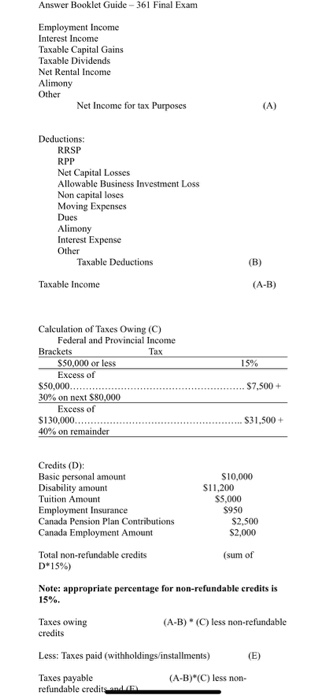
Question 1 (60 MARKS) Mrs. Jane Smith has provided you with the following information with respect to her 2018 taxation year. She has asked you to review the information and provide her with an approximation of her taxes payable for 2018 taking into consideration all the provisions available to her pursuant to the Income Tax Act. 1) Salary, net Income taxes withheld $148,952 $38,000 2,500 950 41.450 $190.402 EI 2) Mrs. Smith paid professional fees of $1,000 to the Professional Engineers of Ontario. 3) Five years ago, Mrs. Smith invested in ABC Inc., a Canadian private company which is a small business corporation". She invested in ABC Inc. by way of a $100,000 unsecured loan bearing interest at 5% per year. Until December 2017 she received interest payments, however for 2018 she has not received any interest payments and in fact ABC Inc. has filed for bankruptcy. 4) Mrs. Smith's earned income for 2017 for RRSP purposes is $185,000. 5) In February of 2018, Mrs. Smith's employer relocated her from Toronto to Windsor to head up a new manufacturing facility. In her relocation, Mrs. Smith incurred $18,500 of eligible moving expenses. Mrs. Smith's employment income from the new work location was $150,000 for 2018. 6) Mrs. Smith pays alimony of $3,000 per month 7) Mrs. Smith was in a serious car accident in 2014, and as a result she requires the use of a wheelchair. In 2014 she filed the necessary form to qualify for the disability tax credit and was approved for 2014 and future years. 8) In 2018, Mrs. Smith sold the following assets. Also, Mrs. Smith has unclaimed capital losses on listed personal property of $1,000 arising in 2016. Oil Painting (cost - $3,000; proceeds - $850; LPP) Canoe (cost-$750; proceeds - $500; PUP) Rare Coin (cost - S1500; proceeds - $900; LPP) Bible produced in 1635 (cost - $1,500; proceeds - 58500; LPP) Antique car (cost - $12,000; proceeds - $1,000; PUP) Antique chair (cost-$900proceeds - $1,200; PUP) Antique table leastS1200.roceeds - S4000; PUP) 9) Mrs. Smith received a $2 million settlement as a result of the car accident. In 2017 she invested these funds and earned interest income of $50,000 that was reported on her 2017 tax return. This did not make her happy as she paid almost $20,000 in taxes as a result. In April 2018 she (on the advice of a friend) transferred S1 million to a savings account in the name of her 16 year old daughter Jennifer and $1 million to a savings account in the name of her 19 year old daughter Kate. For 2018, the savings account in Jennifer's name earned $28,000 and the savings account in Kate's name earned $28,200. 10) In 2018, Mrs. Smith sold her residences. The following information relates to the disposition of the residences. Mrs. Smith has never used the principal residency exemption. Toronto Home (cost - $120,000; selling price - $280,000; year of purchase - 2009) Farm in Quebec (cost - $140,000; selling price - $168,000; year of purchase - 2011) Florida Condo (cost-$110,000; selling price - $170,000; year of purchase - 2014) 11) In 2018, Mrs. Smith sold 1000 shares of Shy High Limited for $80 per share, a Canadian public corporation. The following are the details of these shares: Nov 8, 2009 - purchased 400 shares at $11 per share April 15, 2010 - purchased 800 shares at $16 per share July 2, 2011 - purchased 1400 shares at $19 per share June 30, 2013 - sold 600 shares at $28 per share Oct 23, 2014 - received a stock dividend of 10% of shares held; stock dividend increased corporation's paid up capital by S1 per share. 12) Mrs. Smith contributed $20,000 to RRSP's for 2018. 13) Mrs. Smith incurred $8,000 of eligible medical expenses for 2018. 14) Mrs. Smith is also a landlord. She owns/owned several rental properties. The following information relates to cach rental property: Property A - Rental Income - $68,000; interest expenses $28,000; property taxes - $8,000; CCA - $10,000. Property B - Sold January 1, 2018 for total proceeds of $875,000. Consideration of the purchase price was $500,000 cash paid on January 1, 2018 and a $375,000 note at 5%. On December 31, 2018, Mrs. Smith received $15,000 on account of interest on the note. The following information relates to the allocation of the purchase price as well as the tax attributes of the land and building. Land - (cost-$100,000; proceeds - $400,000) Building - (cost-$200,000: UCC - $135,000: proceeds - $475,000) Property C-Sold January 1, 2018 for $450,000. The allocation of the purchase price was $300,000 for the building and $150,000 for the land. At December 31, 2017 the building had a cost of $400,000 and UCC of $350,000, and the land had a cost of $100,000. The building was the last remaining asset in the class. Property D-A commercial rental property whereby the tenants carried on active business income. In February of 2018, Mrs. Smith decided to sell the property for $1,750,000 of which $1,500,000 was allocated to the building and $250,000 was allocated to the land. The building had a cost of $600,000 and a UCC of $365,000. The land had a cost of $200,000. However, on January 1, 2019 Mrs. Smith used the proceeds to purchase another commercial property. The purchased price of the new property was $2,000,000 ($1,650,000 for building: $350,000 for land). 15) Mrs. Smith has a rather active investment portfolio in the stock market. A summary of her investment returns are as follows: Interest on bonds - $15,800 Capital Gains - $75,000 16) Mrs. Smith has unused net capital losses of $175.000 17) Mrs. Smith made charitable contributions in 2018 of S14,100 18) The RRSP limit for 2018 is $24.000 Answer Booklet Guide - 361 Final Exam Employment Income Interest Income Taxable Capital Gains Taxable Dividends Net Rental Income Alimony Other Net Income for tax Purposes Deductions: RRSP RPP Net Capital Losses Allowable Business Investment Loss Non capital loses Moving Expenses Dues Alimony Interest Expense Other Taxable Deductions Taxable income (A-B) 15% Calculation of Taxes Owing (C) Federal and Provincial Income Brackets $50,000 or less Excess of $50,000.. 30% on next $80.000 Excess of $130,000......... 40% on remainder $7,500+ ...................$31.500+ Credits (D): Basic personal amount Disability amount Tuition Amount Employment Insurance Canada Pension Plan Contributions Canada Employment Amount S10,000 $11,200 S5.000 $950 $2,500 $2,000 Total non-refundable credits D*15%) (sum of Note: appropriate percentage for non-refundable credits is 15%. Taxes owing (A-B) (C) less non-refundable credits Less: Taxes paid (withholdings/installments) (E) (A-B)*(C) less non- Taxes payable refundable credits and Question 1 (60 MARKS) Mrs. Jane Smith has provided you with the following information with respect to her 2018 taxation year. She has asked you to review the information and provide her with an approximation of her taxes payable for 2018 taking into consideration all the provisions available to her pursuant to the Income Tax Act. 1) Salary, net Income taxes withheld $148,952 $38,000 2,500 950 41.450 $190.402 EI 2) Mrs. Smith paid professional fees of $1,000 to the Professional Engineers of Ontario. 3) Five years ago, Mrs. Smith invested in ABC Inc., a Canadian private company which is a small business corporation". She invested in ABC Inc. by way of a $100,000 unsecured loan bearing interest at 5% per year. Until December 2017 she received interest payments, however for 2018 she has not received any interest payments and in fact ABC Inc. has filed for bankruptcy. 4) Mrs. Smith's earned income for 2017 for RRSP purposes is $185,000. 5) In February of 2018, Mrs. Smith's employer relocated her from Toronto to Windsor to head up a new manufacturing facility. In her relocation, Mrs. Smith incurred $18,500 of eligible moving expenses. Mrs. Smith's employment income from the new work location was $150,000 for 2018. 6) Mrs. Smith pays alimony of $3,000 per month 7) Mrs. Smith was in a serious car accident in 2014, and as a result she requires the use of a wheelchair. In 2014 she filed the necessary form to qualify for the disability tax credit and was approved for 2014 and future years. 8) In 2018, Mrs. Smith sold the following assets. Also, Mrs. Smith has unclaimed capital losses on listed personal property of $1,000 arising in 2016. Oil Painting (cost - $3,000; proceeds - $850; LPP) Canoe (cost-$750; proceeds - $500; PUP) Rare Coin (cost - S1500; proceeds - $900; LPP) Bible produced in 1635 (cost - $1,500; proceeds - 58500; LPP) Antique car (cost - $12,000; proceeds - $1,000; PUP) Antique chair (cost-$900proceeds - $1,200; PUP) Antique table leastS1200.roceeds - S4000; PUP) 9) Mrs. Smith received a $2 million settlement as a result of the car accident. In 2017 she invested these funds and earned interest income of $50,000 that was reported on her 2017 tax return. This did not make her happy as she paid almost $20,000 in taxes as a result. In April 2018 she (on the advice of a friend) transferred S1 million to a savings account in the name of her 16 year old daughter Jennifer and $1 million to a savings account in the name of her 19 year old daughter Kate. For 2018, the savings account in Jennifer's name earned $28,000 and the savings account in Kate's name earned $28,200. 