Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Question 1 A decline in short-run aggregate supply would be caused by which of the following? Select one: a. Lower personal income in France

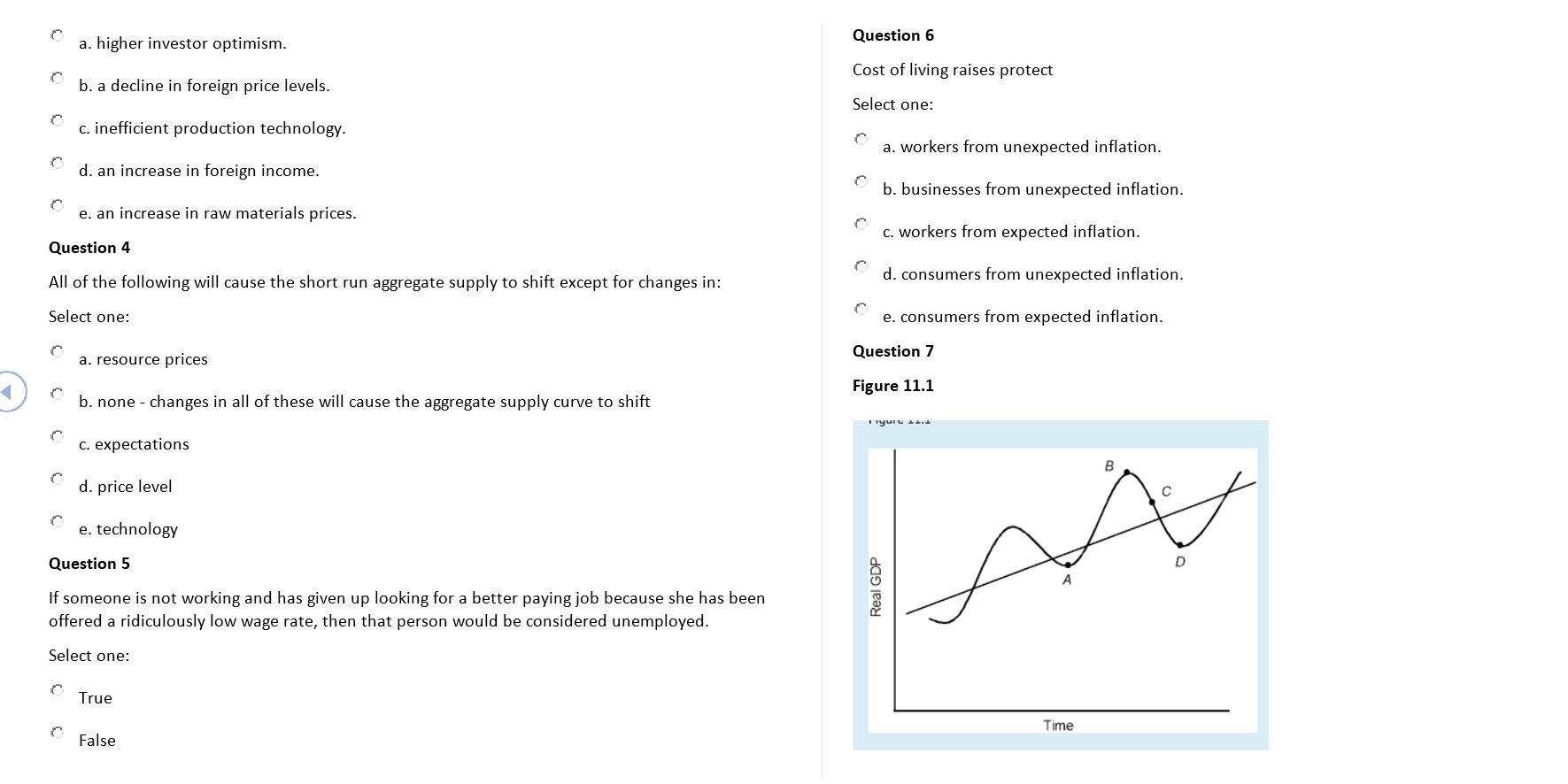






Question 1 A decline in short-run aggregate supply would be caused by which of the following? Select one: a. Lower personal income in France b. The discovery of new mineral deposits in Arizona c. Rapid depreciation of the Swiss franc d. Cutbacks in government spending e. Higher real wage rates Question 2 indicator(s) are used to identify the peaks and troughs in business cycles. Select one: a. Leading and lagging b. Leading c. Leading, coincident, and lagging d. Coincident e. Lagging Question 3 A leftward shift of the aggregate demand curve can be explained by Select one: C C C C a. higher investor optimism. b. a decline in foreign price levels. c. inefficient production technology. C d. an increase in foreign income. e. an increase in raw materials prices. Question 4 All of the following will cause the short run aggregate supply to shift except for changes in: Select one: a. resource prices b. none - changes in all of these will cause the aggregate supply curve to shift c. expectations d. price level e. technology Question 5 If someone is not working and has given up looking for a better paying job because she has been offered a ridiculously low wage rate, then that person would be considered unemployed. Select one: True False C a. higher investor optimism. b. a decline in foreign price levels. c. inefficient production technology. d. an increase in foreign income. e. an increase in raw materials prices. Question 4 All of the following will cause the short run aggregate supply to shift except for changes in: Select one: a. resource prices b. none - changes in all of these will cause the aggregate supply curve to shift c. expectations d. price level e. technology Question 5 If someone is not working and has given up looking for a better paying job because she has been offered a ridiculously low wage rate, then that person would be considered unemployed. Select one: True False Question 6 Cost of living raises protect Select one: C C b. businesses from unexpected inflation. C a. workers from unexpected inflation. C C d. consumers from unexpected inflation. c. workers from expected inflation. Real GDP e. consumers from expected inflation. Question 7 Figure 11.1 Figure d A Time B D At point D in Figure 11.1, lagging economic indicators should show that real GDP Select one: a. is contracting. b. growth is zero. c. growth has reached a trough. d. is expanding. e. growth will be positive over time. Question 8 For a given year, the nominal interest rate is 9 percent, and inflation rises to 11 percent, a 4 percent higher rate than anticipated. Which group of people is made better off by the increase in the inflation rate? Select one: C a. Those who borrow at fixed interest rates C b. Those who lend at fixed interest rates C c. Those who borrow at variable interest rates C d. Those who save at variable interest rates e. Those who receive fixed incomes Question 9 The wealth effect refers to the fact that wealthier individuals tend to spend more on foreign goods. Select one: C C True False