Question: PYTHON CODE IS NOT WORKING Write a program that first reads in the name of an input file and then reads the input file using
PYTHON CODE IS NOT WORKING
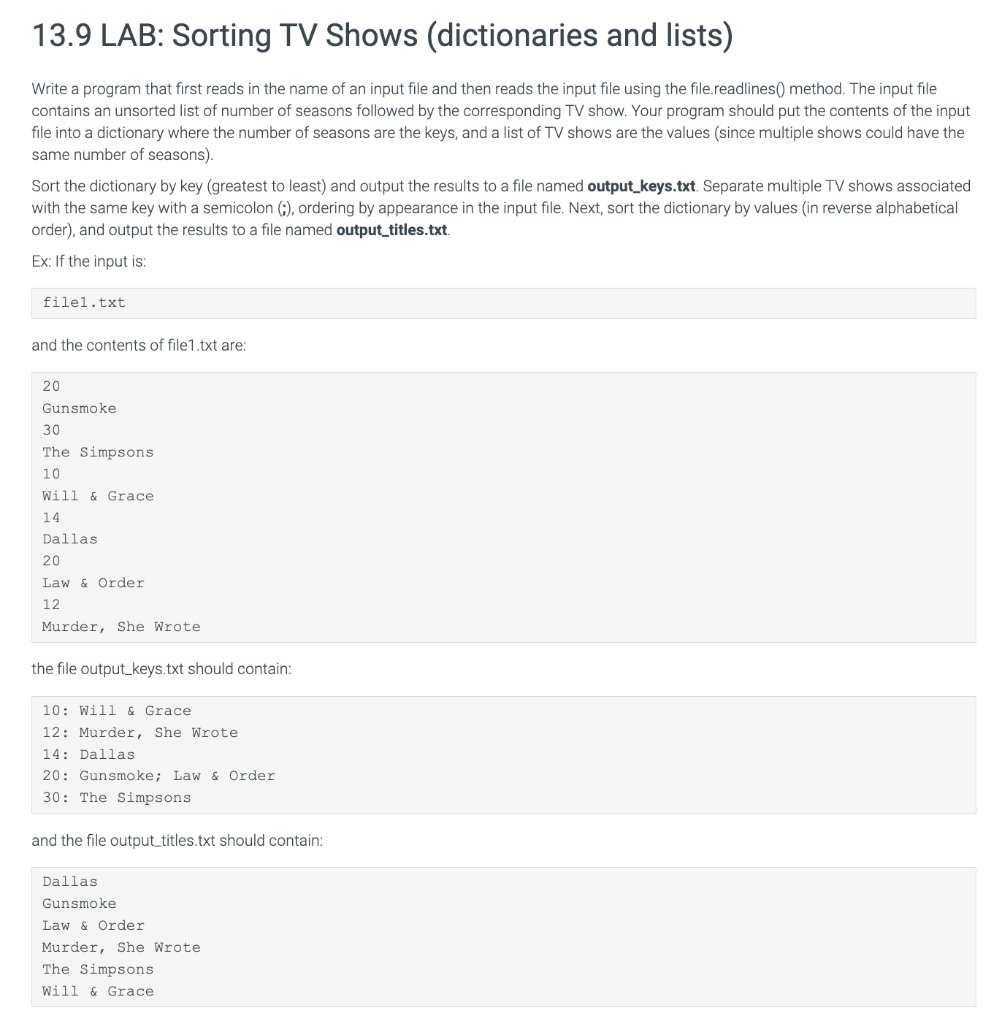
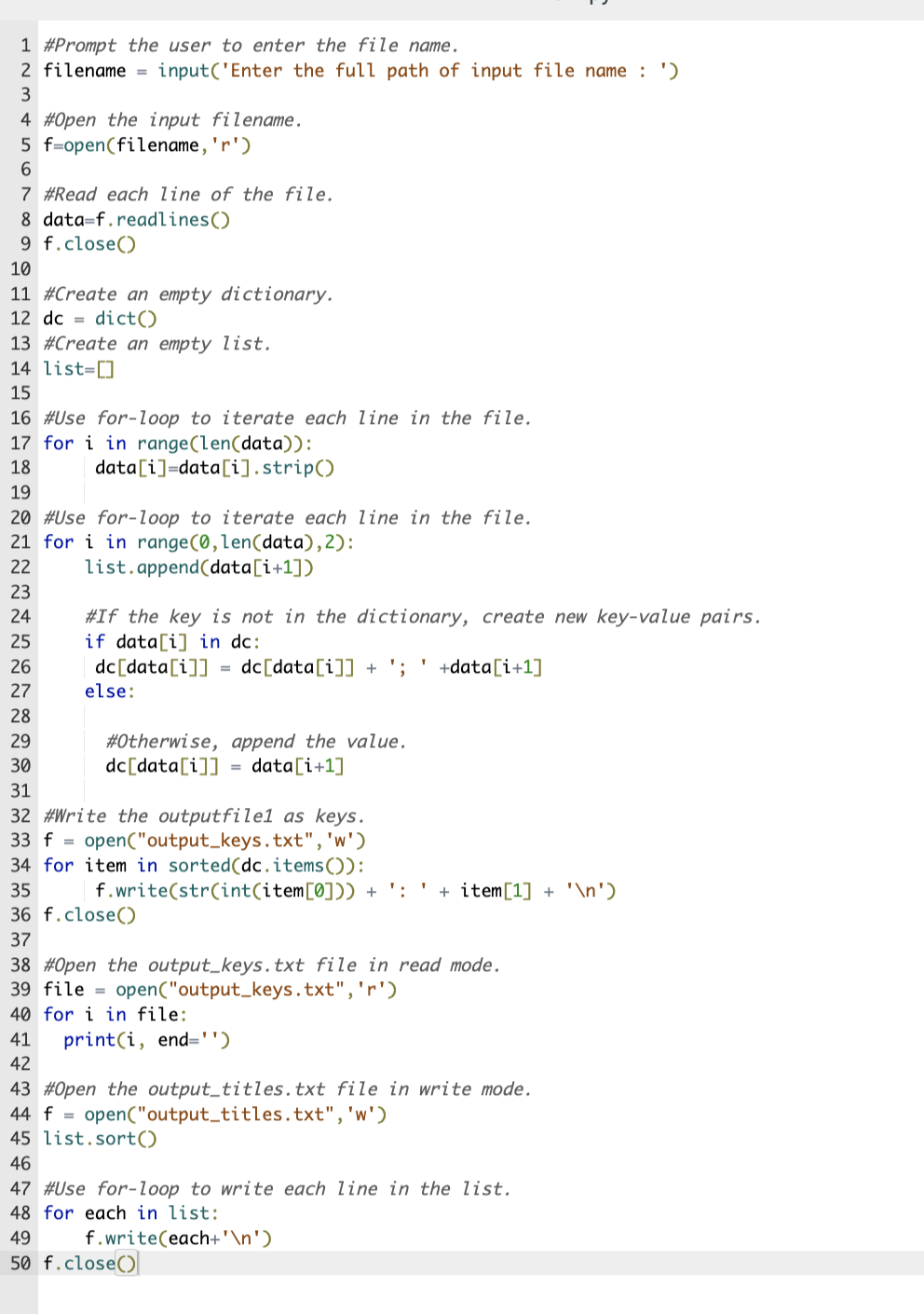
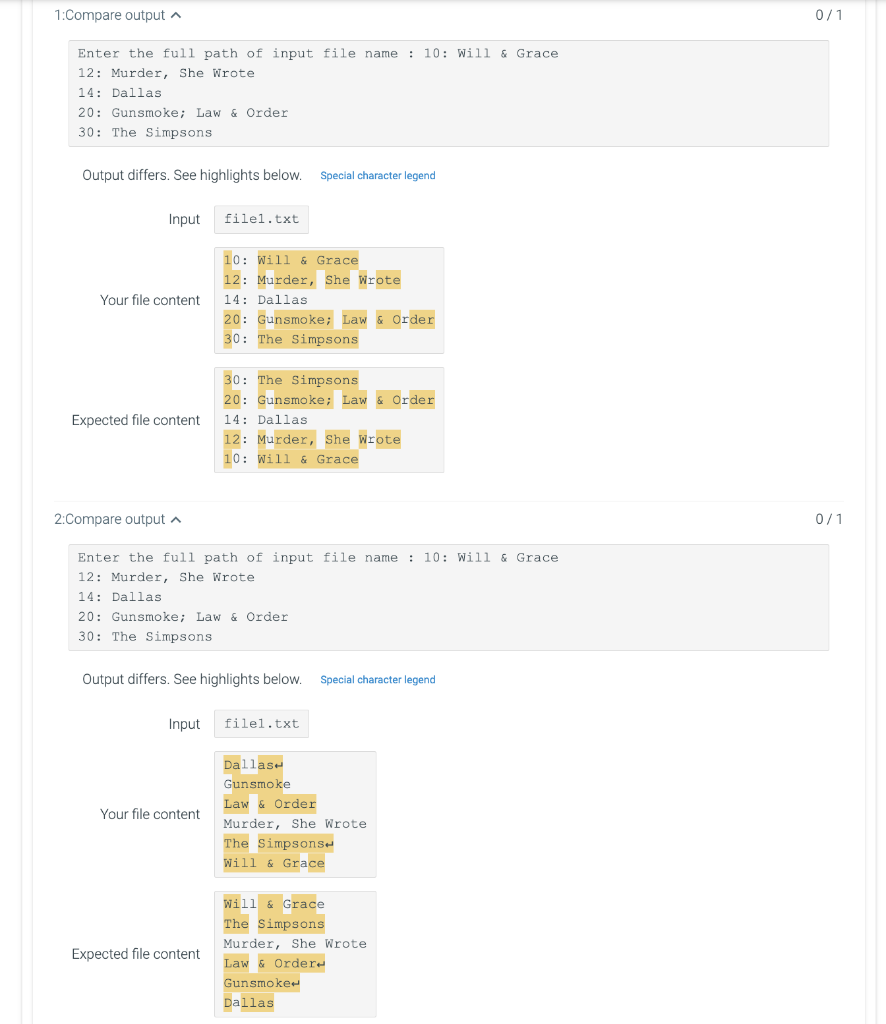
Write a program that first reads in the name of an input file and then reads the input file using the file.readines() method. Ihe input file contains an unsorted list of number of seasons followed by the corresponding TV show. Your program should put the contents of the input file into a dictionary where the number of seasons are the keys, and a list of TV shows are the values (since multiple shows could have the same number of seasons). Sort the dictionary by key (greatest to least) and output the results to a file named output_keys.txt. Separate multiple TV shows associated with the same key with a semicolon (;), ordering by appearance in the input file. Next, sort the dictionary by values (in reverse alphabetical order), and output the