Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Q 1 a: A spherical, rigid, oil droplet with a diameter of 0 . 2 5 m m and density of 8 2 0 k
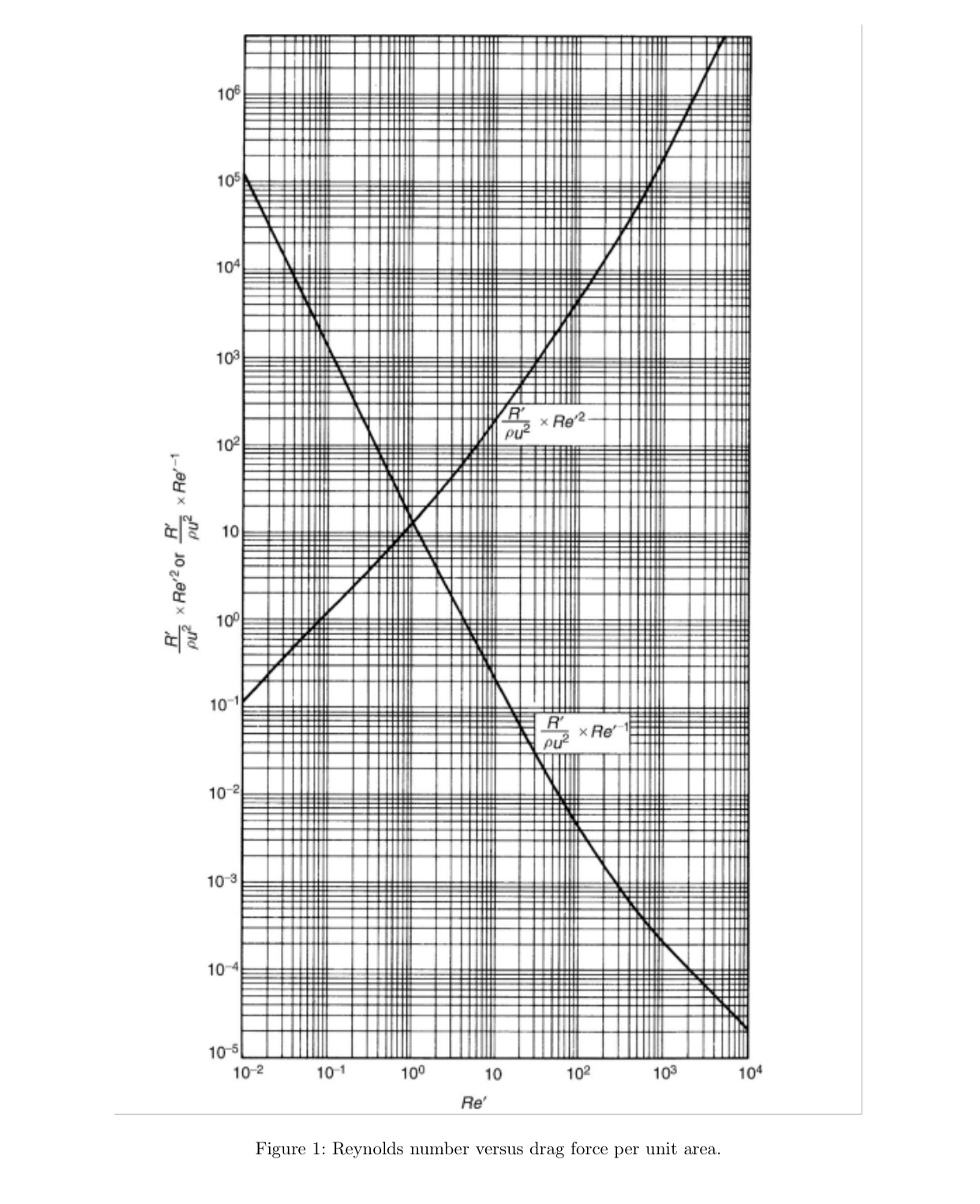
Qa: A spherical, rigid, oil droplet with a diameter of and density of is settled in air assume that air is still The density and viscosity of air are and Pas, respectively. The relationship between the Reynolds number and drag force per unit area, is shown in Figure
In Figure the variables on the vertical axis are defined with physical properties, the Reynolds number and the terminal velocity as:
Here,
: drag force per unit area,
: fluid density,
: terminal velocity particle,
: particle diameter,
: particle density,
: gravitational acceleration,
: fluid viscosity,
: Reynolds number.
: gravitational acceleration,
: fluid viscosity,
Re : Reynolds number.
Answer the following questions:
i Calculate the terminal velocity of the oil droplet in
ii Determine the drag force acting on the oil droplet at equilibrium.
Figure : Reynolds number versus drag force per unit area.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