Question 10 Table 12.2 Table 12.2 Inflation rate Inflation rate (year 1) (year 2) a. $10,000 b. $9,800 United States c. $12,000 d. $10,200 e. $8,000 Question 11 0% 20% Refer to Table 12.2. Assume the exchange rate is fixed at 100 yen = $1 and that price changes for cars are identical to the inflation rate in each country. If a U.S. car is sold to Japanese importers for $10,000 in year 1, what is its price in year 2? Select one: Japan 0% 0% Figure 12.1 Price Level Price Level C C a. A b. D AS Real GDP d. C (C) Real GDP c. None of these AS Price Level Price Level Which of the graphs in Figure 12.1 is consistent with long-run equilibrium analysis? Select one: Real GDP (D) Real GDP AS AS C Question 12 e. B Select one: C unemployment is short term; C Question 13 unemployment is/are always present in a dynamic economy. Select one: C a. seasonal; structural b. seasonal; cyclical c. frictional; structural d. cyclical; frictional e. structural; frictional a. Frictional b. Seasonal, frictional, and structural. c. Seasonal unemployment can be long term. d. Frictional and structural e. Structural Question 14 Given constant real output, a decrease in real income implies that the purchasing power of money is falling. 1 Select one: True Question 15 Countries define unemployment differently and use different methods to count the unemployed. This is evidenced in all of the following except: Select one: False C a. Official Italian unemployment data include people who have not looked for work in the past 30 days, resulting in a rate that is twice as high than if those were excluded. C b. In some countries, only those people who register for unemployment benefits are considered unemployed, so those who have not registered are excluded. c. Through the 1960s and early 1970s, European unemployment rates generally were lower than U.S. and Canadian rates, but in the mid-1980s the U.S. unemployment began to fall and the European unemployment remained high. C d. Some countries conduct monthly surveys of households to estimate the unemployment rate, instead of relying on an unemployment register. A C e. The Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development found that only 80% - 85% of those surveyed as unemployed were registered in Germany, France, and the United Kingdom. Question 16 indicator is a variable that changes. real output changes. C Select one: a. leading; after b. leading; before c. lagging; at the same time that d. coincident; before e. lagging; before Question 17 The aggregate demand curve Select one: C a. is identical to the aggregate expenditures curve. C b. shows total spending in which the economy will engage at alternative price levels. c. implies an inverse relationship between inflation and unemployment. d. has the same slope as a demand curve. e. relates relative prices to the quantity demanded of a particular good. Question 18 Table 11.1 Table 11.1: Price Data 1 pair of jeans 1 pair of shoes 2005 $20 $30 2006 $24 $36 In Table 11.1, what was the inflation rate between 2005 and 2006? Select one: a. 100 percent b. 10 percent c. 20 percent d. 83 percent e. 66 percent Question 19 All of the following would cause an increase in the aggregate quantity demanded except: Select one: a. real value of assets and wealth