10) In 2018, Mrs. Smith sold her residences. The following information relates to the disposition of the residences. Mrs. Smith has never used the principal residency exemption. Toronto Home (cost - $120,000; selling price - $280,000; year of purchase - 2009) Farm in Quebec (cost - $140,000; selling price - $168,000; year of purchase - 2011) Florida Condo (cost-$110,000; selling price - $170,000; year of purchase - 2014) 11) In 2018, Mrs. Smith sold 1000 shares of Shy High Limited for $80 per share, a Canadian public corporation. The following are the details of these shares: Nov 8, 2009 - purchased 400 shares at $11 per share April 15, 2010 - purchased 800 shares at $16 per share July 2, 2011 - purchased 1400 shares at $19 per share June 30, 2013 - sold 600 shares at $28 per share Oct 23, 2014 - received a stock dividend of 10% of shares held; stock dividend increased corporation's paid up capital by S1 per share. 12) Mrs. Smith contributed $20,000 to RRSP's for 2018. 13) Mrs. Smith incurred $8,000 of eligible medical expenses for 2018. 14) Mrs. Smith is also a landlord. She owns/owned several rental properties. The following information relates to cach rental property: Property A - Rental Income - $68,000; interest expenses $28,000; property taxes - $8,000; CCA - $10,000. Property B - Sold January 1, 2018 for total proceeds of $875,000. Consideration of the purchase price was $500,000 cash paid on January 1, 2018 and a $375,000 note at 5%. On December 31, 2018, Mrs. Smith received $15,000 on account of interest on the note. The following information relates to the allocation of the purchase price as well as the tax attributes of the land and building. Land - (cost-$100,000; proceeds - $400,000) Building - (cost-$200,000: UCC - $135,000: proceeds - $475,000) Property C-Sold January 1, 2018 for $450,000. The allocation of the purchase price was $300,000 for the building and $150,000 for the land. At December 31, 2017 the building had a cost of $400,000 and UCC of $350,000, and the land had a cost of $100,000. The building was the last remaining asset in the class. Property D-A commercial rental property whereby the tenants carried on active business income. In February of 2018, Mrs. Smith decided to sell the property for $1,750,000 of which $1,500,000 was allocated to the building and $250,000 was allocated to the land. The building had a cost of $600,000 and a UCC of $365,000. The land had a cost of $200,000. However, on January 1, 2019 Mrs. Smith used the proceeds to purchase another commercial property. The purchased price of the new property was $2,000,000 ($1,650,000 for building: $350,000 for land). 15) Mrs. Smith has a rather active investment portfolio in the stock market. A summary of her investment returns are as follows: Interest on bonds - $15,800 Capital Gains - $75,000 16) Mrs. Smith has unused net capital losses of $175.000 17) Mrs. Smith made charitable contributions in 2018 of S14,100 18) The RRSP limit for 2018 is $24.000 Answer Booklet Guide - 361 Final Exam Employment Income Interest Income Taxable Capital Gains Taxable Dividends Net Rental Income Alimony Other Net Income for tax Purposes Deductions: RRSP RPP Net Capital Losses Allowable Business Investment Loss Non capital loses Moving Expenses Dues Alimony Interest Expense Other Taxable Deductions Taxable income (A-B) 15% Calculation of Taxes Owing (C) Federal and Provincial Income Brackets $50,000 or less Excess of $50,000.. 30% on next $80.000 Excess of $130,000......... 40% on remainder $7,500+ ...................$31.500+ Credits (D): Basic personal amount Disability amount Tuition Amount Employment Insurance Canada Pension Plan Contributions Canada Employment Amount S10,000 $11,200 S5.000 $950 $2,500 $2,000 Total non-refundable credits D*15%) (sum of Note: appropriate percentage for non-refundable credits is 15%. Taxes owing (A-B) (C) less non-refundable credits Less: Taxes paid (withholdings/installments) (E) (A-B)*(C) less non- Taxes payable refundable credits and