Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Question 1 1 pts Exploring an errors dataset, the production manager at a manufacturing plant puts together a sample of automatically measured production errors
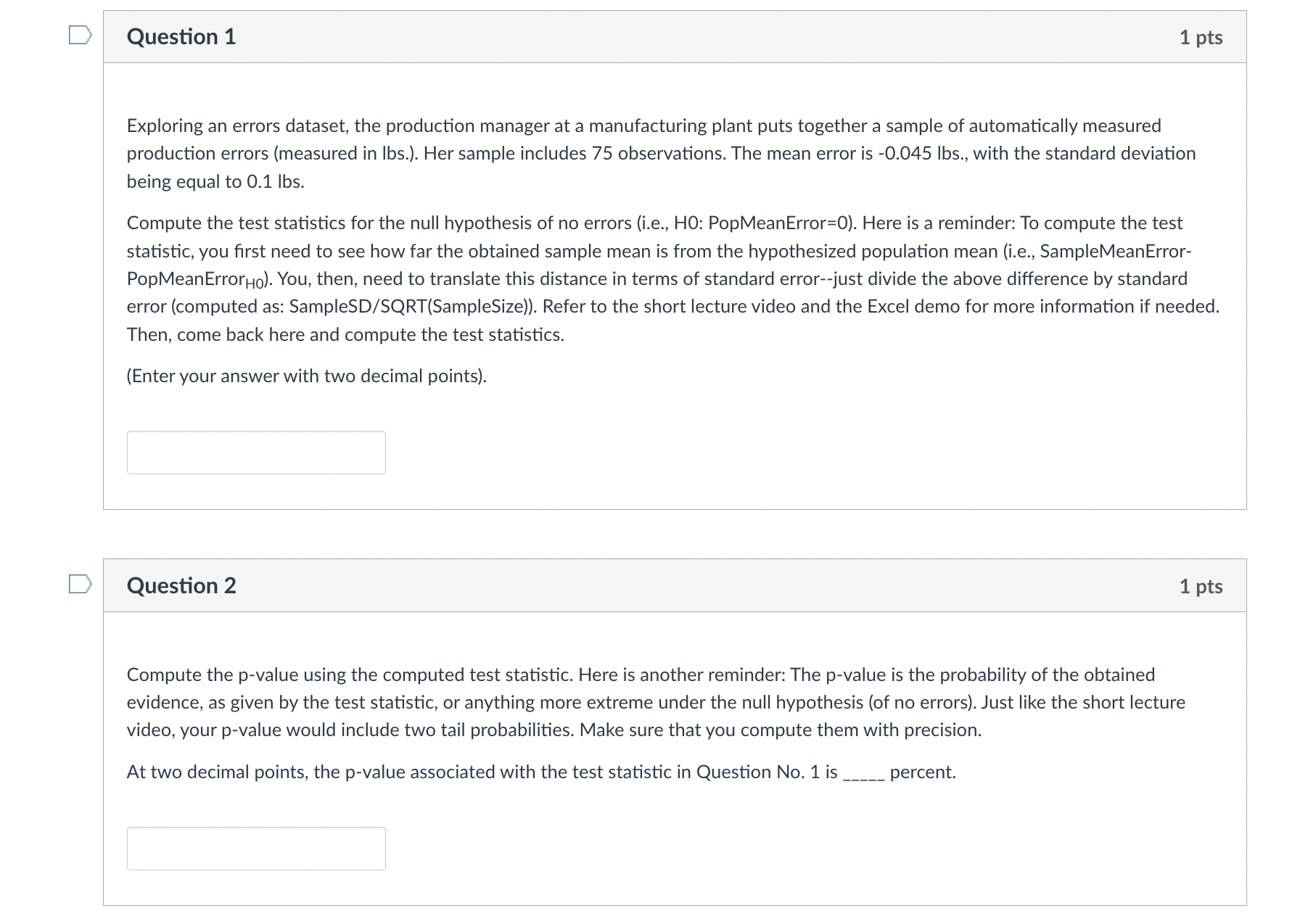
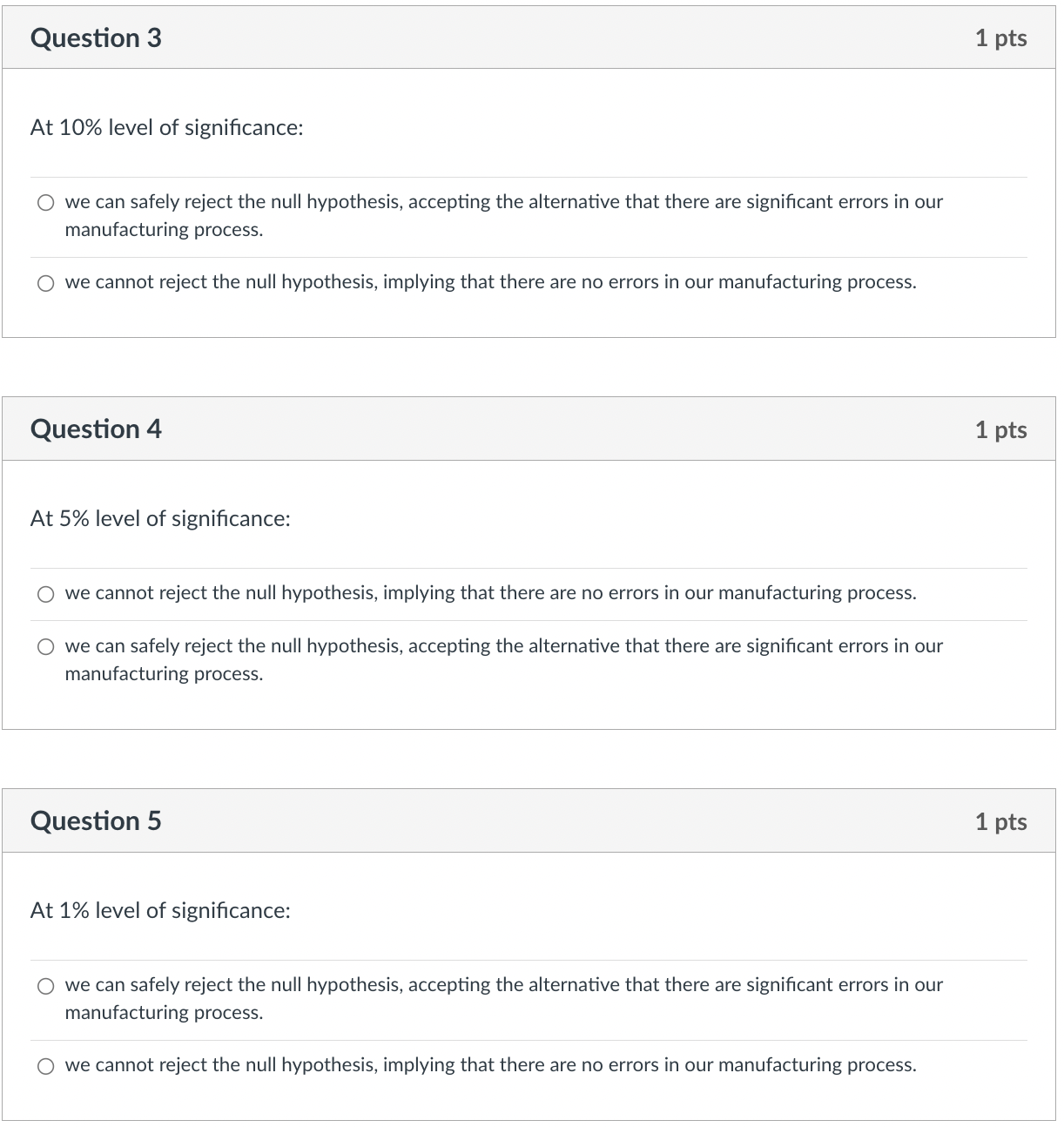
Question 1 1 pts Exploring an errors dataset, the production manager at a manufacturing plant puts together a sample of automatically measured production errors (measured in lbs.). Her sample includes 75 observations. The mean error is -0.045 lbs., with the standard deviation being equal to 0.1 lbs. Compute the test statistics for the null hypothesis of no errors (i.e., HO: PopMeanError=0). Here is a reminder: To compute the test statistic, you first need to see how far the obtained sample mean is from the hypothesized population mean (i.e., SampleMeanError- PopMeanErrorHo). You, then, need to translate this distance in terms of standard error--just divide the above difference by standard error (computed as: SampleSD/SQRT(SampleSize)). Refer to the short lecture video and the Excel demo for more information if needed. Then, come back here and compute the test statistics. (Enter your answer with two decimal points). Question 2 Compute the p-value using the computed test statistic. Here is another reminder: The p-value is the probability of the obtained evidence, as given by the test statistic, or anything more extreme under the null hypothesis (of no errors). Just like the short lecture video, your p-value would include two tail probabilities. Make sure that you compute them with precision. At two decimal points, the p-value associated with the test statistic in Question No. 1 is percent. 1 pts Question 3 At 10% level of significance: we can safely reject the null hypothesis, accepting the alternative that there are significant errors in our manufacturing process. we cannot reject the null hypothesis, implying that there are no errors in our manufacturing process. Question 4 At 5% level of significance: we cannot reject the null hypothesis, implying that there are no errors in our manufacturing process. we can safely reject the null hypothesis, accepting the alternative that there are significant errors in our manufacturing process. Question 5 At 1% level of significance: we can safely reject the null hypothesis, accepting the alternative that there are significant errors in our manufacturing process. we cannot reject the null hypothesis, implying that there are no errors in our manufacturing process. 1 pts 1 pts 1 pts
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


