException;
Entrymin();
EntryremoveMin();
Entrymax();
EntryremoveMax();
}
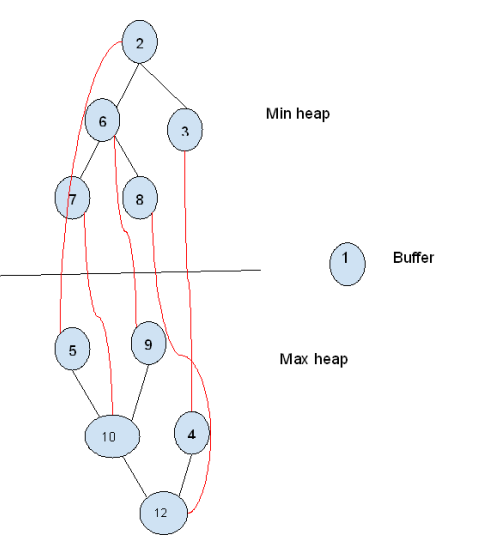
The objective of this programming assignment is to implement a double-ended priority queue; this is a priority queue for which you can obtain both the max and the min element. This double-ended queue will be implemented using two heaps: a min-heap and a max-heap. Half of the elements are stored in one of the heaps and the other half is stored in the second heap. Each element a of the min-heap is associated with one element of the max-heap b with aStep by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