rises. b. increase in purchasing power of money. c. interest rates fall. d. higher domestic inflation, relative to other countries. e. none - all of these would cause an increase in aggregate quantity demanded. Question 20 Question text Table 11.2 Table 11.2: Inflation Data Year Consumer Price Index 1986 1988 1990 1992 Refer to Table 11.2. By how much (rounded to the first decimal place) did consumer prices rise between 1988 and 1992? Select one: C C C 100.00 110.50 118.50 125.00 C a. 14.5 percent b. 10.5 percent c. None of these numbers are correct d. 5.5 percent e. 13.1 percent Question 21 A reduction in resource prices tends to be associated with a Select one: a. leftward shift of the aggregate supply curve. b. movement up the aggregate supply curve. c. movement up the aggregate demand curve. d. rightward shift of the aggregate supply curve. e. rightward shift of the aggregate demand curve. Question 22 Question text Table 12.3 Table 12.3 Average hourly wage Price index a. supply increases. The data in Table 12.3 suggest that, in year 2, aggregate Select one: b. demand decreases. c. supply remains constant. d. supply decreases. e. demand increases. Year 1 $6.00 Question 23 100 Year 2 $9.00 200 The substitution effect, based on relative commodity price changes, represents one reason for the downward slope of the aggregate demand curve. Select one: Question 24 Which of the following will not shift the short-run aggregate supply curve? Select one: C C C C True C False C a. A change in raw material supplies b. A change in technology c. A change in price expectations Question 25 A decline in production costs Select one: d. A change in the domestic price level e. A change in wage rates a. reduces the amount of output produced. b. increases business revenues. c. reduces business profits. d. increases the opportunity cost of doing business. e. reduces the opportunity cost of doing business. Question 26 If a student borrowed $5,000 at 6 percent to pay for this year's college expenses and the annual inflation rate turns out to be 8 percent, then the student's purchasing power for the year has increased. Select one: C True False Question 27 The slope of the aggregate supply curve becomes steeper the faster the costs of production adjust and the smaller the amount of excess capacity in the economy. Select one: C True False Question 28 All of the following lead to a change in aggregate expenditures except a change in Select one: a. domestic wealth. b. the price of apples. c. interest rates. d. exchange rates. C e. the foreign price level. Question 29 Cost-push inflation is caused by Select one: C C C C C C a. excessive government spending. C e. full employment of resources in the economy. Question 30 Frictional unemployment most likely arises due to Select one: C b. the demand side of the market. C c. excess raw materials. d. the supply side of the market. C b. a labor force where people elect to change jobs. a. conflicts between union and labor. c. seasonal adjustments in demand. d. business cycles. e. technological changes. End of document
Step by Step Solution
★★★★★
3.50 Rating (163 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
1 D 2 C 3 E 4 D 5 TRUE 6E 7 A 8 A ...
Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


