Question
Q1) Find the asymmetric equilibrium value of x for the Type H insurance customers. Round your answer to at least three decimal places. Q2) Find
Q1) Find the asymmetric equilibrium value of x for the Type H insurance customers. Round your answer to at least three decimal places.
Q2) Find the asymmetric equilibrium value of y for the Type H insurance customers. Round your answer to at least three decimal places.
Q3) Find the asymmetric equilibrium value of c for the Type H insurance customers. Round your answer to at least three decimal places.
Q4) Find the asymmetric equilibrium value of f for the Type H insurance customers. Round your answer to at least three decimal places.
Q5) Find the asymmetric equilibrium value of x for the Type L insurance customers.
Q6) Find the asymmetric equilibrium value of y for the Type L insurance customers. Round your answer to at least three decimal places.
Q7) Find the symmetric equilibrium value of c for the Type L insurance customers. Round your answer to at least three decimal places.
Q8) Find the symmetric equilibrium value of f for the Type L insurance customers. Round your answer to at least three decimal places.
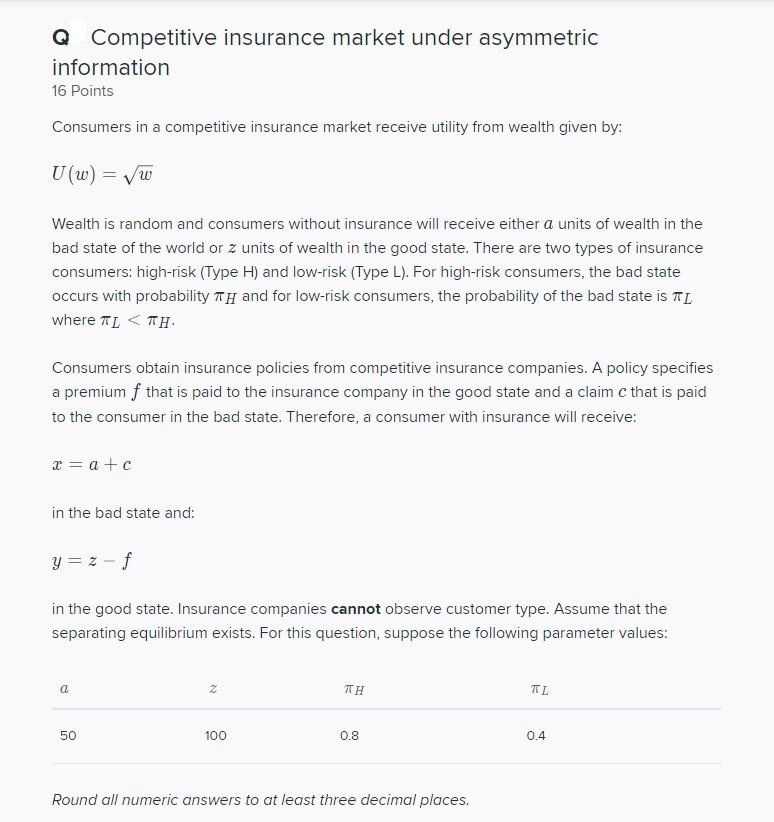
Q Competitive insurance market under asymmetric information 16 Points Consumers in a competitive insurance market receive utility from wealth given by: U(W) = VW Wealth is random and consumers without insurance will receive either a units of wealth in the bad state of the world or z units of wealth in the good state. There are two types of insurance consumers: high-risk (Type H) and low-risk (Type L). For high-risk consumers, the bad state occurs with probability T and for low-risk consumers, the probability of the bad state is TL where LTTH Consumers obtain insurance policies from competitive insurance companies. A policy specifies a premium f that is paid to the insurance company in the good state and a claim c that is paid to the consumer in the bad state. Therefore, a consumer with insurance will receive: = a + c in the bad state and: y = 2 - f in the good state. Insurance companies cannot observe customer type. Assume that the separating equilibrium exists. For this question, suppose the following parameter values: a 2 TTH TI 50 100 0.8 0.4 Round all numeric answers to at least three decimal places. Q Competitive insurance market under asymmetric information 16 Points Consumers in a competitive insurance market receive utility from wealth given by: U(W) = VW Wealth is random and consumers without insurance will receive either a units of wealth in the bad state of the world or z units of wealth in the good state. There are two types of insurance consumers: high-risk (Type H) and low-risk (Type L). For high-risk consumers, the bad state occurs with probability T and for low-risk consumers, the probability of the bad state is TL where LTTH Consumers obtain insurance policies from competitive insurance companies. A policy specifies a premium f that is paid to the insurance company in the good state and a claim c that is paid to the consumer in the bad state. Therefore, a consumer with insurance will receive: = a + c in the bad state and: y = 2 - f in the good state. Insurance companies cannot observe customer type. Assume that the separating equilibrium exists. For this question, suppose the following parameter values: a 2 TTH TI 50 100 0.8 0.4 Round all numeric answers to at least three decimal placesStep by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