results to a file named output_titles.txt. Ex: If the input is: file1.txt and the contents of file1.txt are: 20 Gunsmoke 30 The Simpsons 10 Will \& Grace 14 Dallas 20 Law \& Order 12 Murder, She Wrote the file output_keys.txt should contain: 10: Will \& Grace 12: Murder, She Wrote 14: Dallas 20: Gunsmoke; Law \& Order 30: The Simpsons and the file output_titles.txt should contain: Dallas Gunsmoke Law \& Order Murder, She Wrote 1 \#Prompt the user to enter the file name. 2 filename = input('Enter the full path of input file name : ') \#Open the input filename. f=open(fil ename, ' r ') \#Read each line of the file. 8 data =f. readlines() f. close() \#Create an empty dictionary. dc=dict() \#Create an empty list. list = [ \#Use for-loop to iterate each line in the file. for i in range(len(data)): data[i]=data[i]strip() \#Use for-loop to iterate each line in the file. for i in range (0, len ( data ),2) : list. append (data [i+1]) \#If the key is not in the dictionary, create new key-value pairs. if data [i] in dc: dc[data[i]]=dc[dataa[i]]+;+data[i+1] else: \#Otherwise, append the value. dc[data[i]]=data[i+1] \#Write the outputfile1 as keys. f= open("output_keys.txt", 'w') for item in sorted(dc. items()): f.write(str(int(item[0])) +::+item[1]+ ) f. close() \#open the output_keys. txt file in read mode. file = open("output_keys.txt" , r ') for i in file: print(i, end = ') \#Open the output_titles.txt file in write mode. f= open("output_titles.txt", 'w') list.sort() \#Use for-loop to write each line in the list. for each in list: f.write ( each + ) f. close () 1:Compare output 0/1 Enter the full path of input file name : 10: will \& Grace 12: Murder, She wrote 14: Dallas 20: Gunsmoke; Law \& Order 30: The Simpsons Output differs. See highlights below. Special character legend 2:Compare output n 0/1 Enter the full path of input file name : 10: Will \& Grace 12: Murder, She wrote 14: Dallas 20: Gunsmoke; Law \& Order 30: The Simpsons Output differs. See highlights below. Special character legend
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


