Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Question 1 3 Define PD as the ( expected ) probability of default and LGD as the loss given default. Take EAD, exposure at default,
Question
Define PD as the expected probability of default and LGD as the loss given default. Take
EAD, exposure at default, as fixed and ignore it At a portfolio level, unexpected credit losses
are driven by:
PD LGD correlations across defaults and LGD
the distribution of LGD
PD LGD correlations across defaults
PD onlyQuestion
For which of the following purposes is a high confidence level VAR advisable?
as a benchmark measure of downside risk for trading desks
none of the above
for capital adequacy purposes
for backtesting purposesQuestion
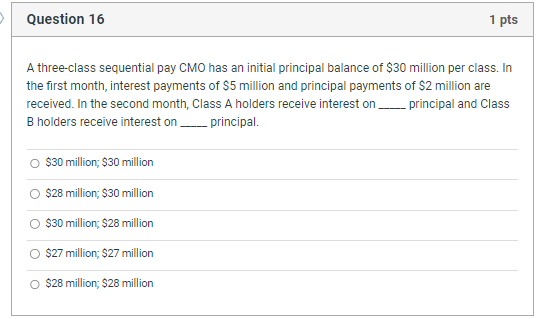
A threeclass sequential pay CMO has an initial principal balance of $ million per class. In
the first month, interest payments of $ million and principal payments of $ million are
received. In the second month, Class A holders receive interest on
principal and Class
holders receive interest on
principal.
$ million; $ million
$ million; $ million
$ million; $ million
$ million; $ million
$ million; $ million
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


