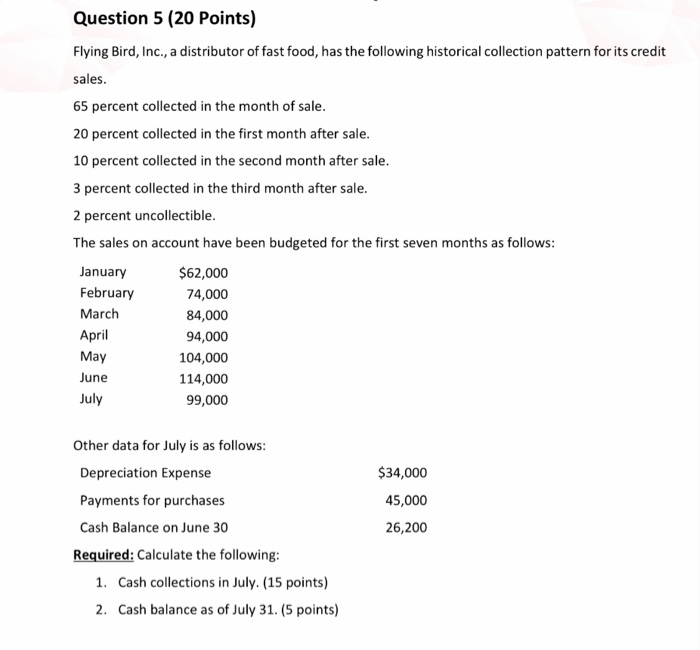
Question 1 (25 Points) Macintosh Inc. produces covers for smartphones. The product is sold as single units, which have the following price and variable costs. $40 7 Sales price Direct material Direct labor Variable overhead 4 2. Budgeted fixed overhead in 2019, the company's first year of operations, was $420,000. Actual production was 30,000 units, of which 25,000 were sold. There is no beginning finished goods inventory. Macintosh Inc. incurred the following selling and administrative expenses. Fixed in 2019 Variable per unit sold Required: $65,000 3 1. Compute the product cost per container of smartphone cover under (a) variable costing and (b) absorption costing. (10 points) 2. Prepare operating income statements for 2019 using (a) absorption costing and (b) variable costing. (10 points) 3. Reconcile the operating income reported under the two methods using the shortcut method. (5 points) Question 2 (15 Points) What are the qualities of information? Define them with your own example. Question 3 (20 Points) PLC Makers Company manufactured 8,000 units during August of a PLC device. Records indicate the following: Direct labor 49,600 hr. at $12.20 per hr. Direct material purchased 54,000 lb. at $3.85 per Ib. Direct material used 42,400 lb. The PLC device has the following standard prime costs: Direct material: 5 lb. at $3.50 per lb Direct labor: 6 hr. at $12.00 per hr Standard prime cost per unit $17.50 72.00 $89.50 Required: For the month of August, compute the following variances, indicating whether each i favorable or unfavorable. (4 points each) a. Direct-material price variance. b. Direct-material quantity variance. C. Direct-material purchase price variance. d. Direct-labor rate variance. e. Direct-labor efficiency variance. Question 4 (20 Points) ESOB Sound Company plans to sell 50,000 units in August and 60,000 units in September. The desired monthly ending inventory in units of finished product is 70 percent of the next month's estimated sales. There are 35,000 finished units in inventory on July 31. Each unit of finished product requires six kilograms of raw material at a cost of $3.65 per pound. There are 70,000 kilograms of raw material in inventory on July 31. Required: Compute the total estimated cost of raw-material purchases for the month of August. Question 5 (20 Points) Flying Bird, Inc., a distributor of fast food, has the following historical collection pattern for its credit sales. 65 percent collected in the month of sale. 20 percent collected in the first month after sale. 10 percent collected in the second month after sale. 3 percent collected in the third month after sale. 2 percent uncollectible. The sales on account have been budgeted for the first seven months as follows: January $62,000 February 74,000 March 84,000 April 94,000 May 104,000 June 114,000 July 99,000 Other data for July is as follows: Depreciation Expense Payments for purchases Cash Balance on June 30 Required: Calculate the following: 1. Cash collections in July (15 points) 2. Cash balance as of July 31. (5 points) $34,000 45,000 26,200 Question 1 (25 Points) Macintosh Inc. produces covers for smartphones. The product is sold as single units, which have the following price and variable costs. $40 7 Sales price Direct material Direct labor Variable overhead 4 2. Budgeted fixed overhead in 2019, the company's first year of operations, was $420,000. Actual production was 30,000 units, of which 25,000 were sold. There is no beginning finished goods inventory. Macintosh Inc. incurred the following selling and administrative expenses. Fixed in 2019 Variable per unit sold Required: $65,000 3 1. Compute the product cost per container of smartphone cover under (a) variable costing and (b) absorption costing. (10 points) 2. Prepare operating income statements for 2019 using (a) absorption costing and (b) variable costing. (10 points) 3. Reconcile the operating income reported under the two methods using the shortcut method. (5 points) Question 2 (15 Points) What are the qualities of information? Define them with your own example. Question 3 (20 Points) PLC Makers Company manufactured 8,000 units during August of a PLC device. Records indicate the following: Direct labor 49,600 hr. at $12.20 per hr. Direct material purchased 54,000 lb. at $3.85 per Ib. Direct material used 42,400 lb. The PLC device has the following standard prime costs: Direct material: 5 lb. at $3.50 per lb Direct labor: 6 hr. at $12.00 per hr Standard prime cost per unit $17.50 72.00 $89.50 Required: For the month of August, compute the following variances, indicating whether each i favorable or unfavorable. (4 points each) a. Direct-material price variance. b. Direct-material quantity variance. C. Direct-material purchase price variance. d. Direct-labor rate variance. e. Direct-labor efficiency variance. Question 4 (20 Points) ESOB Sound Company plans to sell 50,000 units in August and 60,000 units in September. The desired monthly ending inventory in units of finished product is 70 percent of the next month's estimated sales. There are 35,000 finished units in inventory on July 31. Each unit of finished product requires six kilograms of raw material at a cost of $3.65 per pound. There are 70,000 kilograms of raw material in inventory on July 31. Required: Compute the total estimated cost of raw-material purchases for the month of August. Question 5 (20 Points) Flying Bird, Inc., a distributor of fast food, has the following historical collection pattern for its credit sales. 65 percent collected in the month of sale. 20 percent collected in the first month after sale. 10 percent collected in the second month after sale. 3 percent collected in the third month after sale. 2 percent uncollectible. The sales on account have been budgeted for the first seven months as follows: January $62,000 February 74,000 March 84,000 April 94,000 May 104,000 June 114,000 July 99,000 Other data for July is as follows: Depreciation Expense Payments for purchases Cash Balance on June 30 Required: Calculate the following: 1. Cash collections in July (15 points) 2. Cash balance as of July 31. (5 points) $34,000 45,000 26,200